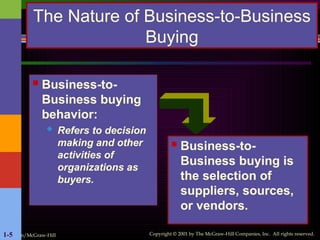
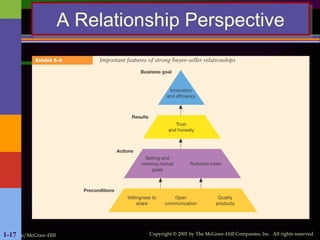
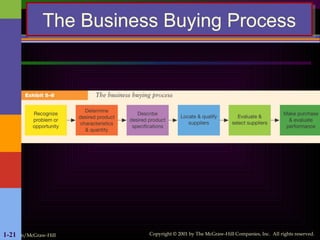
Crafting a single paragraph of 300 words presents a unique challenge, as it requires a careful balance of detail and flow to avoid feeling like a long, run-on sentence. The key is to build a cohesive idea, with each sentence adding a new layer of information or perspective. Imagine a scene: a lone traveler stands on a windswept cliff, gazing out at the vast, churning ocean below. The sky is a dramatic canvas of bruised purples and fiery oranges, the last remnants of a sun that has already dipped below the horizon. The air, thick with the scent of salt and damp earth, bites at their exposed skin, a constant reminder of the wildness surrounding them. This person, a silhouette against the fading light, carries a story etched in the lines of their face and the tired slump of their shoulders. They aren't just looking at the sea; they are communing with it, sharing a silent understanding of its relentless power and its profound, unending mystery. The roar of the waves crashing against the rocks is not a sound of chaos but a powerful symphony, a rhythm that resonates deep within their soul. For a moment, all the noise of the world—the worries, the plans, the regrets—melts away, replaced by a singular, overwhelming sense of presence. Here, on this precipice between land and sea, between past and future, they are simply and completely in the now. It is a moment of profound solitude, yet it feels anything but lonely. The universe, in all its silent grandeur, seems to hold its breath with them, a shared witness to a quiet, personal epiphany. This simple act of observation becomes a deeply spiritual experience, a pilgrimage not to a physical place, but to a state of being where clarity and peace are the only things that matter. In the face of such raw, untamed beauty, the small anxieties of life lose their grip, and the traveler finds a temporary, but total, release.