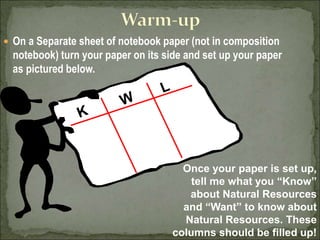
The document discusses natural resources and differentiates between renewable and non-renewable resources, with renewable resources like water and trees being able to replenish relatively quickly while non-renewable resources like coal and oil take thousands or millions of years to replenish or are finite; it also covers energy resources and alternatives to fossil fuels which are non-renewable, highlighting the need for conservation and renewable alternatives like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.