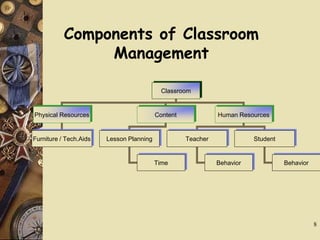
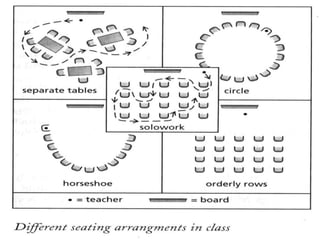
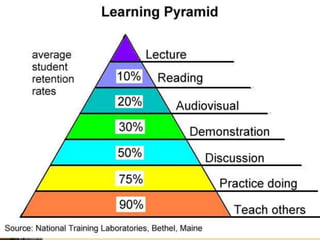
The document outlines the essential components and objectives of effective classroom management, emphasizing its critical role in student learning. It discusses strategies for managing physical and human resources, setting behavior standards, and creating a positive learning environment. Additionally, it provides guidance on addressing the needs of slow learners and the importance of establishing clear classroom rules.