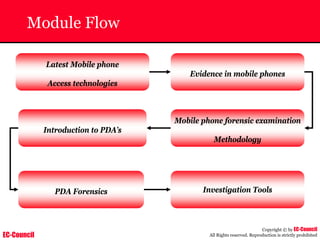
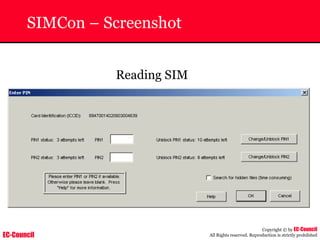
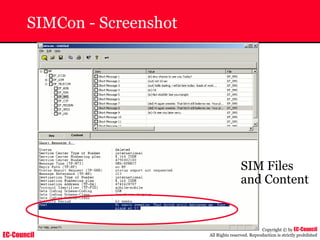
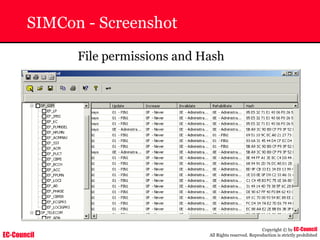
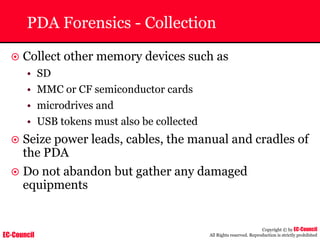
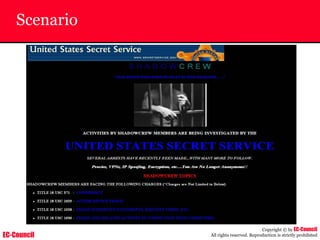
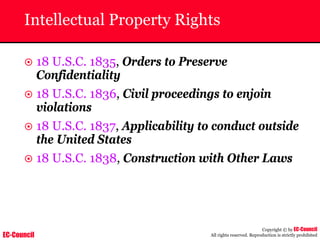
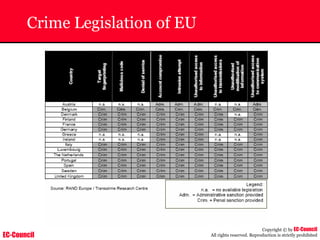
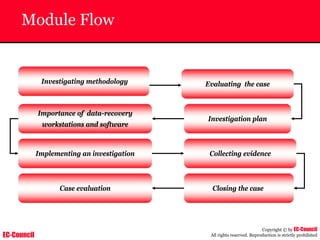
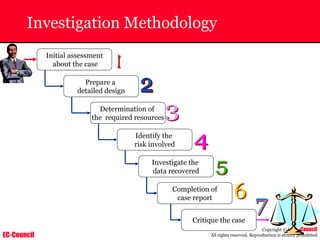
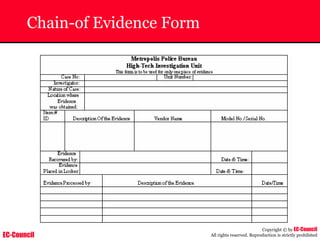
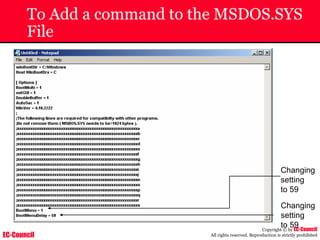
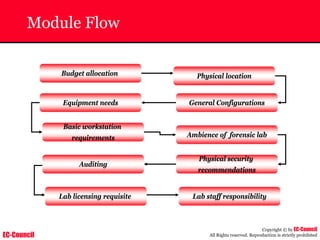
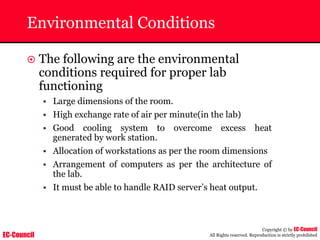
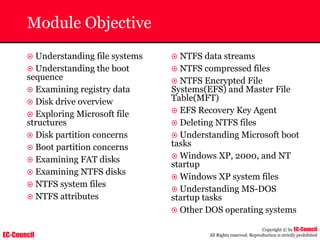
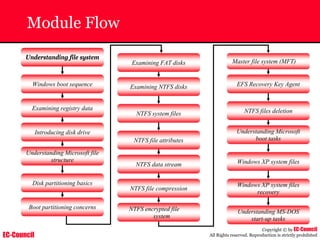
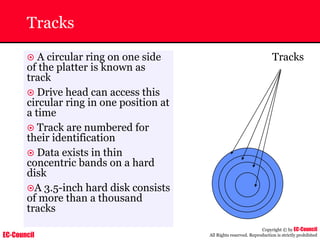
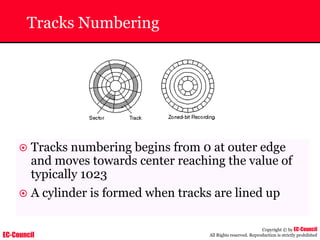
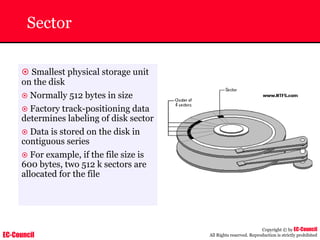
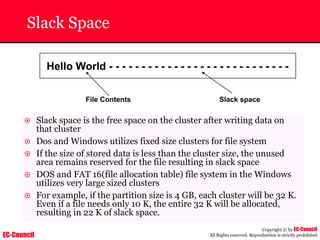
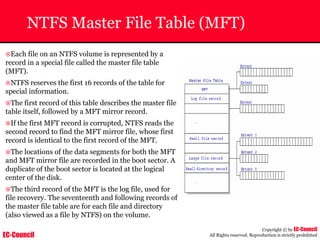
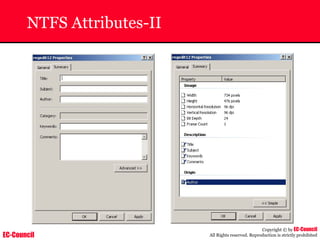
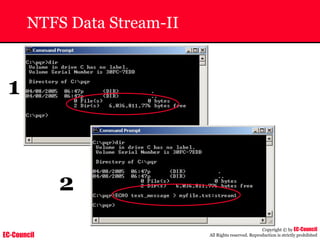
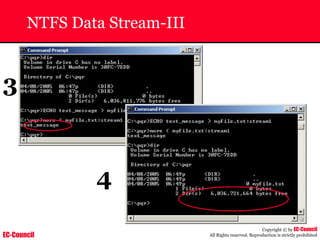
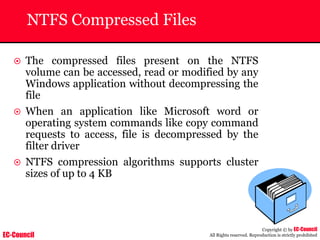
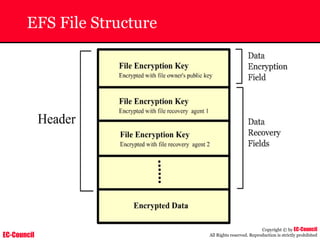
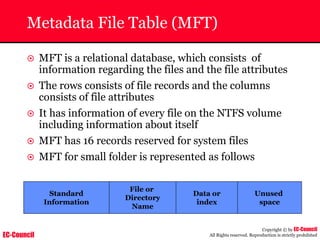
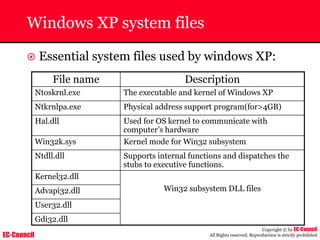
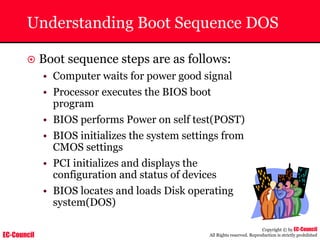
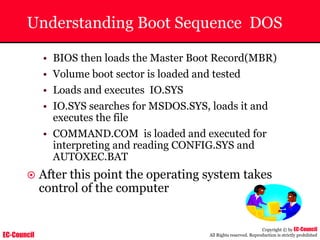
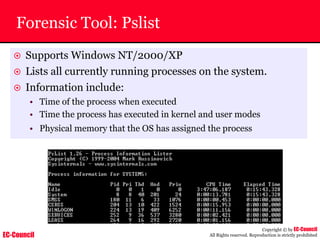
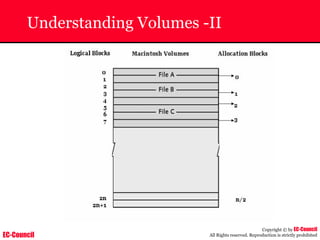
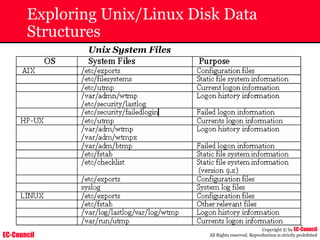
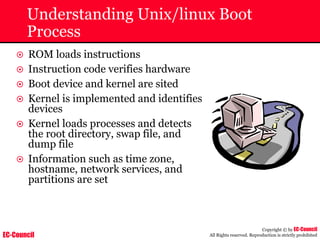
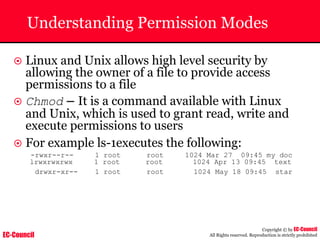
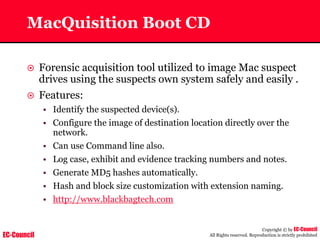
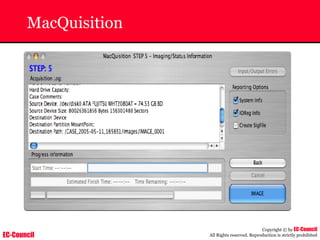
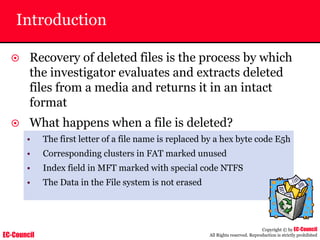
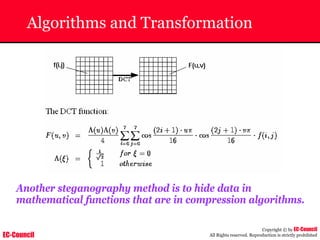
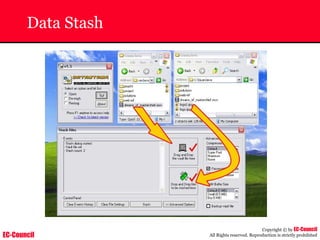
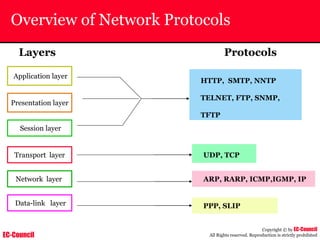
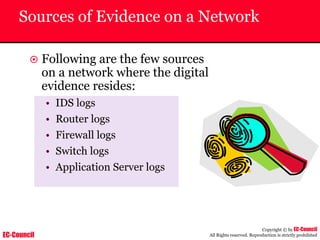
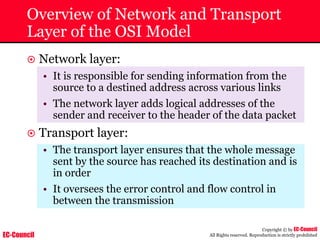
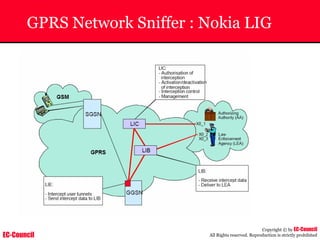
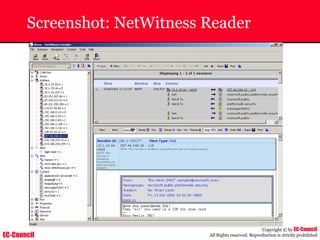
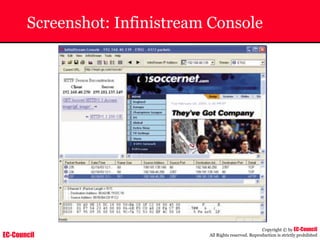
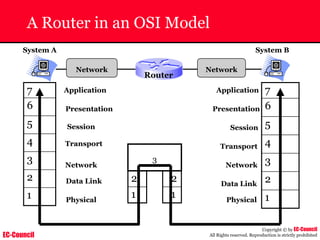
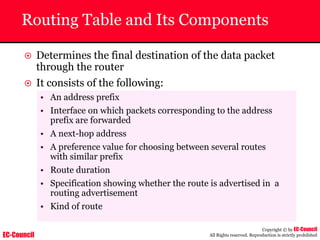
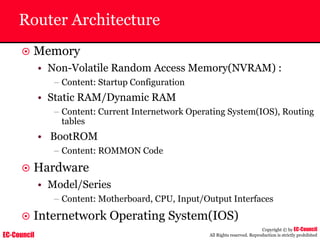
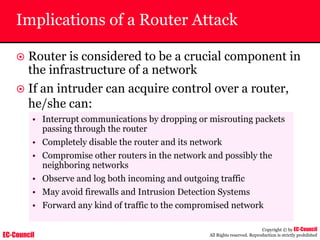
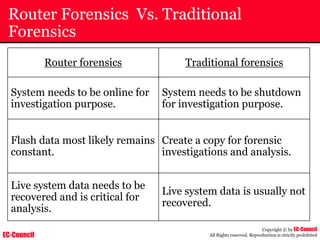
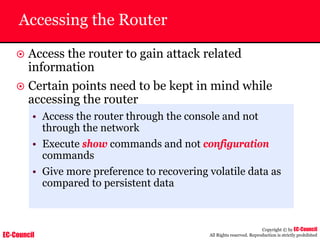
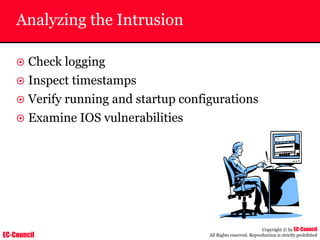
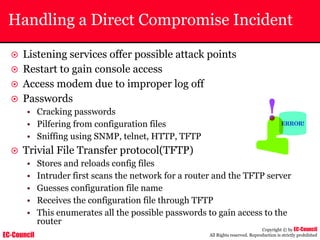
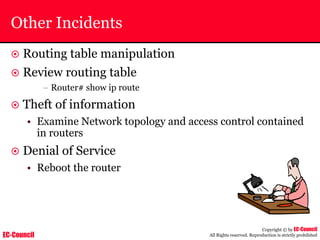
The document outlines the EC-Council's Computer Hacking Forensic Investigator (CHFI) program, including its course modules and objectives related to computer forensics and cyber crime. It emphasizes the need for computer forensics in preventing and investigating cyber crimes and provides details on methodologies, legal frameworks, and reporting systems to law enforcement. Additionally, it discusses the evolution of forensic practices and the critical role of computer forensics in the modern digital landscape.












































































































































































































































































































































![EC-Council
Copyright © by EC-Council
All Rights reserved. Reproduction is strictly prohibited
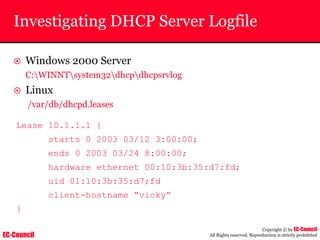
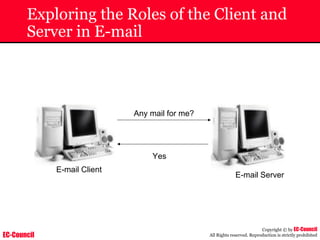
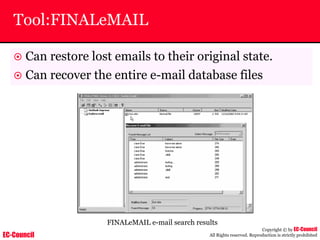
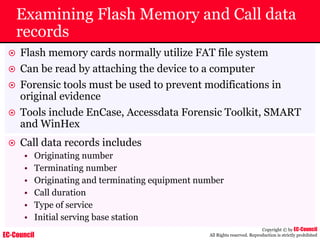
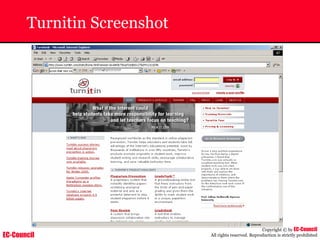
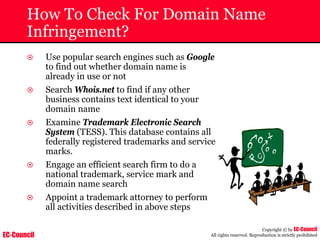
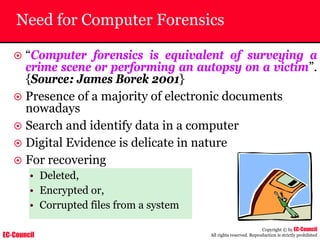
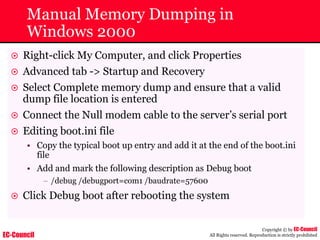
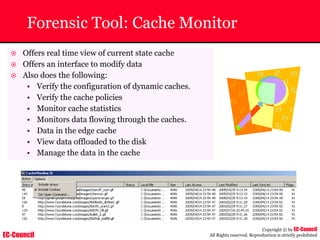
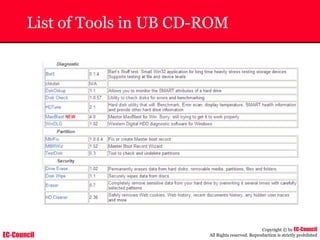
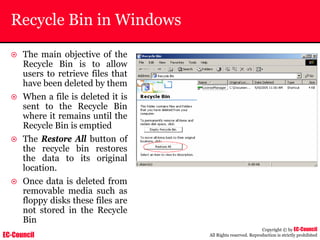
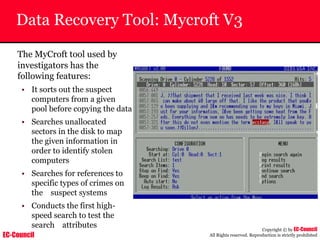
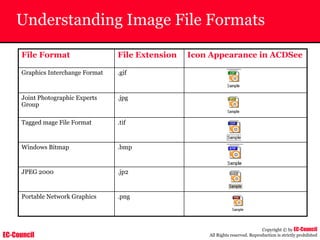
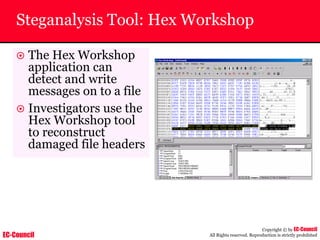
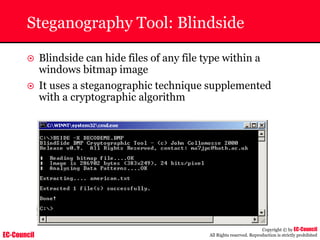
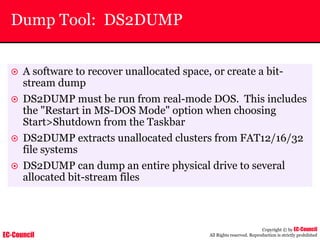
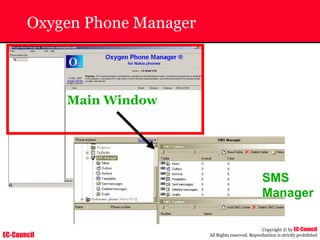
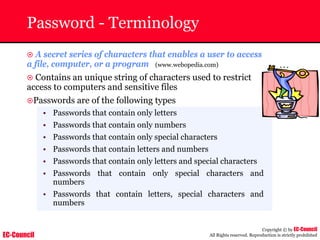
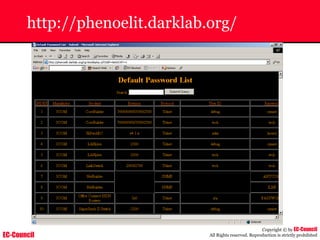
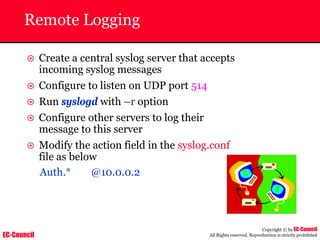
Dump Tool: Chaosreader
~ Used trace TCP/UDP sessions and capture the
application data
~ Data captured from tcpdump or snoop logs
~ It creates html index files and links all the session
details
~ Few the quick commands that are used are
Chaosreader [-aehikqrvxAHIRTUXY] [-D dir]
Chaosreader [-b port[,...]] [-B port[,...]]
Chaosreader [-j IPaddr[,...]] [-J IPaddr[,...]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chfi-230329100810-00449f6f/85/CHFI-pdf-493-320.jpg)


































































![EC-Council
Copyright © by EC-Council
All Rights reserved. Reproduction is strictly prohibited
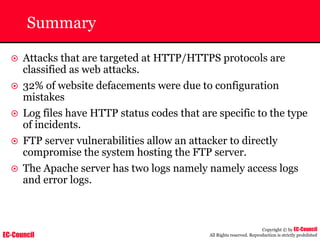
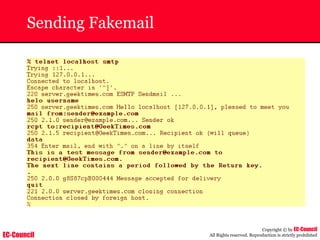
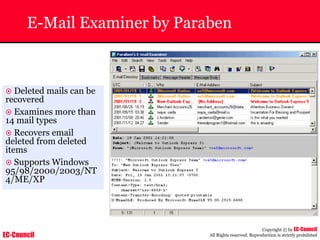
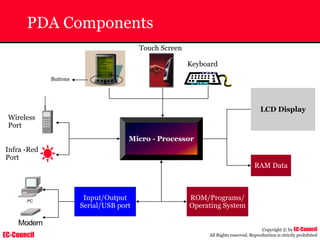
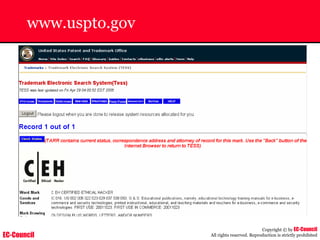
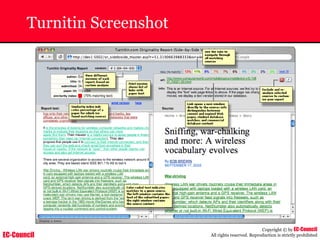
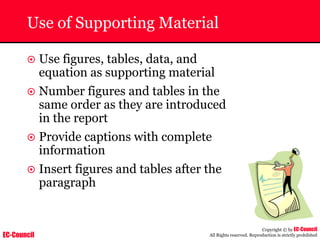
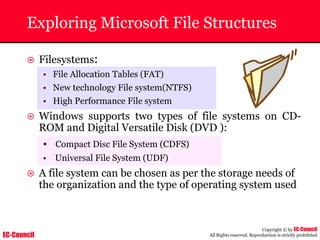
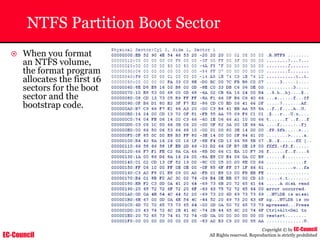
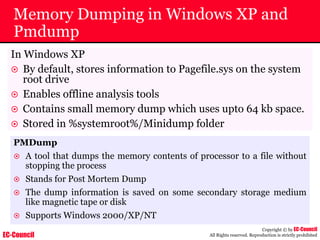
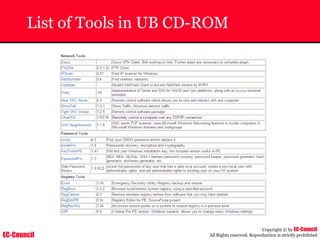
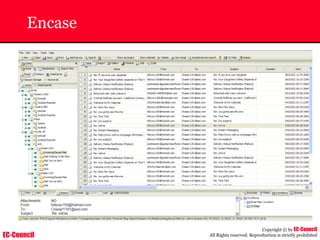
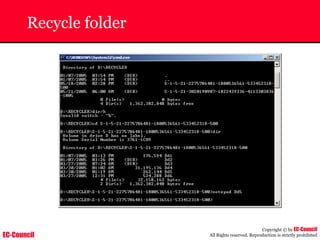
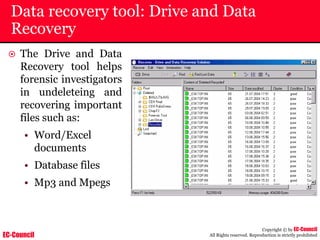
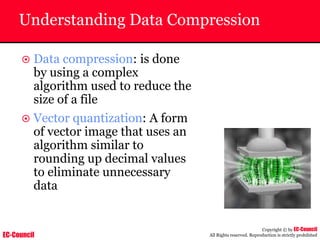
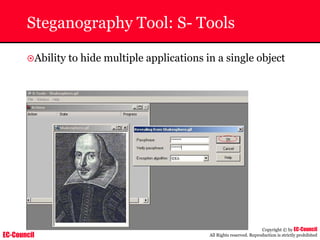
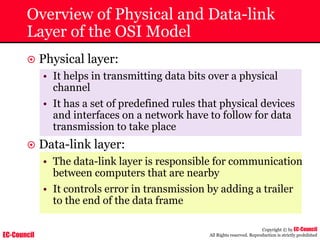
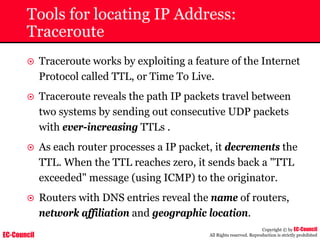
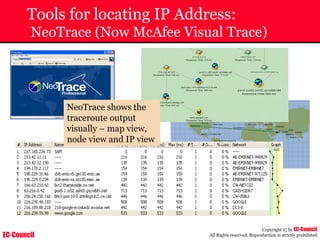
Tool: Windump
~ WinDump is the porting to the Windows platform of tcpdump, the
most used network sniffer/analyzer for UNIX
~ Given below is the output obtained from Windump
20:50:00.037087 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 128, id 2572, len 46) 192.168.2.24.1036 >
64.12.24.42.5190: P [tcp sum ok] 157351:157357(6) ack 2475757024 win 8767 (DF)
The above entry can be deciphered as:
timestamp Æ 20:50:00.037087
IP [protocol header] Æ tos 0x0, ttl 128, id 2572, len 46
source IP:port Æ 192.168.2.24.1036
destination IP:portÆ 64.12.24.42.5190:
P [push flag] [tcp sum ok] Æ157351:157357
[sequence numbers] (6) [bytes of data]
acknowledgement and sequence number Æack 2475757024
window size (DF) [don’t fragment set]Æ win 8767](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chfi-230329100810-00449f6f/85/CHFI-pdf-592-320.jpg)















































![EC-Council
Copyright © by EC-Council
All Rights reserved. Reproduction is strictly prohibited
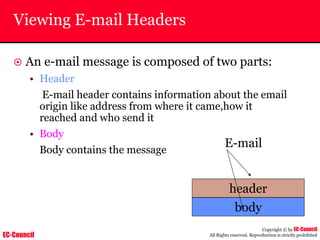
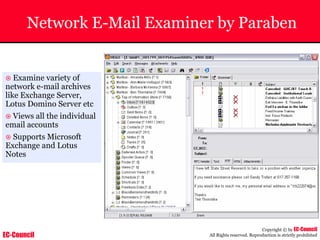
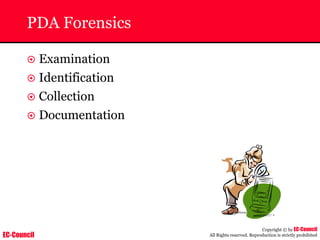
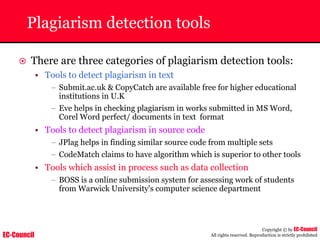
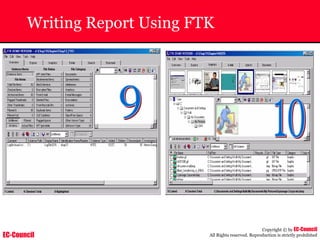
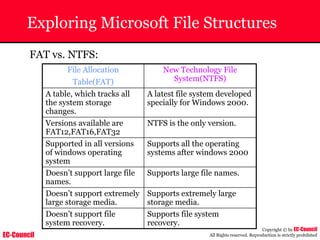
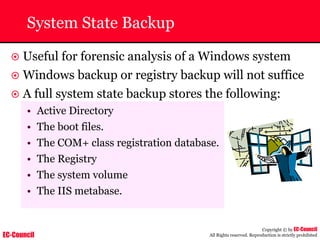
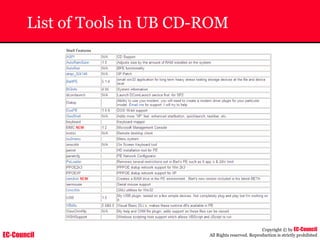
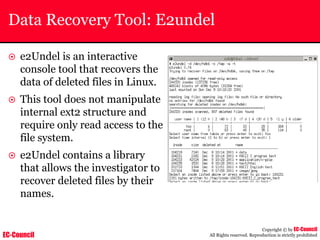
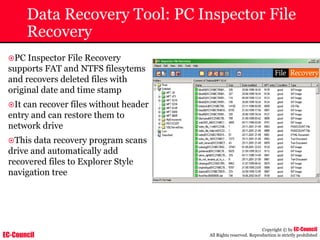
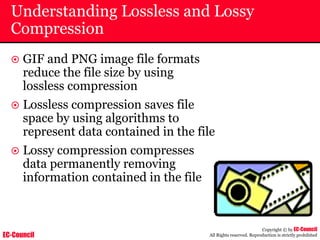
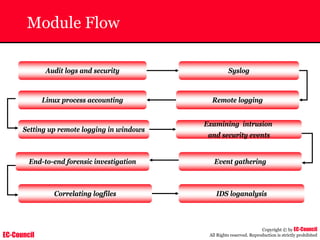
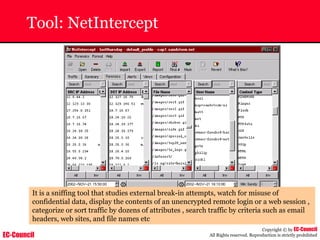
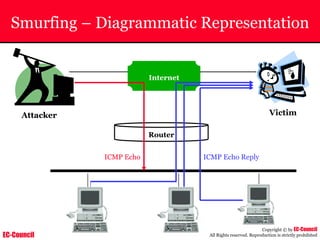
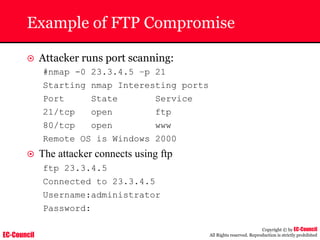
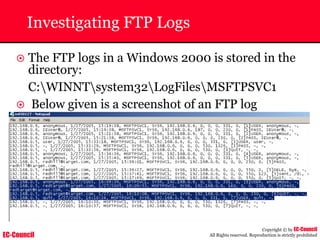
Investigating Apache Logs
~ The Apache server has two logs namely:
• Error log:
– The Apache server saves diagnostic information and error messages that it
encounters while processing requests.
– The default path of this file is usr/local/apache/logs/error_log in Linux
– It is an important piece of evidence from investigator’s point of view.
[Sat Dec 11 7:12:36 2004] [error] [client 202.116.1.3] Client sent malformed
Host header
• Access log:
– Requests processed by the Apache server are contained in this.
– By default access logs are stored in the common log format.
– The default path of this file is usr/local/apache/logs/access_log in
Linux
202.116.1.3 - shilp [11/Dec/2004:6:23:13 -0500] "GET /apache_ft.gif HTTP/1.0"
200 1577](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chfi-230329100810-00449f6f/85/CHFI-pdf-669-320.jpg)