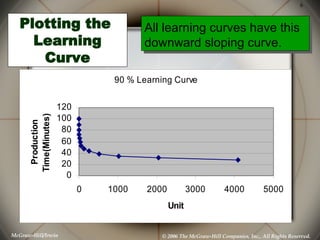
This document discusses learning curves and how they can be used to improve performance. It explains that when a task is repeated, the time it takes to complete the task decreases in a predictable pattern. An example is given of an individual's times decreasing for completing a term paper. There are two types of learning curves: individual learning from repetition and organizational learning from groups improving over time. Lastly, the document outlines ways companies can use learning curve data to enhance training, specialization, tools, and process redesign to boost performance.