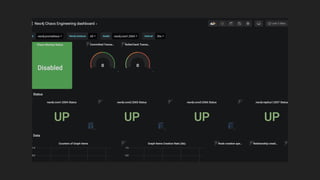
The document discusses chaos engineering as a method of experimenting on software systems, particularly using Neo4j, to improve resilience against failures. It outlines the principles of chaos engineering, experiment execution steps, and practical applications such as simulating failures and injecting faults. Additionally, it provides tools for implementing chaos engineering and resources for further exploration, including quizzes to test understanding.