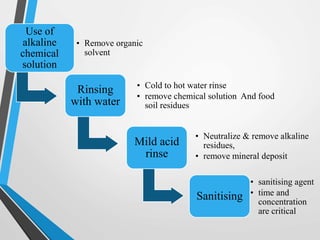
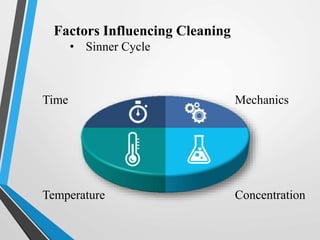
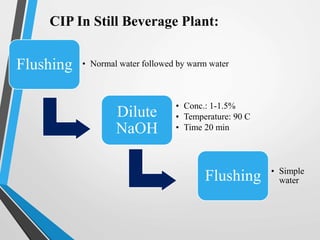
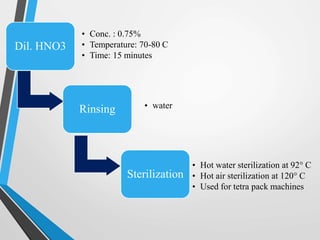
This document discusses cleaning and sanitizing procedures for food plant equipment. It outlines the fundamentals of cleaning including pre-rinsing, cleaning cycles using alkaline and acid solutions, and sanitizing. Factors that influence the cleaning process like contact time, temperature, detergent concentration, mechanical force, and water quality are explained. Clean-in-place (CIP) procedures for still beverage plants are provided as an example. Methods to evaluate cleaning like visual inspection, chemical analysis, microbiological testing, electron spectroscopy, and ATP bioluminescence monitoring are also summarized.