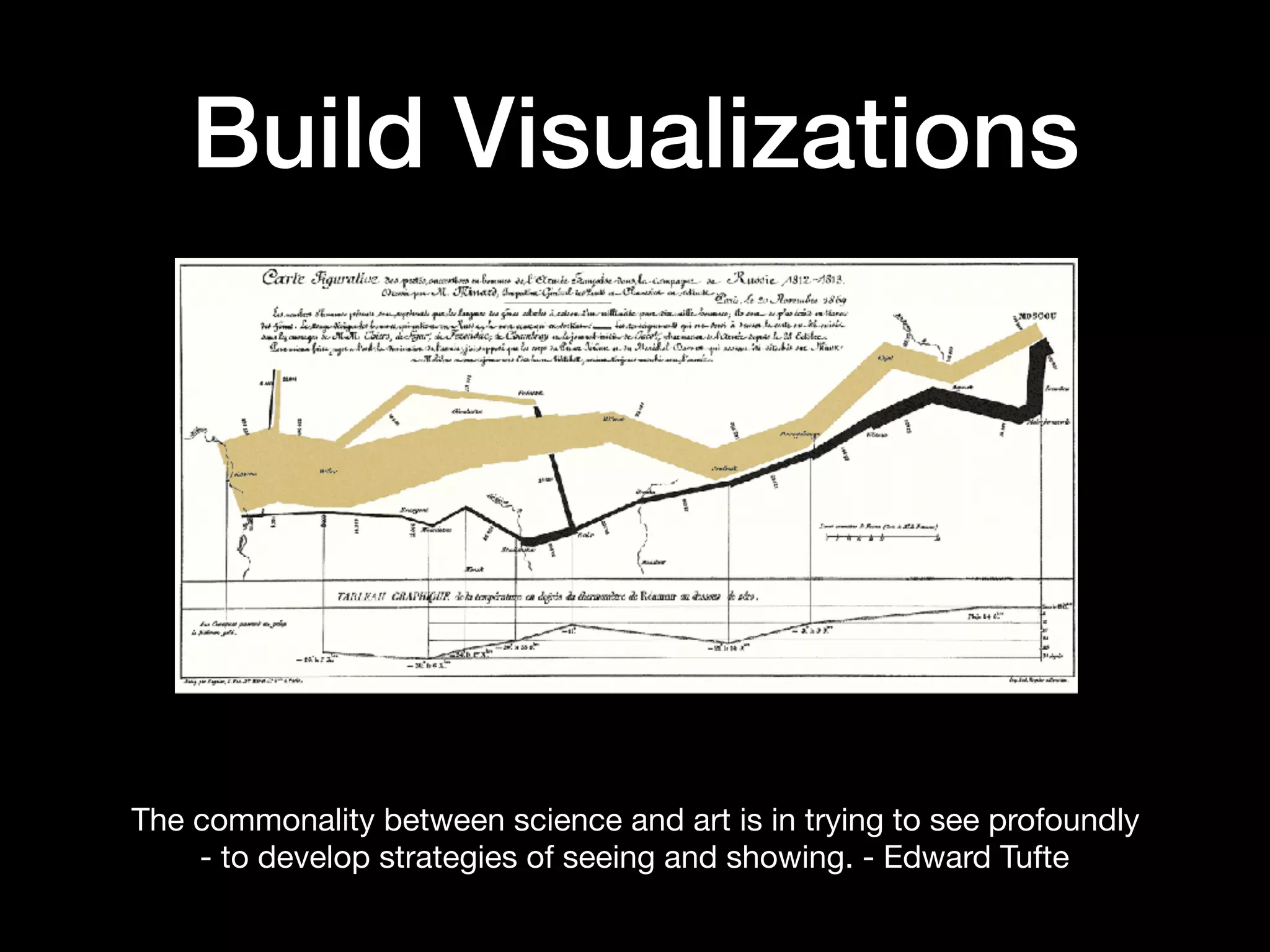
The document summarizes a presentation on data visualization with D3.js given by Brian Greig to the Charlotte Front-End Developers group. The presentation covered data visualization concepts, accessing data via APIs, basic D3 components like binding data, building visualizations, and making visualizations interactive. It provided examples of good data visualizations and discussed key terms. It also outlined the steps to structure a D3 application, including initializing scales and domains, entering and updating data, and cleaning up.









![Basic Components
Your basic D3 Starter Kit
• Define the dataset [1]
• Create a container [3-5]
• Bind your data [8]
• Append visual
components & set
attributes [11-18]
• Clean up [24]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfe-d3jscopy-170724022236/75/Charlotte-Front-End-D3-11-2048.jpg)