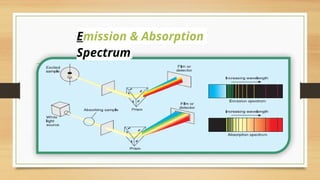
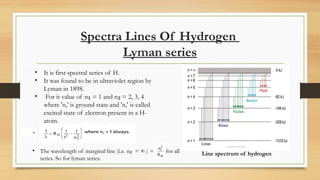
The document discusses the structure of the hydrogen atom and its emission spectrum, specifically noting Rydberg's formula and the spectral lines resulting from electron transitions between energy levels. It outlines the Lyman series, the first spectral series of hydrogen discovered in the ultraviolet region, and describes Bohr's model of the atom, including the fixed orbits of electrons around the nucleus. Key points include the behaviors of electrons in different shells and their energy transitions.