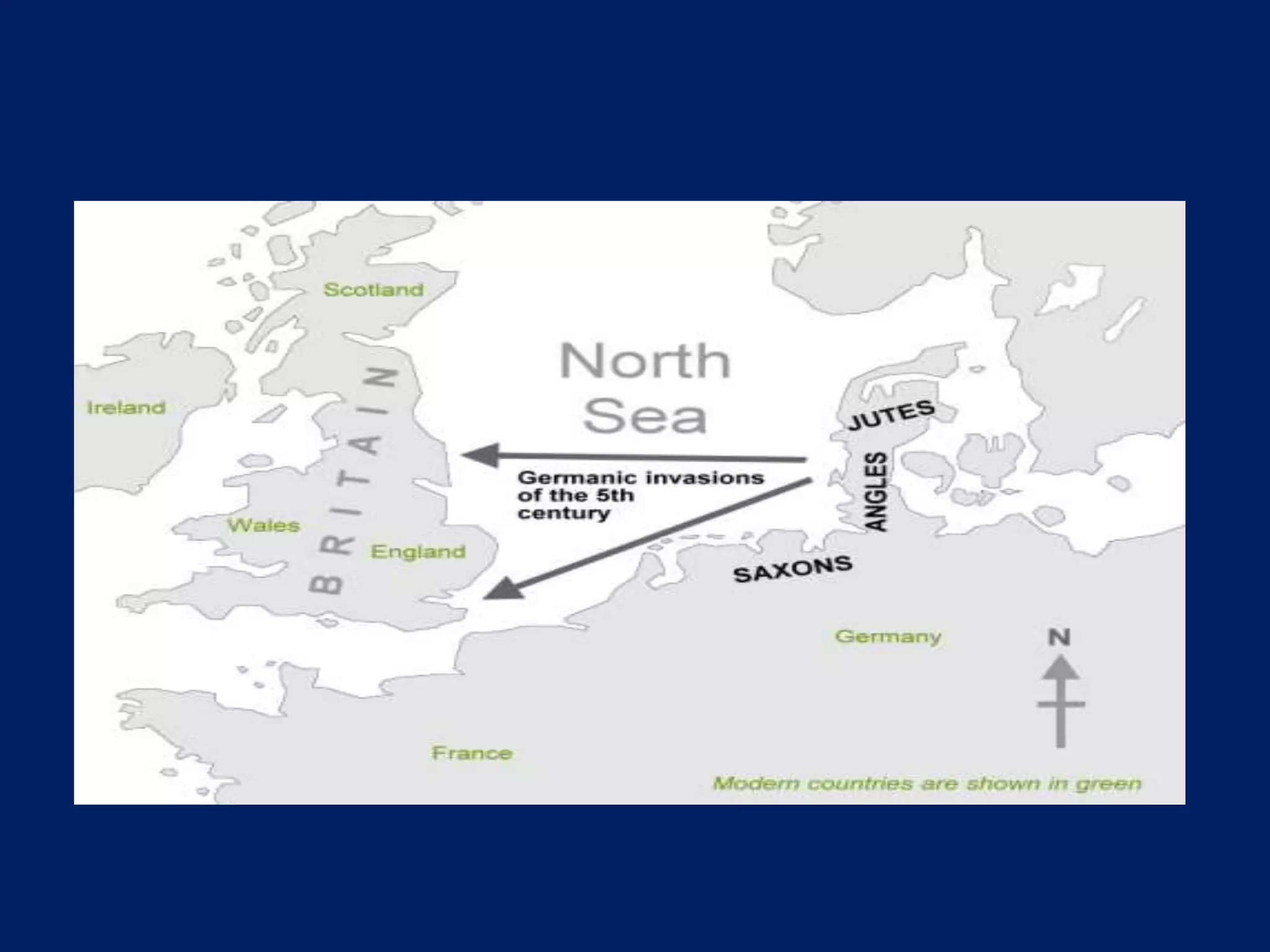
This document summarizes the history and development of the English language from its origins to modern times. It traces English back to West Germanic roots and discusses the influences of Latin, Old Norse, Norman French and later globalization and colonization. Key periods discussed include Old English, Middle English, and Modern English. The document provides numerous examples of word origins and influences across different historical periods and regions on the continuing evolution of the English language.