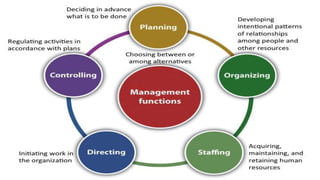
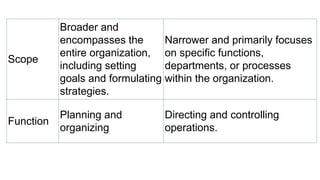
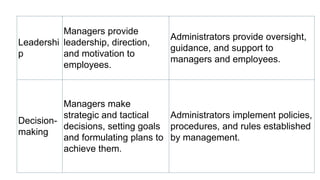
This document discusses various aspects of management including definitions, functions, objectives, and scope. Management is defined as the process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling organizational resources to achieve goals. The main functions of management are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Objectives of management include optimizing resources, increasing efficiency, maximizing profits, promoting personal development, maintaining quality, reducing risk, and identifying talent. The scope of management encompasses financial management, marketing management, human resource management, production management, and office management.