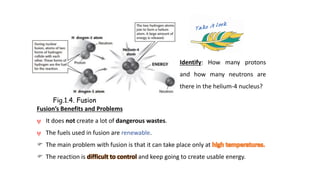
This document provides an overview of different types of energy sources, both renewable and non-renewable. It begins with definitions of renewable and non-renewable resources, giving examples of each. The main types of energy sources discussed include fossil fuels like petroleum, coal and natural gas; alternative sources like nuclear fission, solar, wind and hydroelectric; as well as geothermal, biomass and fusion energy. For each type, the document describes how the energy is produced, benefits and drawbacks. Figures and diagrams are included to illustrate concepts like the nuclear fission process and geothermal power plant design. Students are prompted throughout with questions to check understanding.