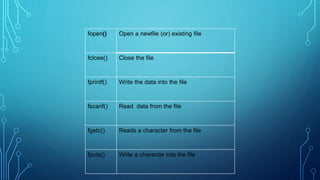
This document provides information about file management and file operations in C programming. It defines what a file is as a collection of stored data or information. It describes two main types of files - text files and binary files. It outlines the need for files to preserve data even after a program terminates. It then explains various file operations in C like opening, reading, writing, and closing files using functions like fopen(), fclose(), fprintf(), fscanf(), etc. It also discusses sequential and random access files and functions used for random access like fseek(), ftell(), and rewind().








![Reading file fscanf() function
#include <stdio.h>
Void main()
{
FILE*f;
Char buff [255];
f=fopen(“f1.txt”,”r”);
While (fscanf (f,”%s”,buff)1=EOF)
{
Printf(“%s”,buff);
}
fclose(f);
}
Output:
Welcome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-filemanagement-230208064136-989989db/85/C-FILE-MANAGEMENT-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![Program:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
int age;
char name[20];
clrscr();
printf(“enter the name & age:”);
Scanf(“%sn”,&name);
Scanf(“%dn”,&age);
fp = fopen(“Demo.txt”,”w”);
fprintf(fp,”name:%sn age:%d”,name ,age);
fclose(fp);
getch();
}
Output:
Enter the name & age : Abi
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-filemanagement-230208064136-989989db/85/C-FILE-MANAGEMENT-pptx-11-320.jpg)


