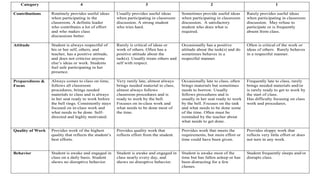
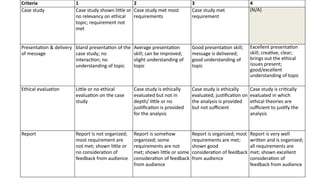
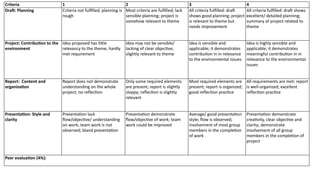
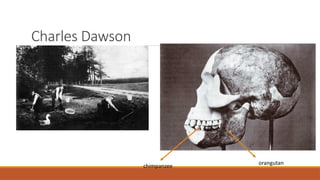
This document outlines the course syllabus for a science and ethics class, detailing topics like the ethical use of humans and animals in research, as well as defining assessment criteria for assignments and group projects. The syllabus emphasizes the development of critical thinking skills regarding ethical dilemmas in science and includes components like class participation, individual and group assignments, and peer evaluations. Students are also expected to engage in discussions on various ethical theories and principles, ultimately reflecting on their learning through presentations and written reports.