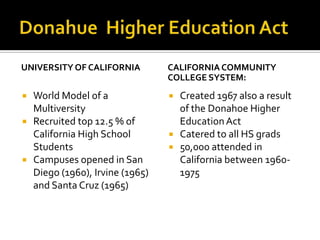
This document discusses the history of higher education in California and the United States from 1960 to present day. It covers major events and legislation that impacted access and diversity, the development of different systems and sectors of higher education, and the rise of student affairs as a field. Key topics covered include the civil rights movement, creation of California's master plan for higher education, increasing diversity of the student population, and growth of student services and affairs.