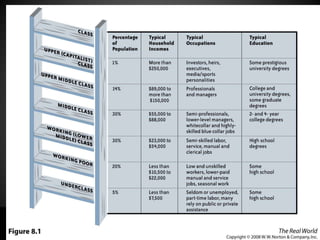
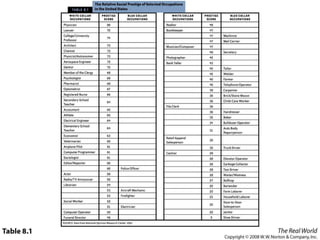
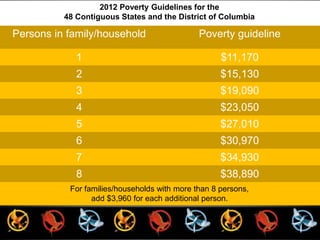
Social stratification separates society into hierarchical social classes. There are four basic principles of social stratification: it is a characteristic of society rather than individuals; social status often persists across generations; different societies use different criteria for ranking members; and social hierarchies are maintained through widely held beliefs. A person's social class influences their life chances in terms of education, health, family life, work opportunities, and criminal justice outcomes. However, social mobility is possible as individuals can move between social classes either vertically or horizontally.