Recommended
PPTX
Software Defined Networking (SDN)
PPTX
software defined networks Introduction.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Lect12-13_MS_Networks.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Software Defined Networking(SDN) and practical implementation_trupti
PPTX
PPTX
Automation & Programmability.pptx
PPTX
TE581-Software Defined Networking-2019aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.pptx
PDF
S&D PPTs sensors and devices presentation
PPTX
CAP Theorem from book readings andnotetaking
PPTX
08-Software Defined Networking Southern Carolina
PDF
HACKING THE BRAIN: Customize Evil Protocol to Pwn an SDN Controller
PPTX
Network programmability: an Overview
PDF
intro lect.pdfkkpkpkpkpkpjjkojkopjjojjoj
PPTX
PPTX
Networking-Fundamentals-Firewall-Access-Points-and-Wireless-Controller.pptx
PPTX
DIT 212 Routing and Switching CCNA 2 - Introduction.pptx
PPTX
PPT
Enabling Active Flow Manipulation (AFM) in Silicon-based Network Forwarding E...
PPTX
PPTX
UNIT-1.pptx SDN INTRODUCTION AND BASICS
PPTX
SOFTWARE DEFINED NETWORKING
PPTX
sdnppt-140325015756-phpapp01.pptx
PPTX
software defined networks software defined networks.pptx
PPTX
PDF
Software Innovations and Control Plane Evolution in the new SDN Transport Arc...
PPTX
Floodlight tutorial - Clemson / Georgia Tech
PPTX
MODULE 1 ON PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE.pptx
DOCX
EAS Security antenna Cross Point RF 30.docx
More Related Content
PPTX
Software Defined Networking (SDN)
PPTX
software defined networks Introduction.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Lect12-13_MS_Networks.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Software Defined Networking(SDN) and practical implementation_trupti
PPTX
PPTX
Automation & Programmability.pptx
Similar to Cisco CCNA v2 Chapter 16 introduction to controler-based Net
PPTX
TE581-Software Defined Networking-2019aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.pptx
PDF
S&D PPTs sensors and devices presentation
PPTX
CAP Theorem from book readings andnotetaking
PPTX
08-Software Defined Networking Southern Carolina
PDF
HACKING THE BRAIN: Customize Evil Protocol to Pwn an SDN Controller
PPTX
Network programmability: an Overview
PDF
intro lect.pdfkkpkpkpkpkpjjkojkopjjojjoj
PPTX
PPTX
Networking-Fundamentals-Firewall-Access-Points-and-Wireless-Controller.pptx
PPTX
DIT 212 Routing and Switching CCNA 2 - Introduction.pptx
PPTX
PPT
Enabling Active Flow Manipulation (AFM) in Silicon-based Network Forwarding E...
PPTX
PPTX
UNIT-1.pptx SDN INTRODUCTION AND BASICS
PPTX
SOFTWARE DEFINED NETWORKING
PPTX
sdnppt-140325015756-phpapp01.pptx
PPTX
software defined networks software defined networks.pptx
PPTX
PDF
Software Innovations and Control Plane Evolution in the new SDN Transport Arc...
PPTX
Floodlight tutorial - Clemson / Georgia Tech
Recently uploaded
PPTX
MODULE 1 ON PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE.pptx
DOCX
EAS Security antenna Cross Point RF 30.docx
DOCX
Semiconductor industry in Southeast Asia.docx
PPT
High resolution tire cross section measurement - 2026
PDF
Sophos Certification - CERTIFICATE OF ACHIEVEMENT
DOC
Gamma-X - Tyre cross section measurement ---Explanation of presentation
Cisco CCNA v2 Chapter 16 introduction to controler-based Net 1. 2. Objectives
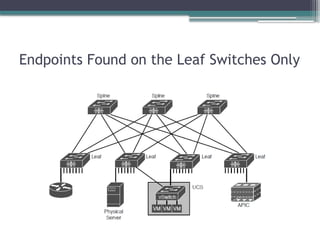
• Explain the role and function of network components
▫ Endpoints
▫ Servers
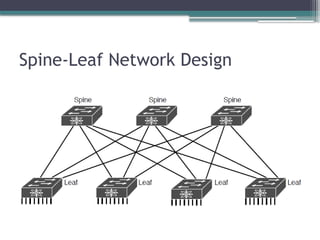
• Describe characteristics of network topology architectures
▫ Spine-leaf
• Explain how automation impacts network management
• Compare traditional networks with controller-based
networking
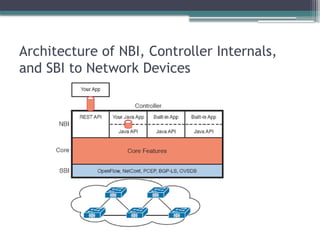
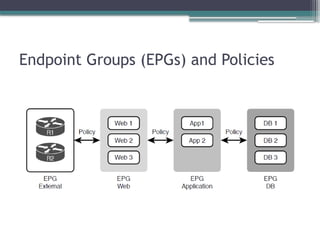
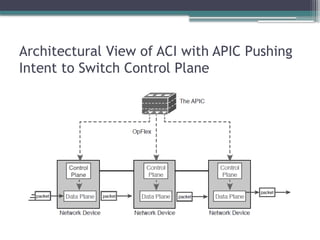
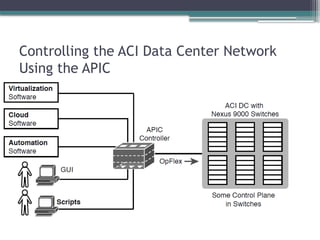
• Describe controller-based and software defined architectures
(overlay, underlay, and fabric)
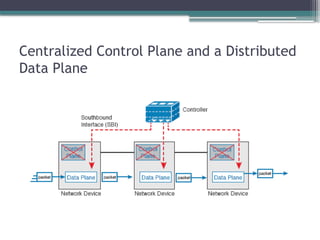
▫ Separation of control plane and data plane
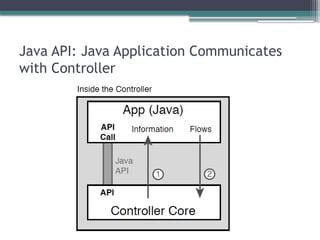
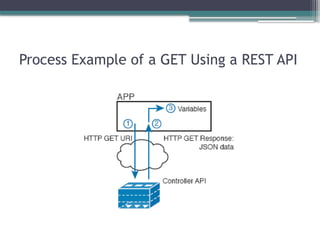
▫ Northbound and southbound APIs
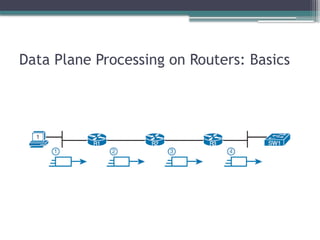
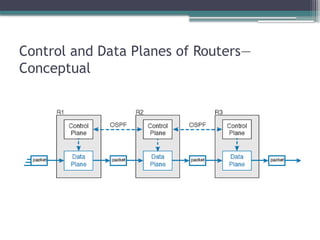
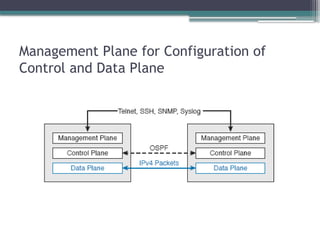
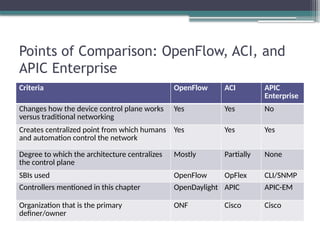
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Points of Comparison: OpenFlow, ACI, and
APIC Enterprise
Criteria OpenFlow ACI APIC
Enterprise
Changes how the device control plane works
versus traditional networking
Yes Yes No
Creates centralized point from which humans
and automation control the network
Yes Yes Yes
Degree to which the architecture centralizes
the control plane
Mostly Partially None
SBIs used OpenFlow OpFlex CLI/SNMP
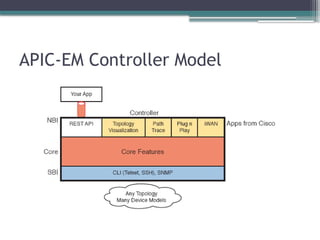
Controllers mentioned in this chapter OpenDaylight APIC APIC-EM
Organization that is the primary
definer/owner
ONF Cisco Cisco
18. 19.