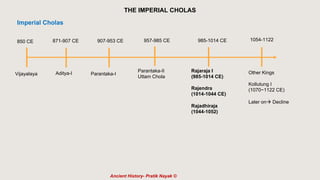
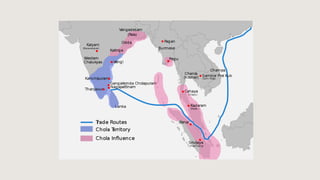
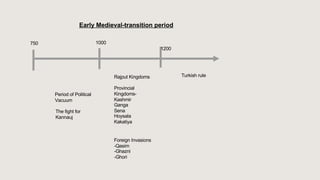
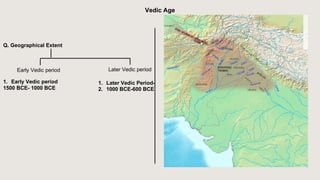
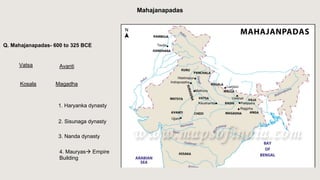
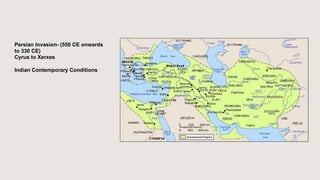
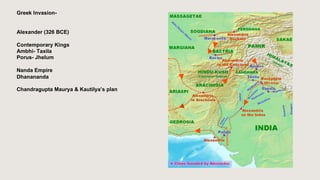
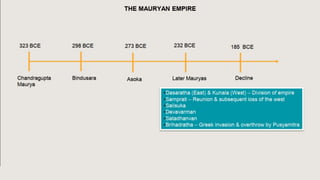
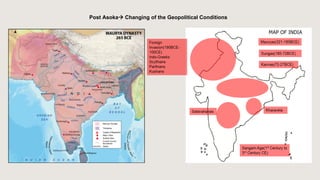
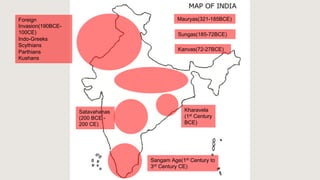
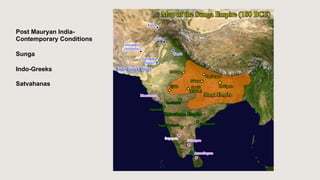
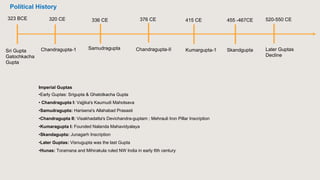
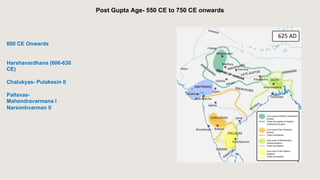
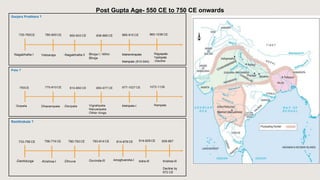
The document outlines the historical timeline of prehistoric India from the Stone Age through significant periods such as the Indus Valley Civilization, the Vedic Age, the Mauryan Empire, and the Gupta Age, culminating in the post-Gupta period. It highlights key dynasties, foreign invasions, and cultural evolution in ancient India while emphasizing the archaeological findings that inform this history. The document further examines political developments and regional kingdoms from around 600 CE to 750 CE.




![UPSC CSE- Prelims 2021
CSP21-SET-C] Q.64) From the declines of Guptas until the rise of Harshavardhana in
the early seventh century, which of the following kingdoms were holding power in
Northern India?
1. The Guptas of Magadha
2. The Paramaras of Malwa
3. The Pushyabhutis of Thanesar
4. The Maukharis of Kanauj
5. The Yadavas of Devagiri
6. The Maitrakas of Valabhi
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
a) 1, 2 and 5
b) 1, 3, 4 and 6
c) 2, 3 and 4
d) 5 and 6
Difficulty : Medium🧐
Type: Theory 📚
Attempt | Skip | 50:50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronology-ancientindiatimelineclean-240901211543-98bc423f/85/Chronology-Ancient-India-Timeline-Clean-pdf-16-320.jpg)
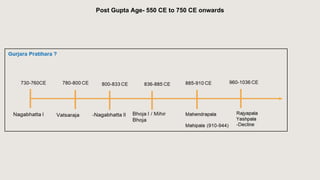
![UPSC CSE- Prelims 2022
CSP22-SET-B] Q.52) Consider the following pairs :
King Dynasty
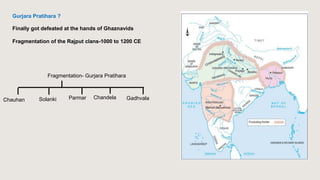
1. Nannuka — Chandela
2. Jayashakti — Paramara
3. Nagabhata II — Gurjara-Pratihara
4. Bhoja — Rashtrakuta
How many pairs given above are correctly matched ?
(a) Only one pair
(b) Only two pairs
(c) Only three pairs
(d) All four pairs
Difficulty : Tough🥵
Type: Theory 📚
Attempt | Skip | 50:50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chronology-ancientindiatimelineclean-240901211543-98bc423f/85/Chronology-Ancient-India-Timeline-Clean-pdf-22-320.jpg)