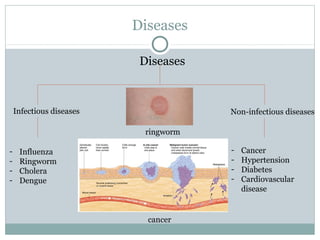
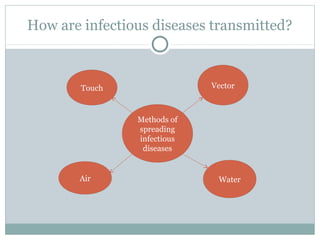
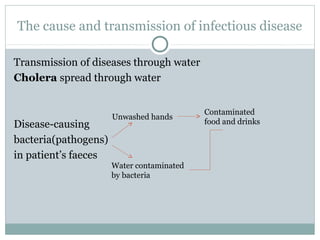
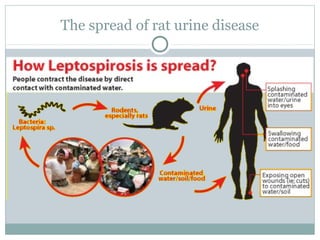
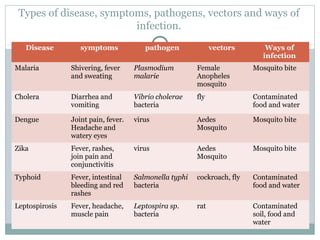
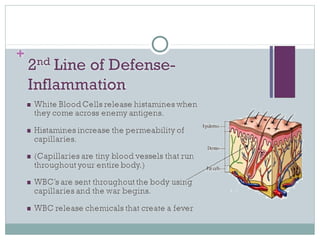
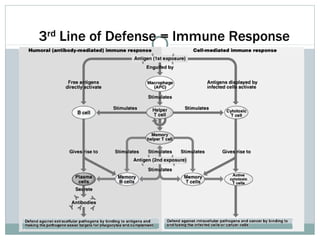
This document discusses infectious and non-infectious diseases. Infectious diseases can spread from person to person through various mediums like water, air, touch, or vectors. Common infectious diseases mentioned include influenza, cholera, dengue, and malaria. Non-infectious diseases like cancer and diabetes cannot spread between individuals. The document then examines in more detail how diseases are transmitted through water, air, touch, and vectors. It provides examples of diseases spread by mosquitoes like dengue, malaria, and Zika. Finally, it discusses the body's defenses against pathogens like skin, saliva, mucus membranes, and more.