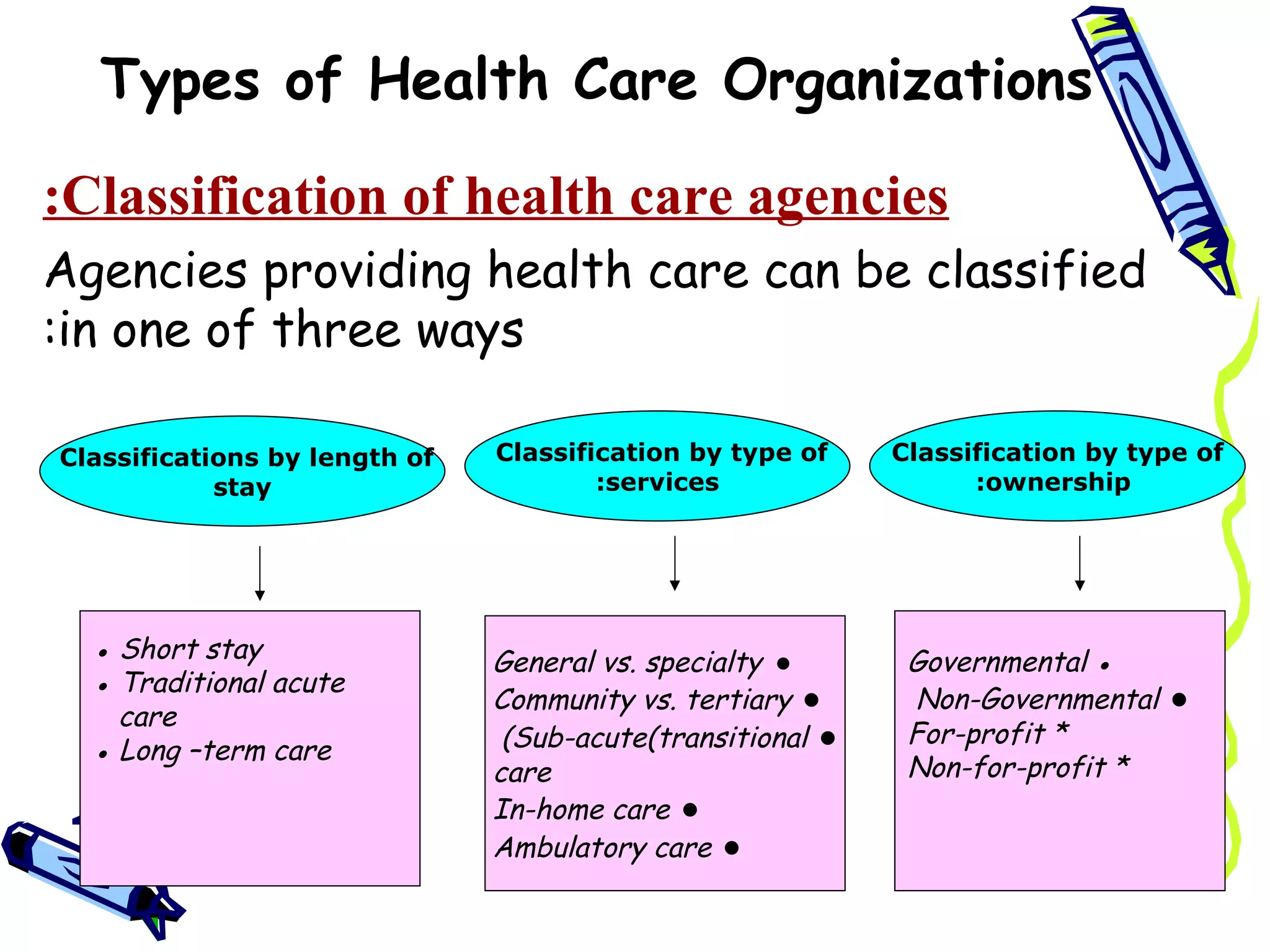
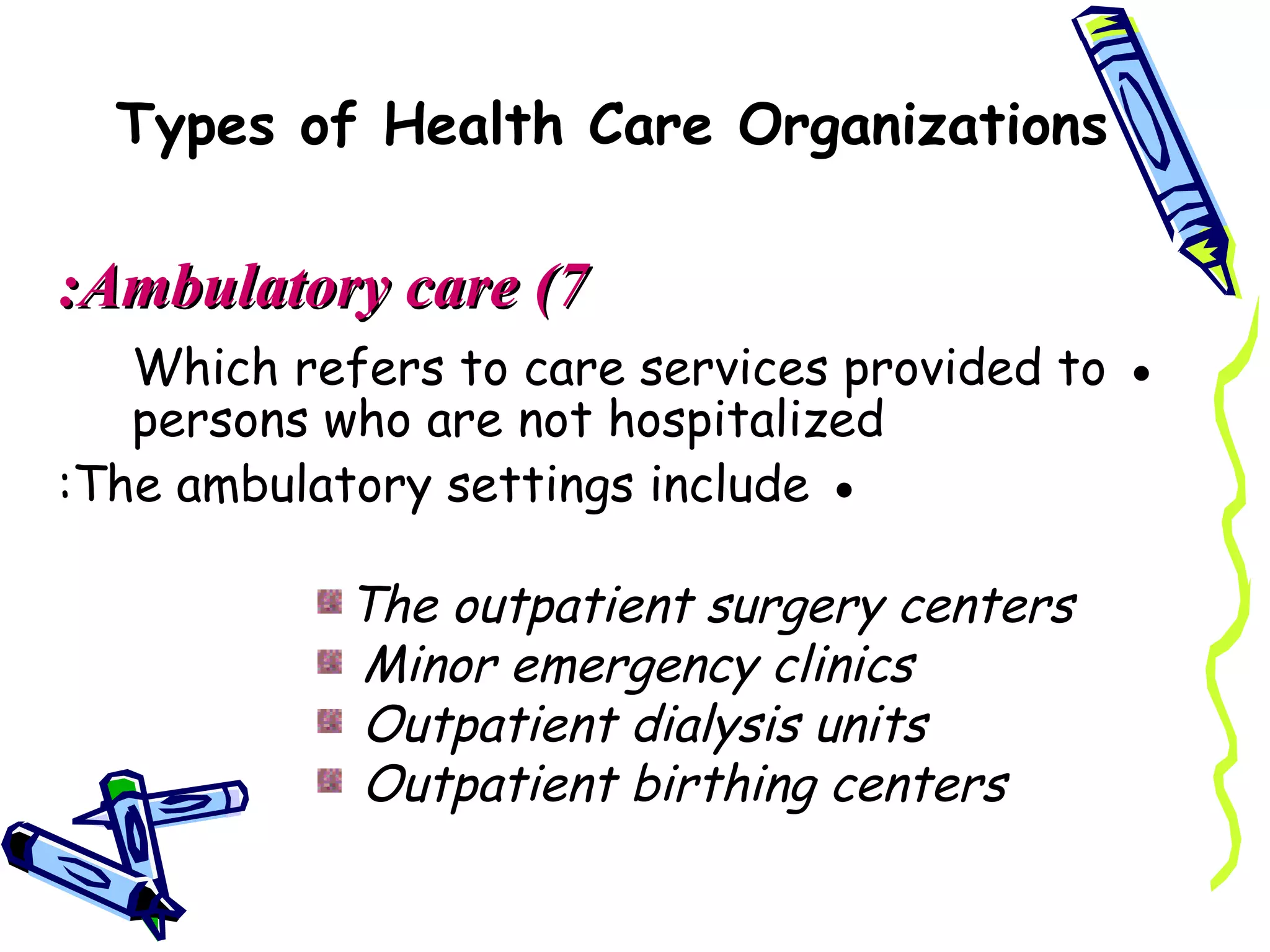
The document discusses different types of health care organizations and classifies them in three ways: by length of stay, type of services provided, and ownership type. It provides details on various organization types such as hospitals, which are defined as institutions that provide medical care and services to both inpatients and outpatients. The functions of hospitals include prevention, cure, training, and research.