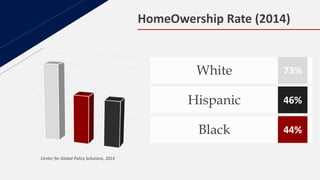
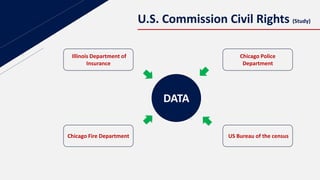
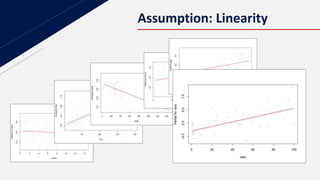
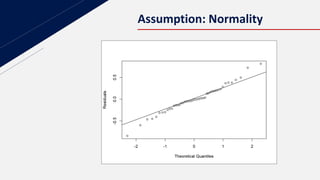
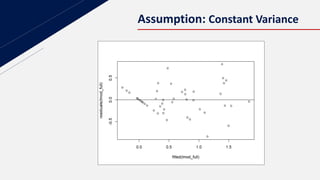
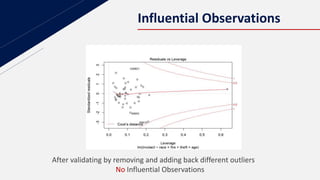
This document discusses insurance redlining in Chicago. Redlining originated in the 1930s when neighborhoods were color-coded on maps to indicate their eligibility for loans and mortgages. Historically redlined neighborhoods were often communities of color and faced discrimination. The document presents statistics on homeownership rates by race and analyzes insurance data from Chicago neighborhoods to build a regression model to study the effects of variables like income, crime rates, housing age and racial composition on insurance availability. It aims to determine if redlining still exists based on this analysis.