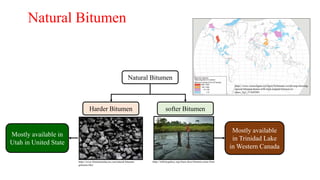
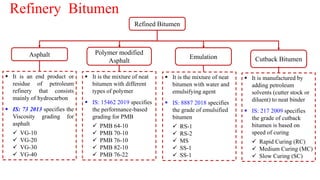
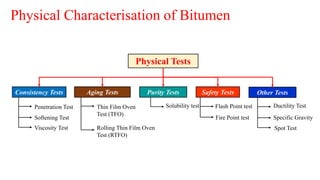
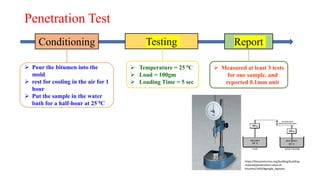
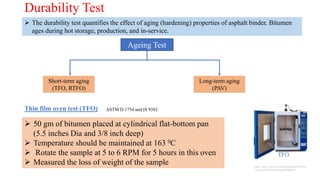
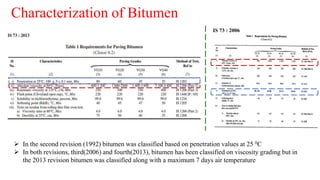
This document provides a summary of a presentation on asphalt binder given by Sunny Kumar at the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati. It discusses the properties and types of bitumen and asphalt, including how they are obtained naturally or through refining crude oil. Various tests used to characterize bitumen are outlined, such as penetration, softening point, viscosity and rolling thin film oven tests. Major bitumen producers in India are listed and standards for grading different types of bitumen and asphalt are referenced.