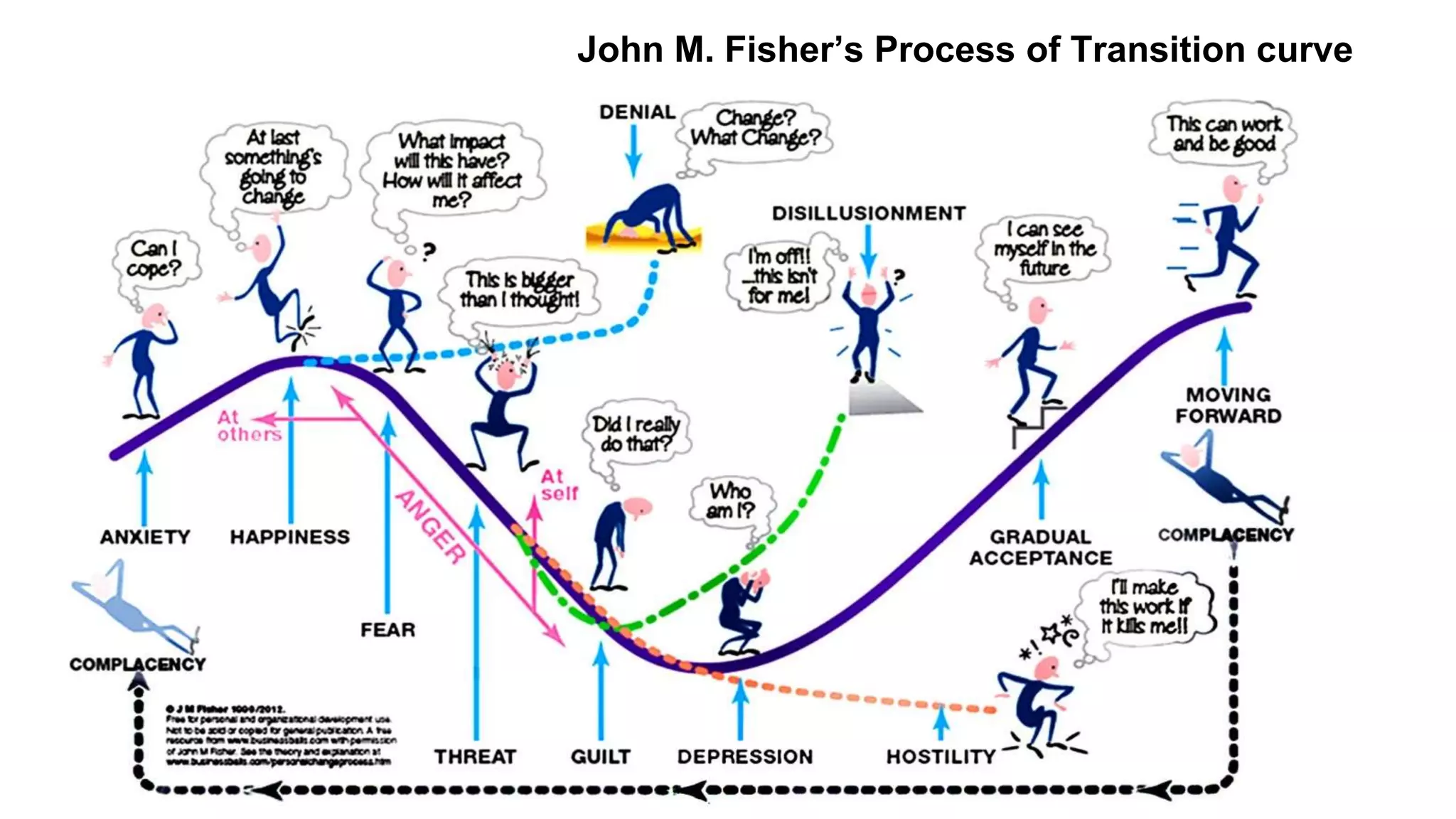
The document discusses change management processes. It defines what is changing through organization design, stakeholder analysis, HR alignment, and business impact assessments. It prepares for change through business readiness assessment, communications planning, and business engagement. The document outlines managing the transition through change guides, executive sponsorship, role mapping, training, and deployment planning. Finally, it focuses on realizing benefits and delivering value.