Embed presentation
Download to read offline





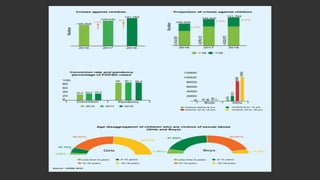



Child rights and women's rights document discusses key issues related to children and legislation in India. It defines a child as anyone under 18 years old. Major issues facing children in India include child labor, gender inequality, malnutrition, poverty, illiteracy, child marriage, trafficking, and sexual harassment. The main laws protecting children are the Juvenile Justice Act, the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, and the Child Labour Act. The document also mentions India's child helpline.








