Embed presentation
Download to read offline
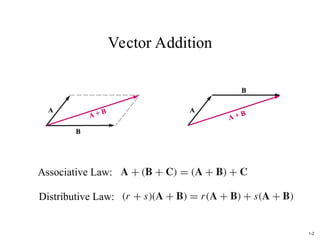
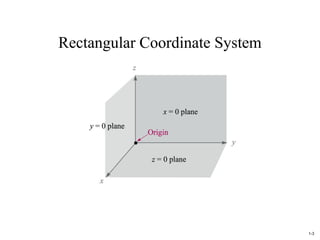
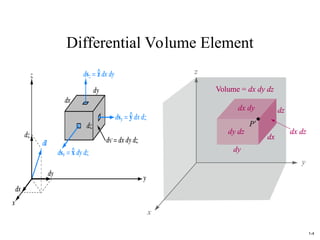
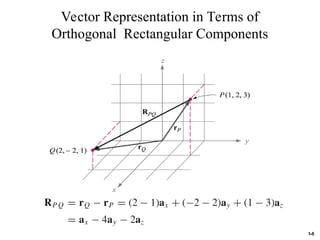

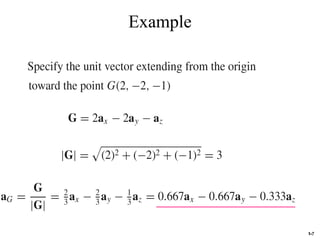
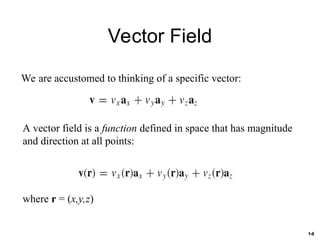
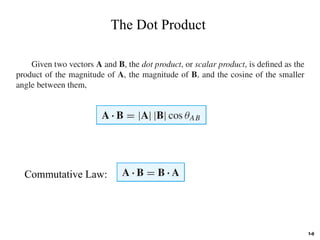
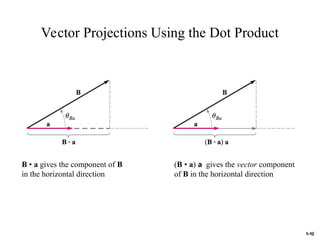

The document discusses foundational concepts in electromagnetics, including vector addition and properties like the associative and distributive laws. It introduces rectangular coordinate systems and vector representations, emphasizing vector fields as functions with magnitude and direction in space. Additionally, it covers the dot product and vector projections.










