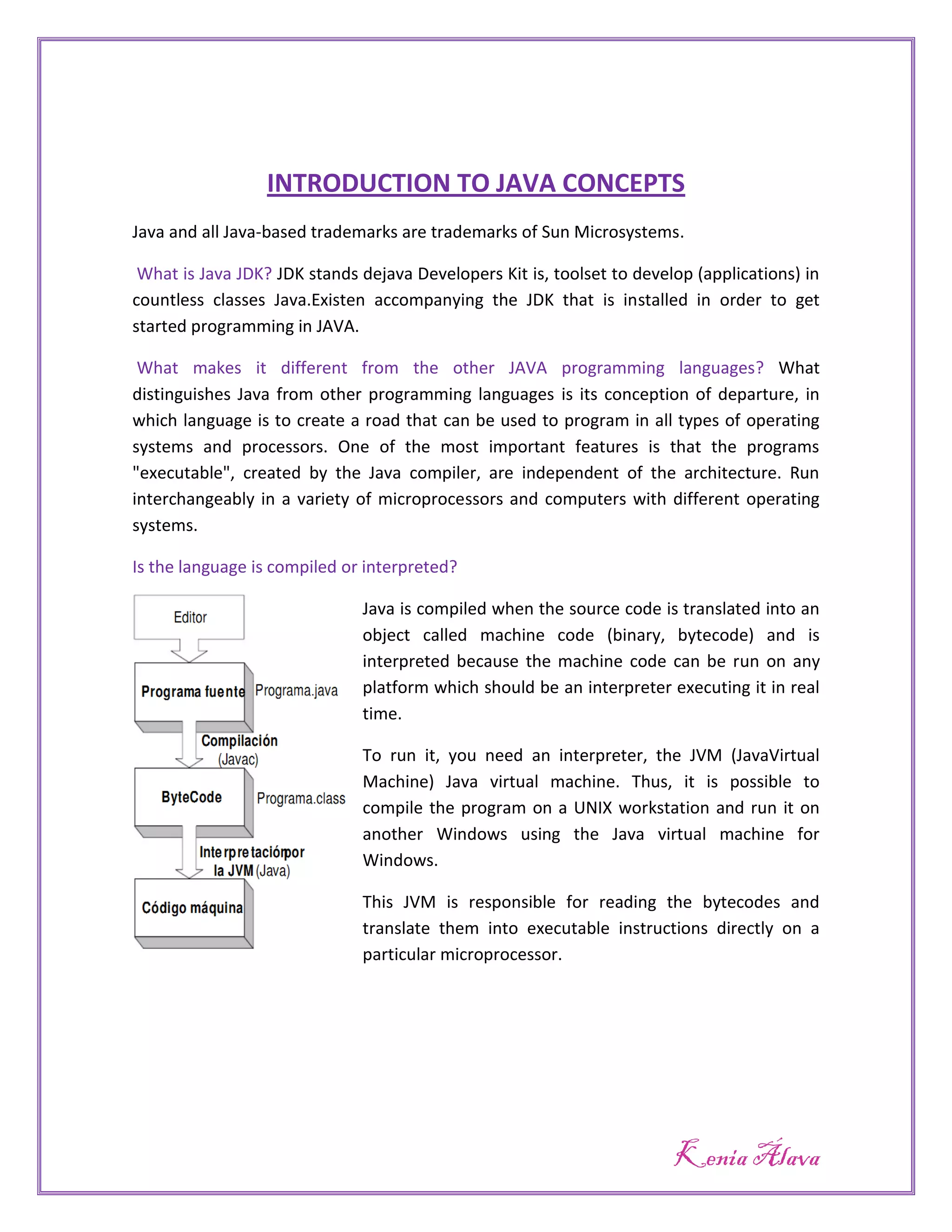
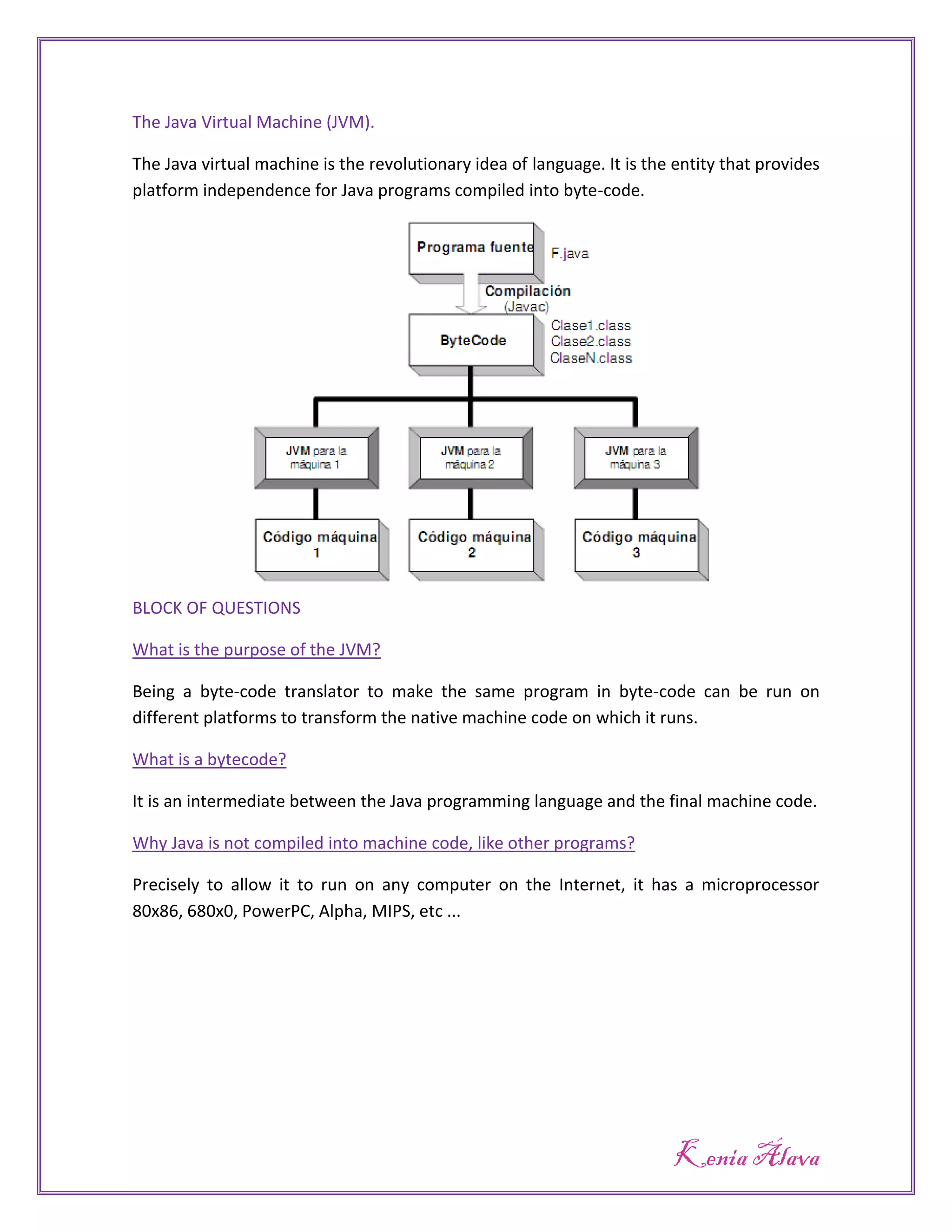
Java is both compiled and interpreted. Source code is compiled into bytecode, which can then be run on any platform using an interpreter called the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM translates the bytecode into executable instructions for the specific microprocessor. This allows Java programs to run on any system that has a JVM, making Java platform independent. The purpose of the JVM is to provide platform independence by acting as a bytecode translator to convert the same bytecode program into the native machine code of whatever system it is running on.