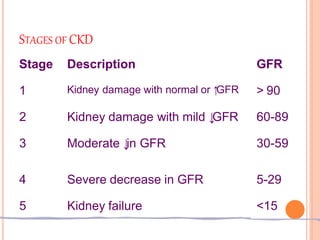
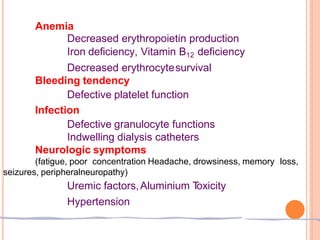
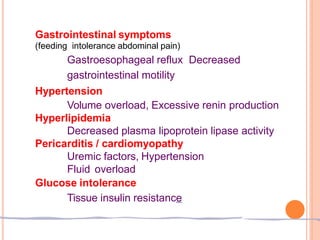
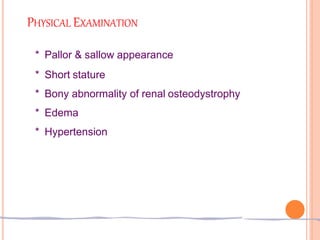
This document discusses chronic kidney disease in children. It defines chronic kidney disease as either kidney damage or a glomerular filtration rate below 60 ml/min/1.73m2 for over 3 months. The causes include congenital abnormalities in children under 5 and acquired or inherited disorders after 5 years of age. The stages of chronic kidney disease are described based on glomerular filtration rate. Treatment aims to replace kidney function, slow progression, and manage fluid, electrolytes, acidosis, nutrition, growth, renal osteodystrophy, anemia, hypertension, and other complications. Strategies to slow progression include controlling hypertension, maintaining phosphorus levels, treating infections, correcting anemia, and controlling hyperlipidemia.