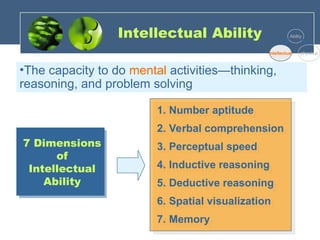
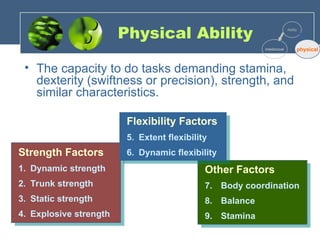
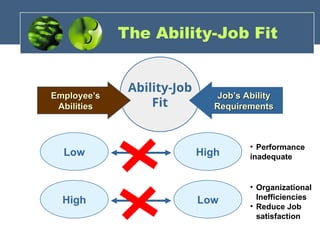
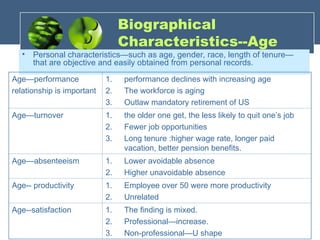
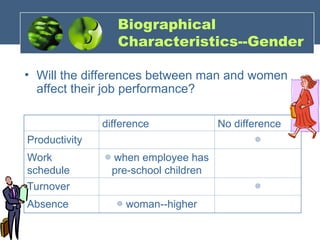
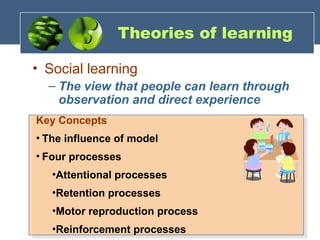
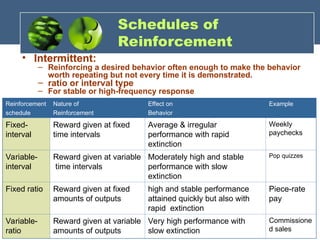
The document discusses the foundations of individual behavior in organizational settings, focusing on types of abilities, biographical characteristics, and learning theories. It emphasizes the distinction between intellectual and physical abilities, their impact on job performance, and the influence of age, gender, and race on workplace behavior. Additionally, it outlines methods for shaping behavior through reinforcement and illustrates the application of these concepts in organizational behavior modification.