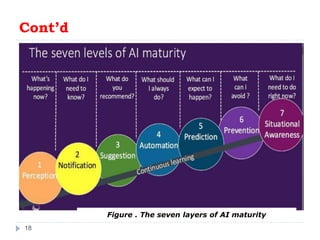
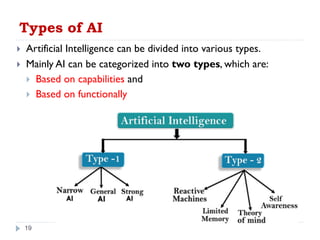
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. These intelligent machines are designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. AI systems use algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions based on that analysis. AI has numerous applications across various fields, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment, and is constantly evolving as technology advances.