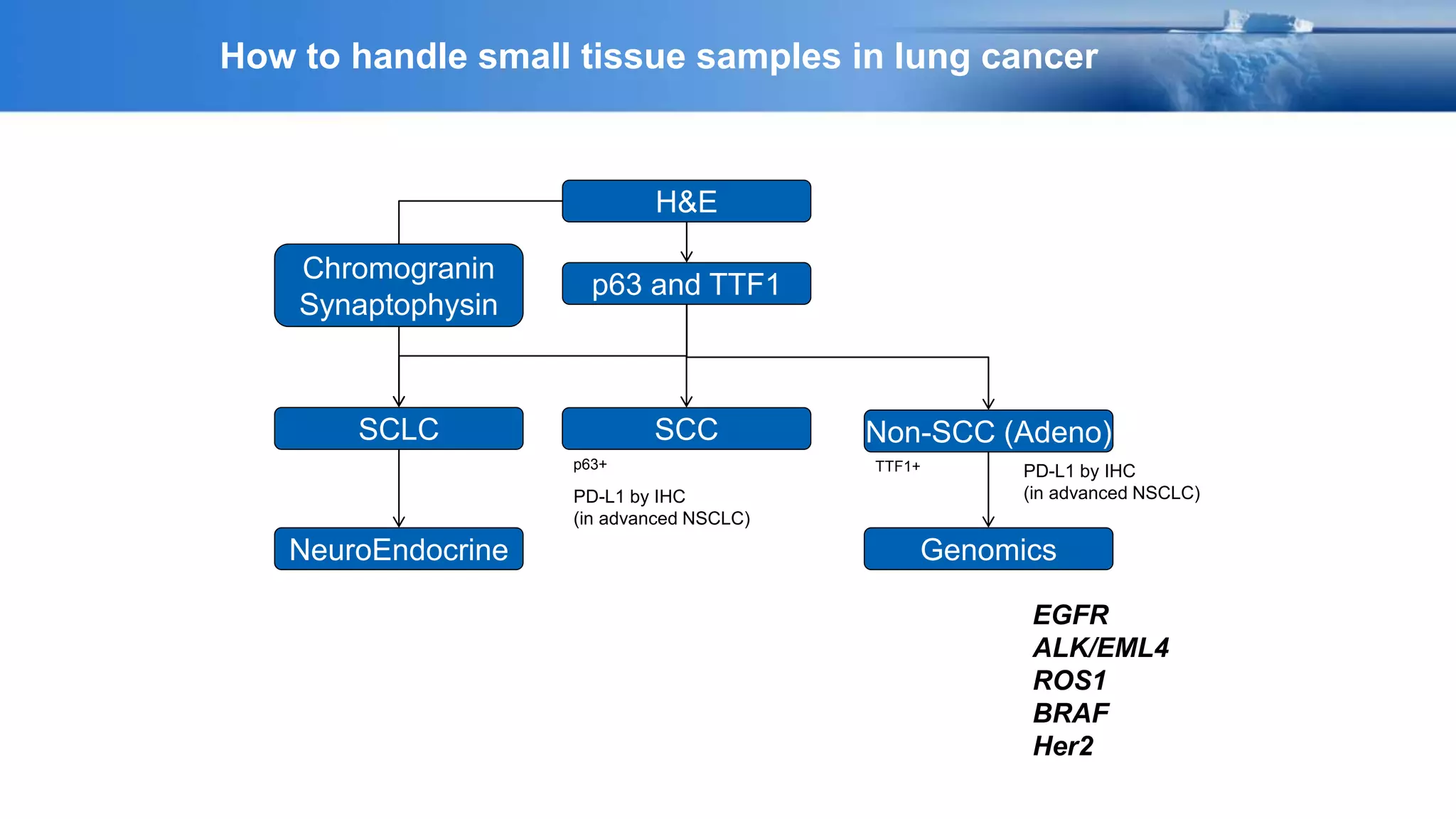
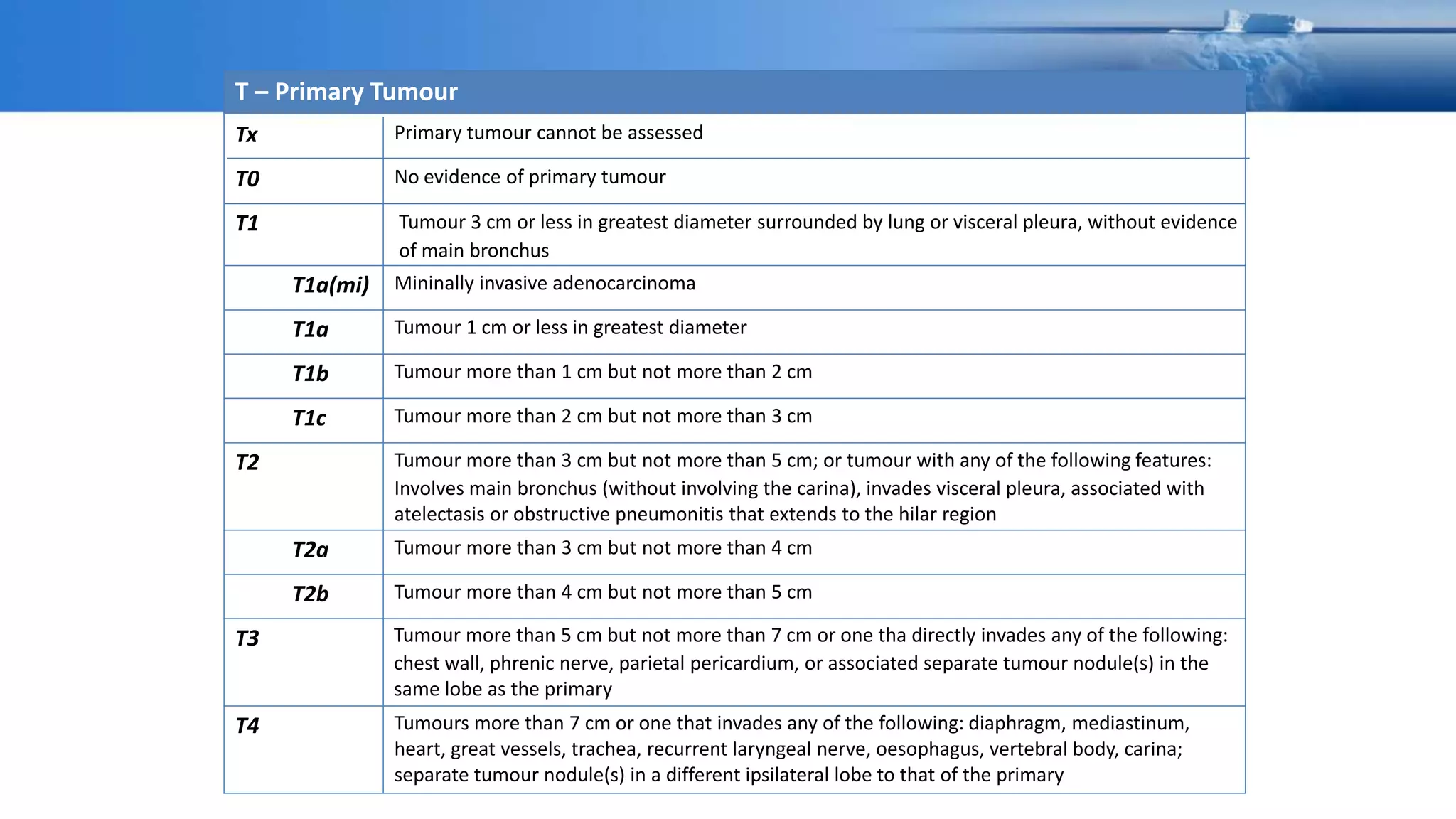
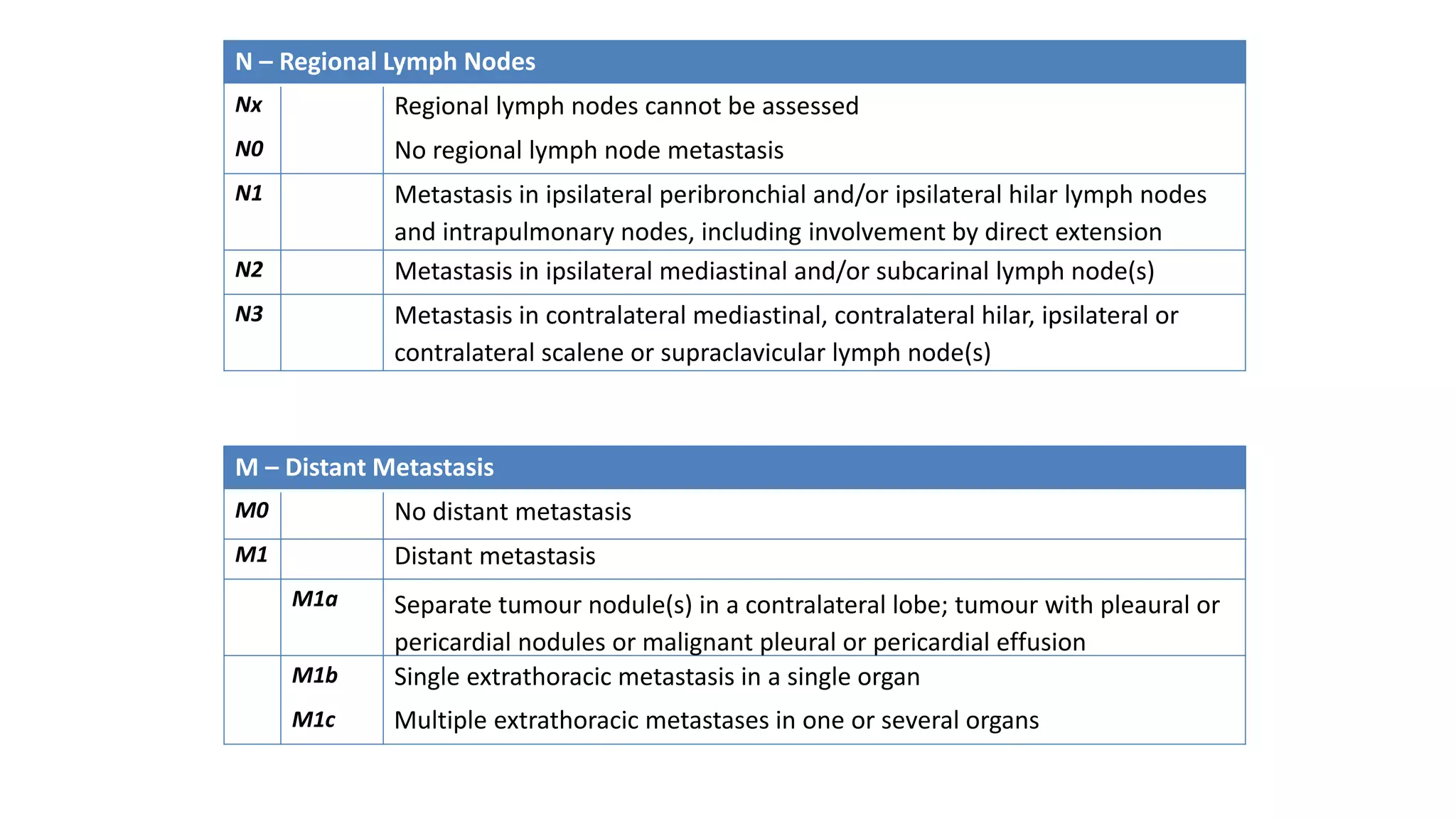
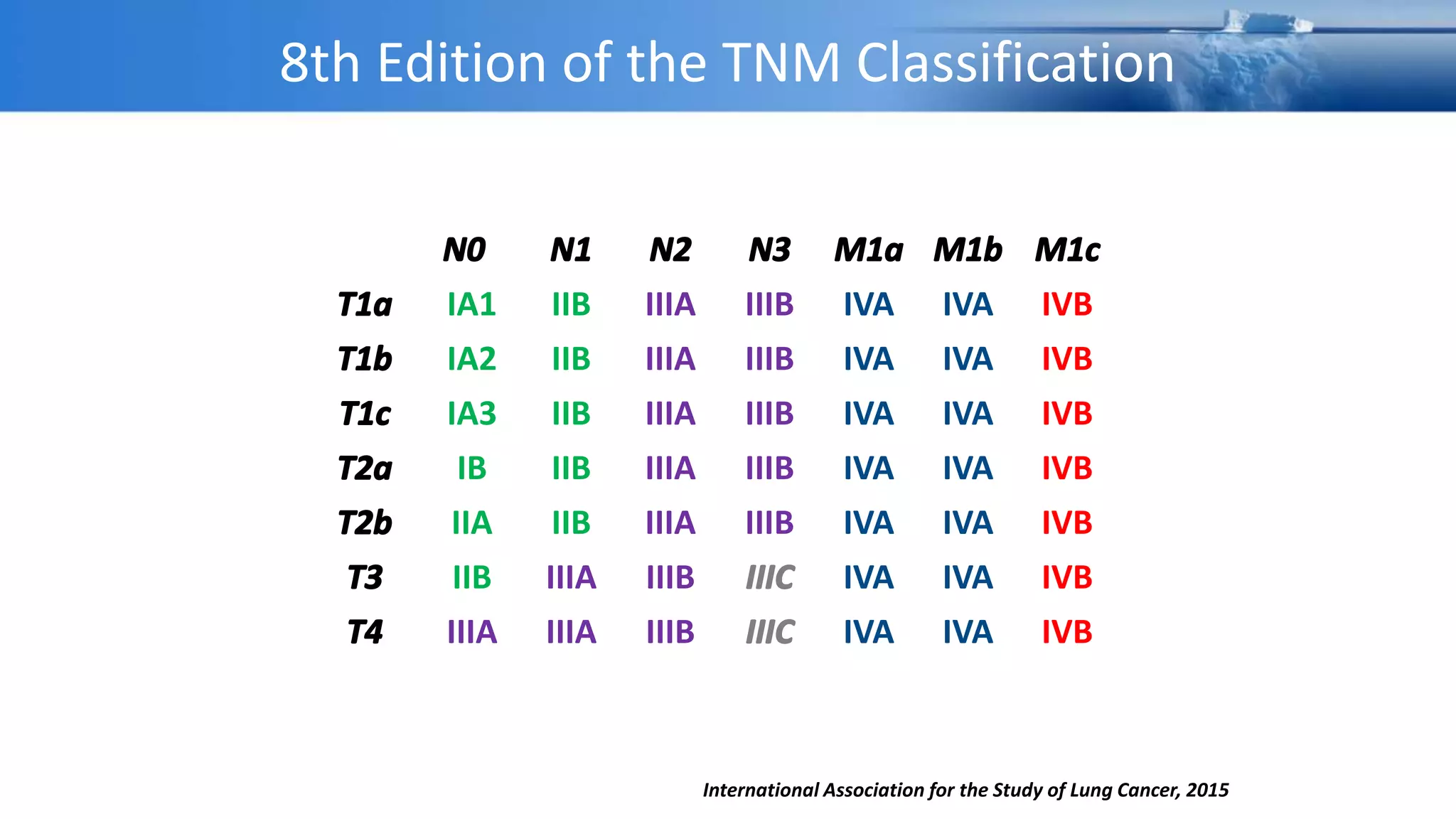
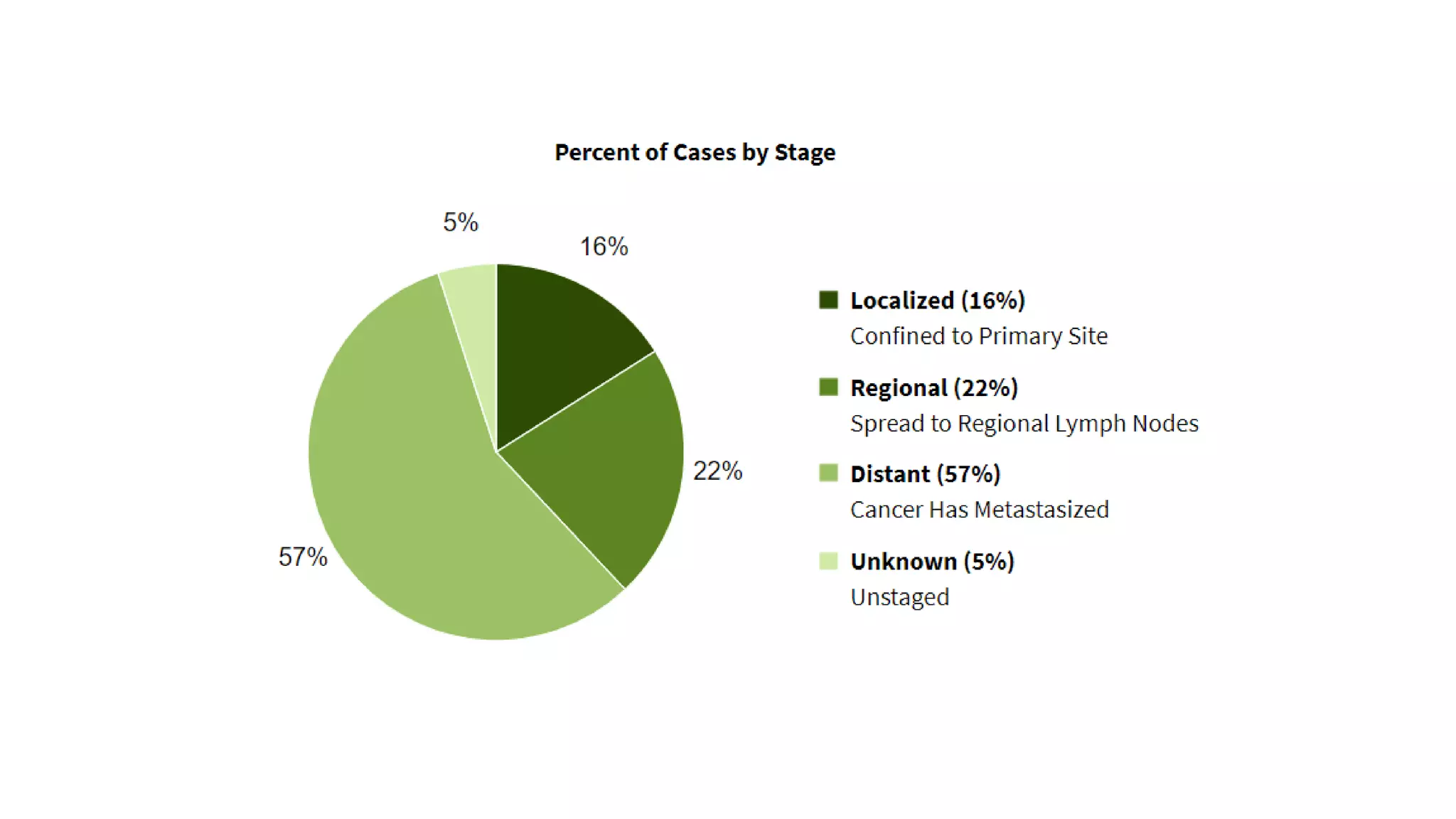
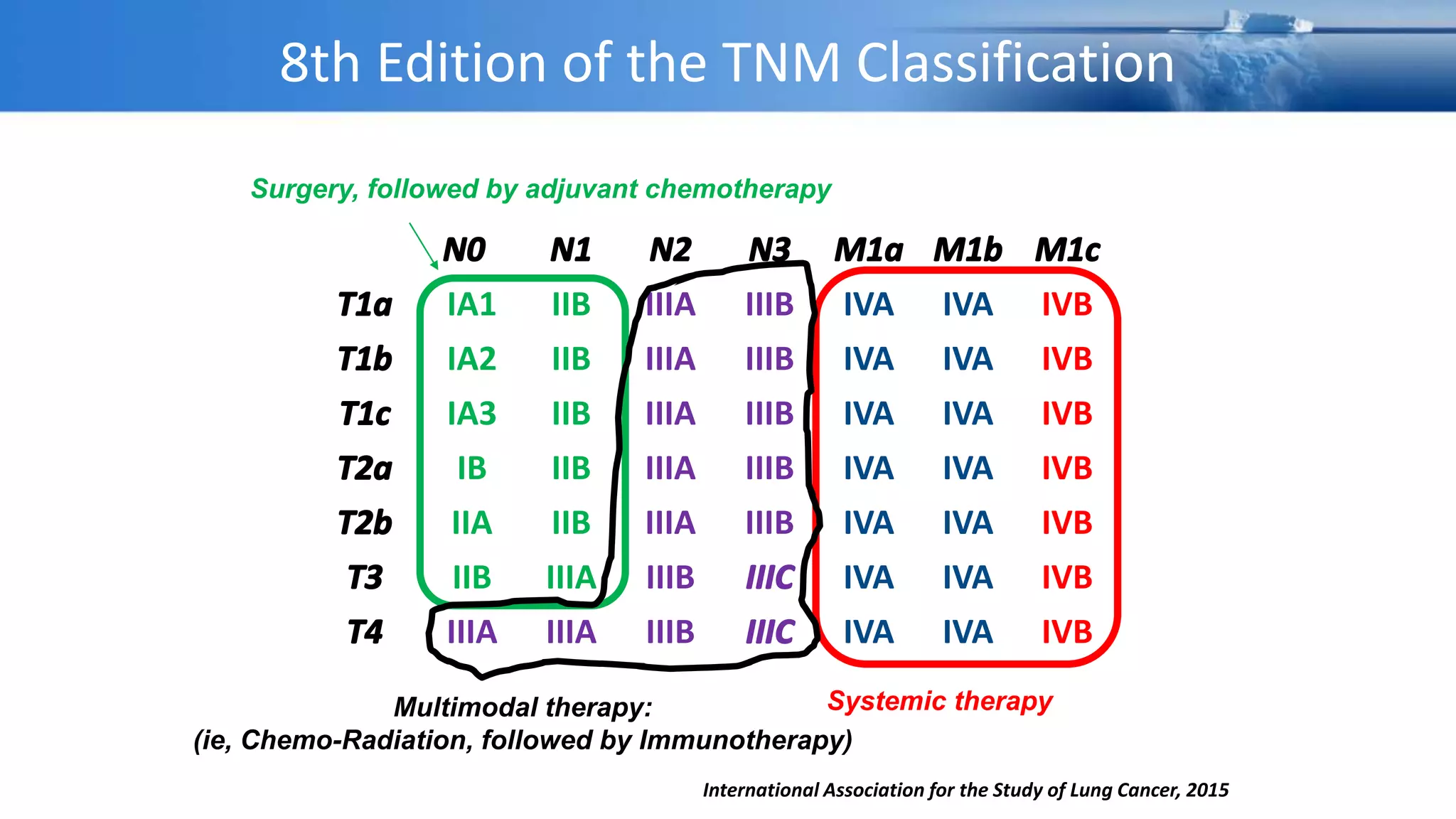
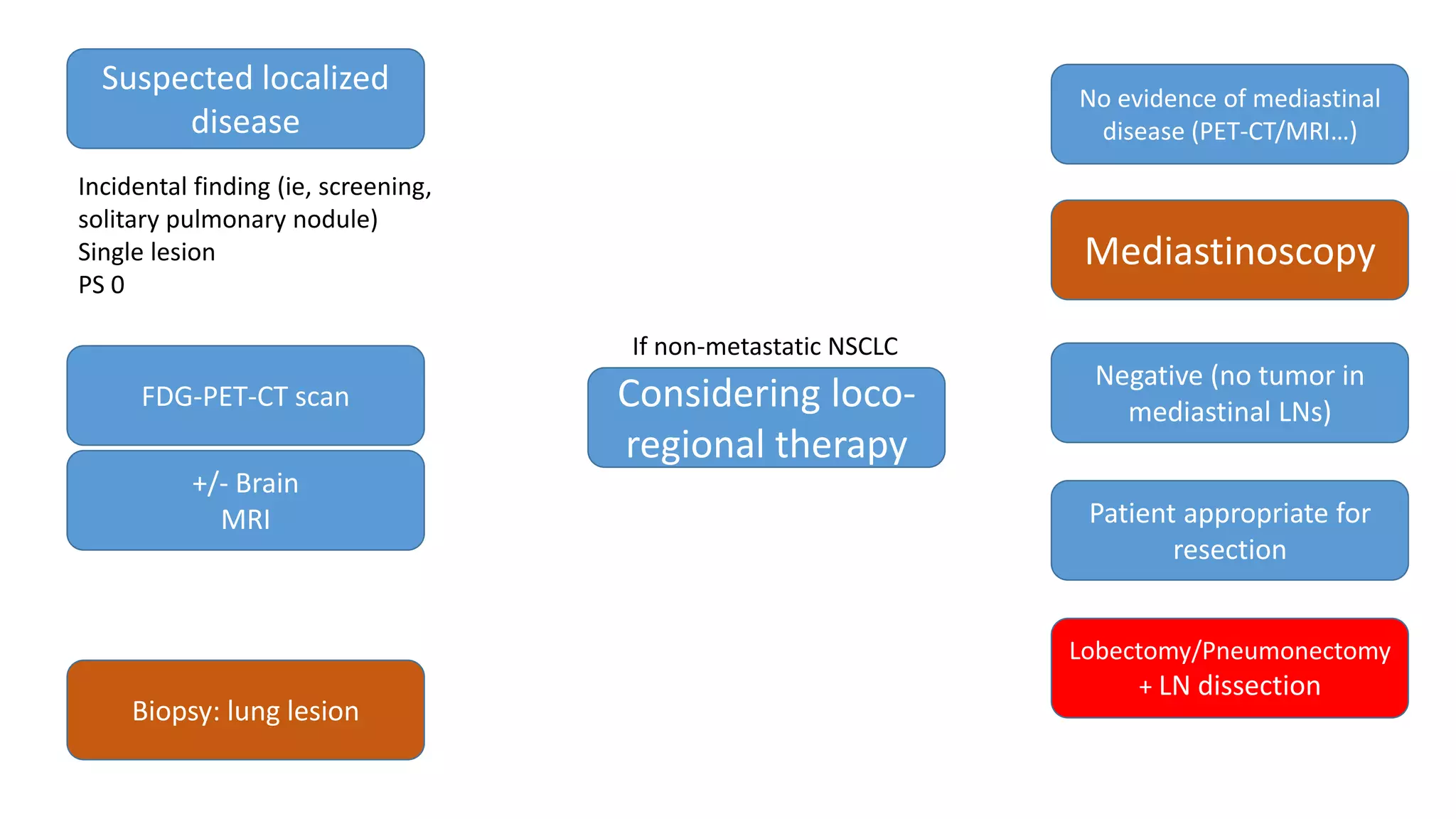
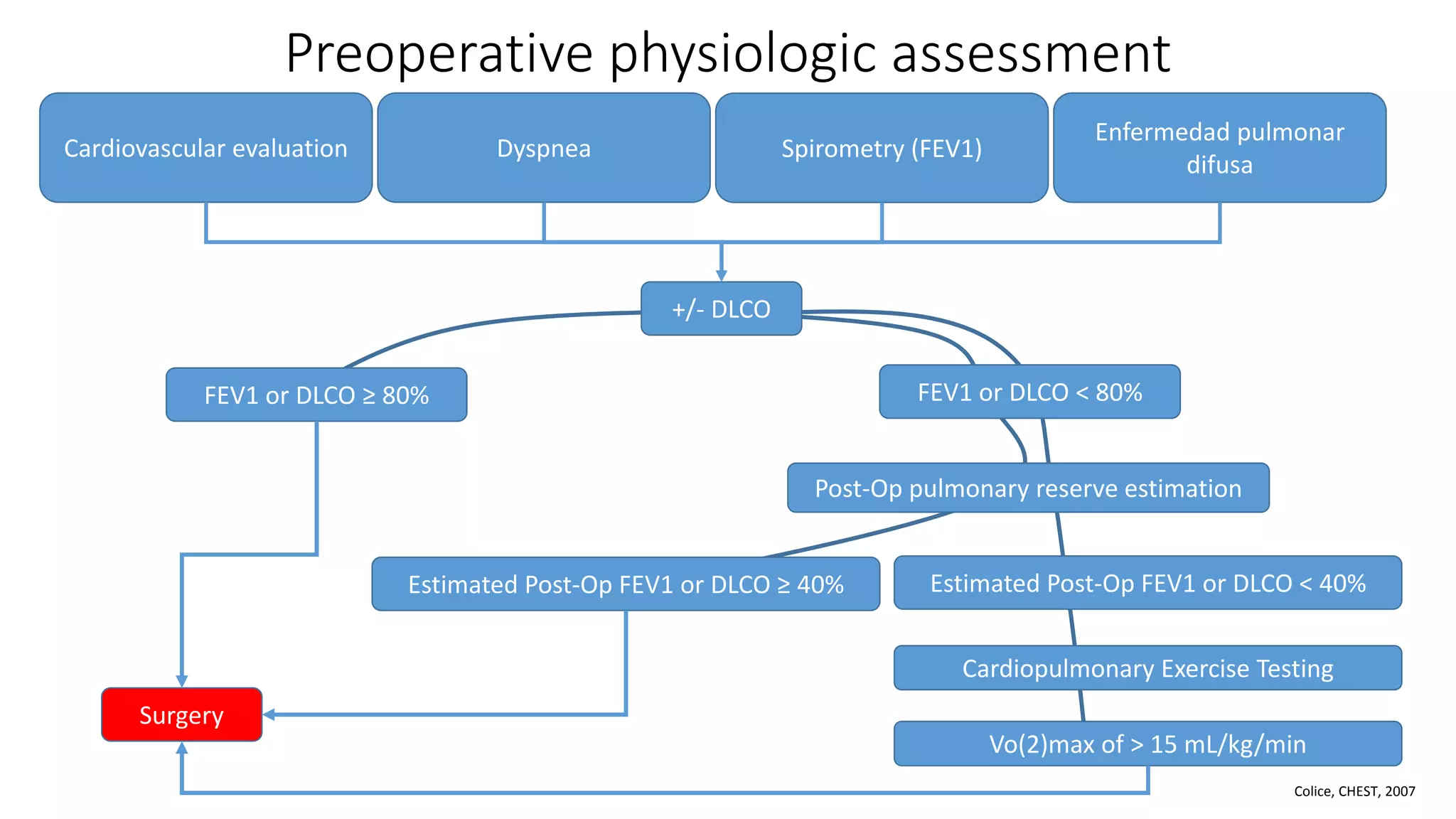
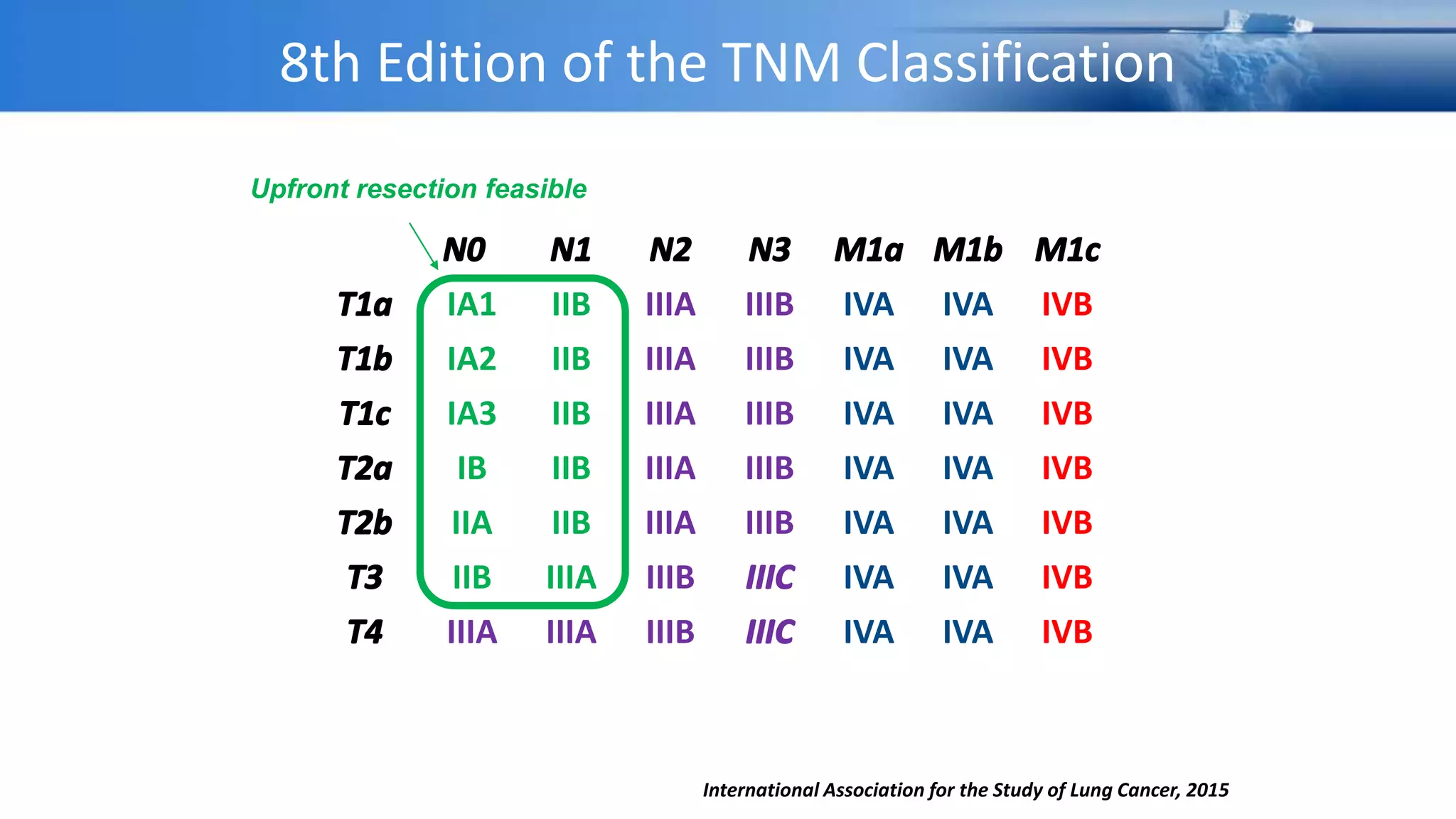
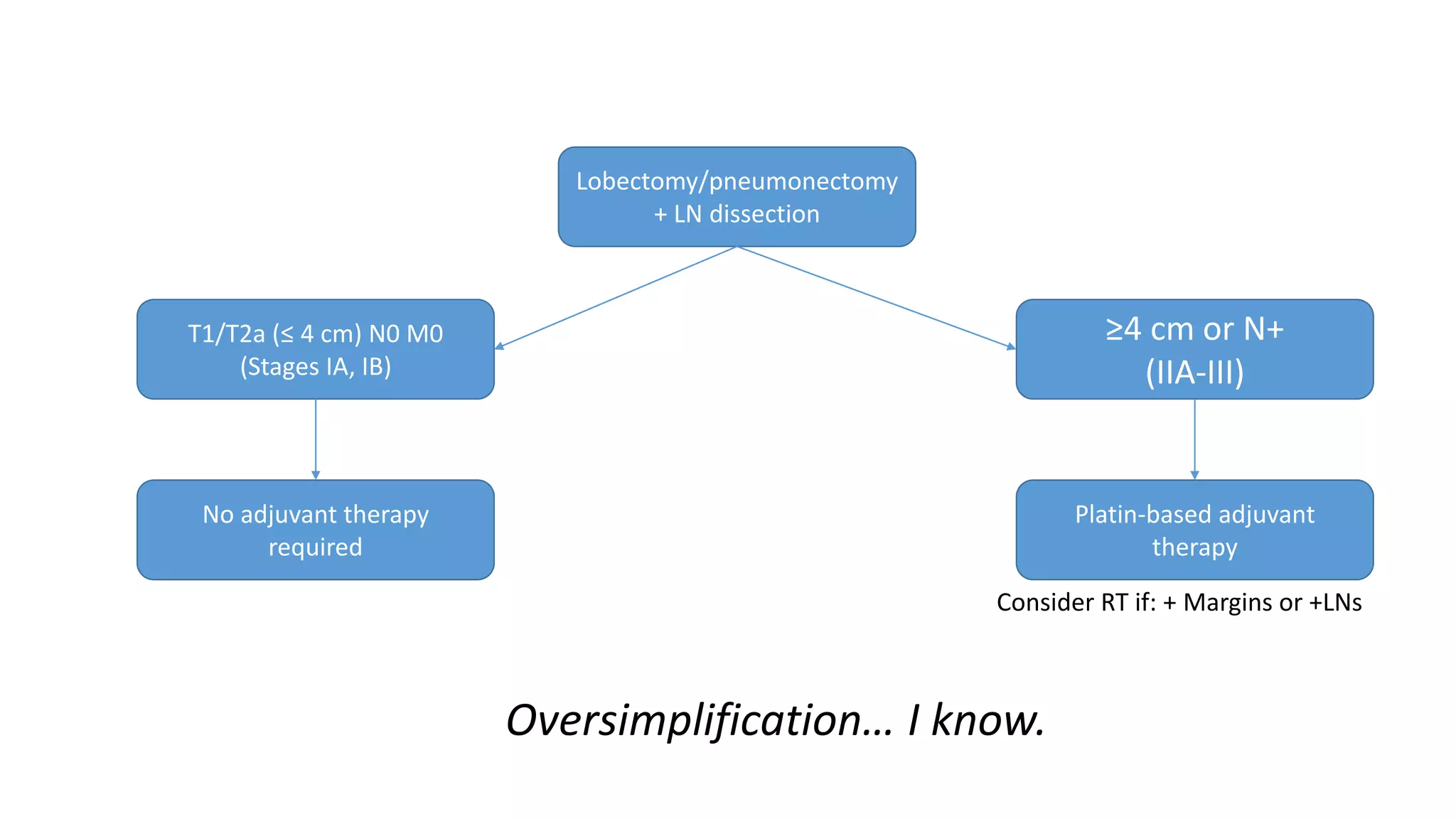
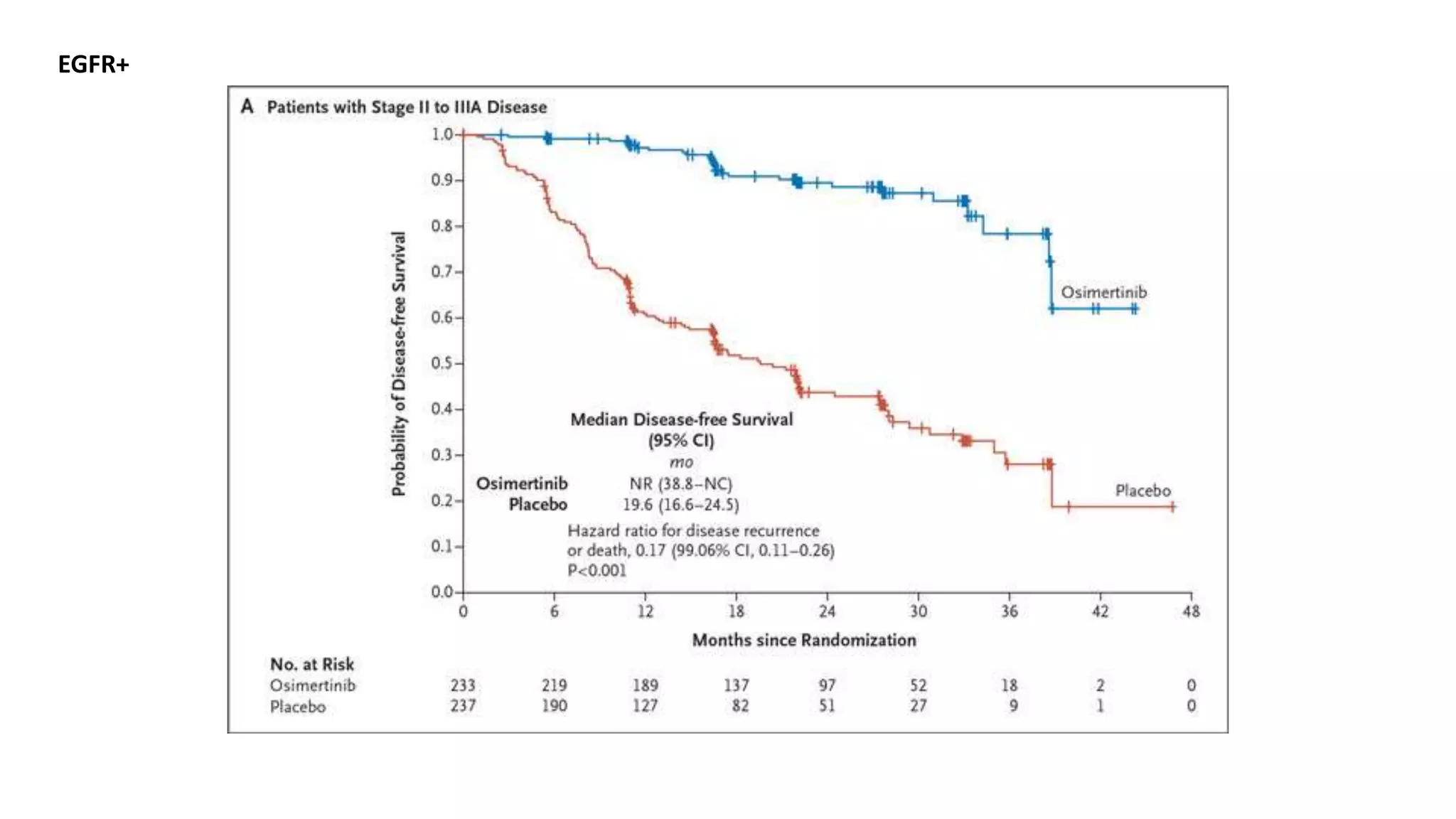
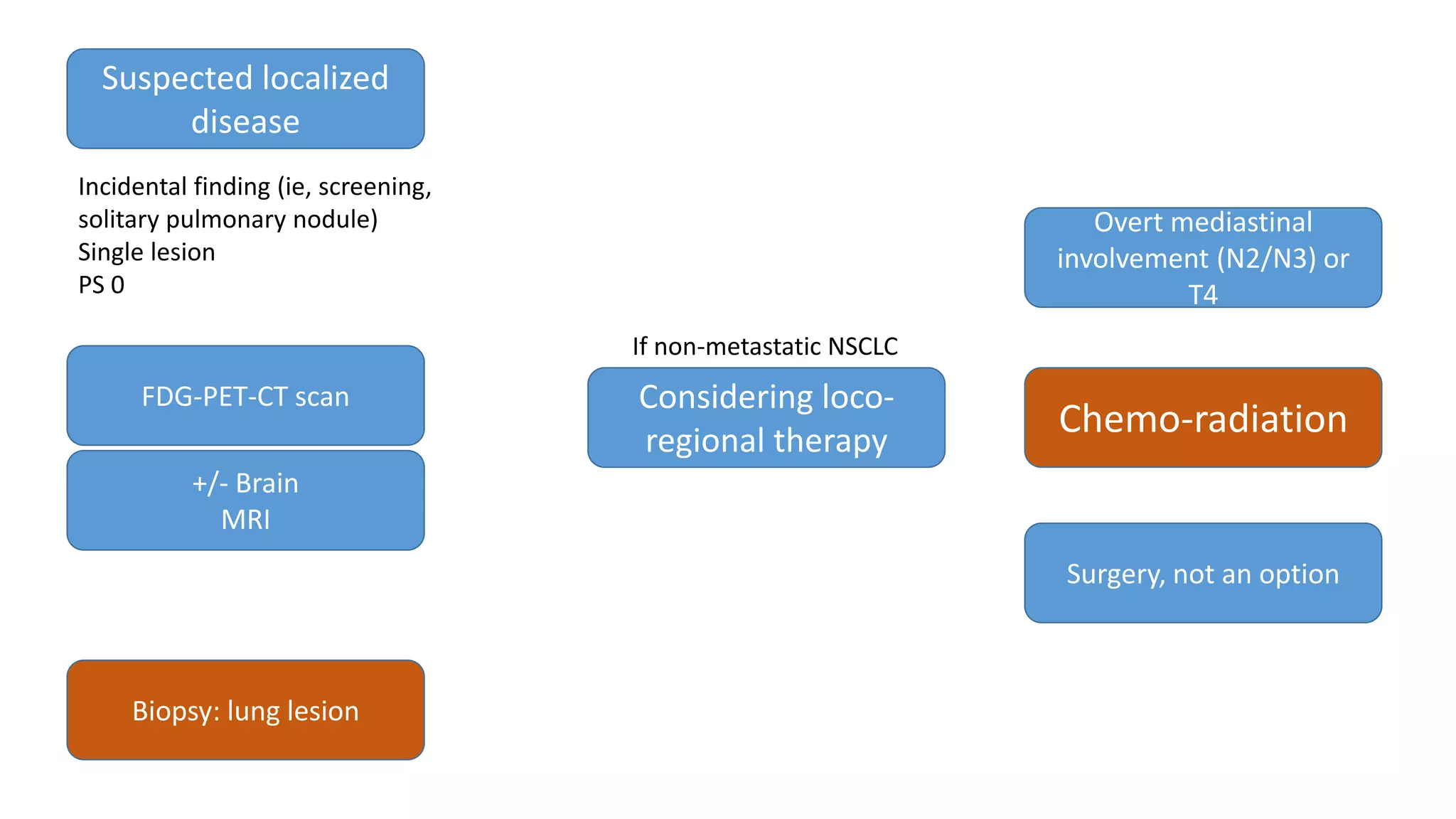
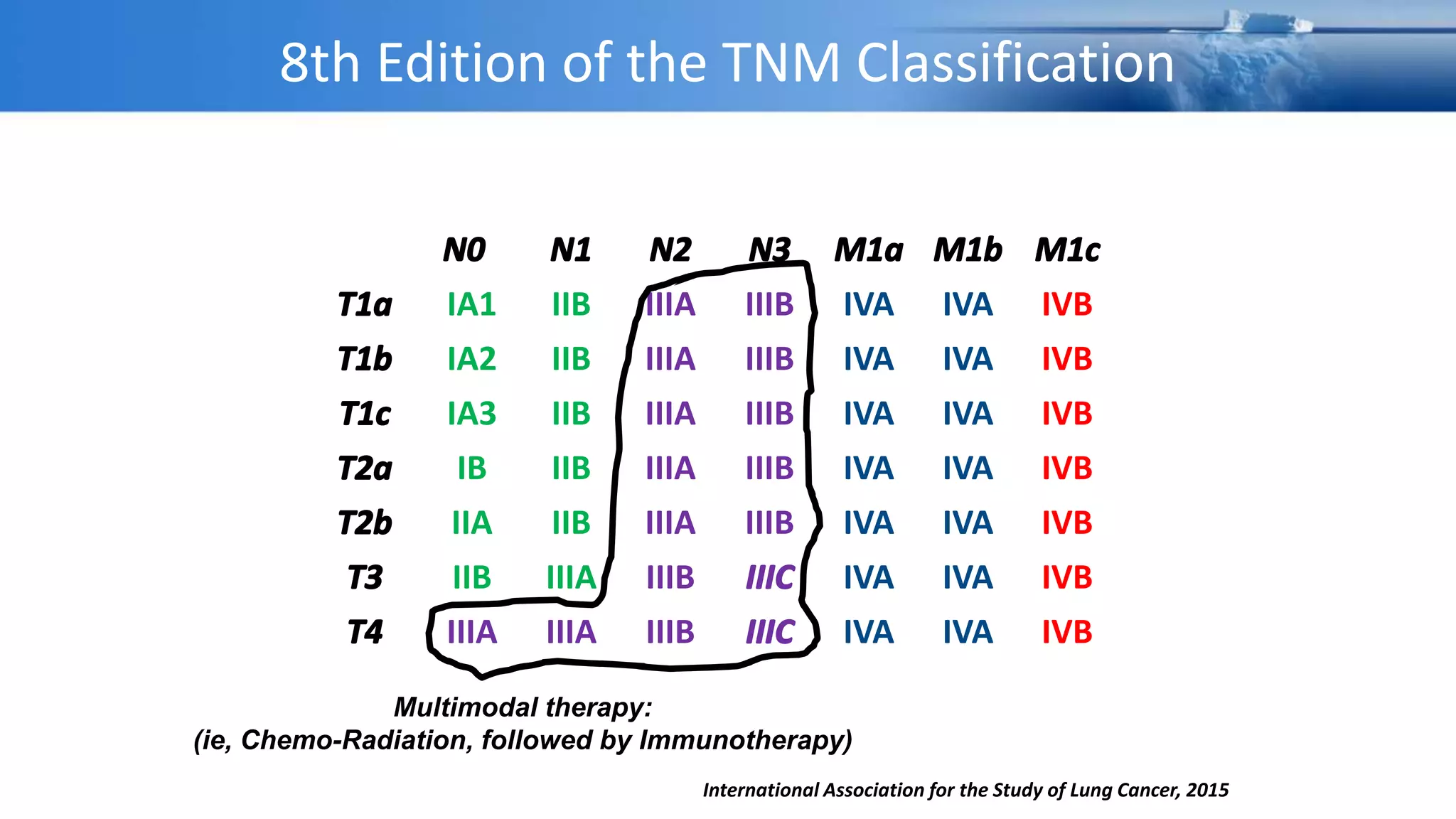
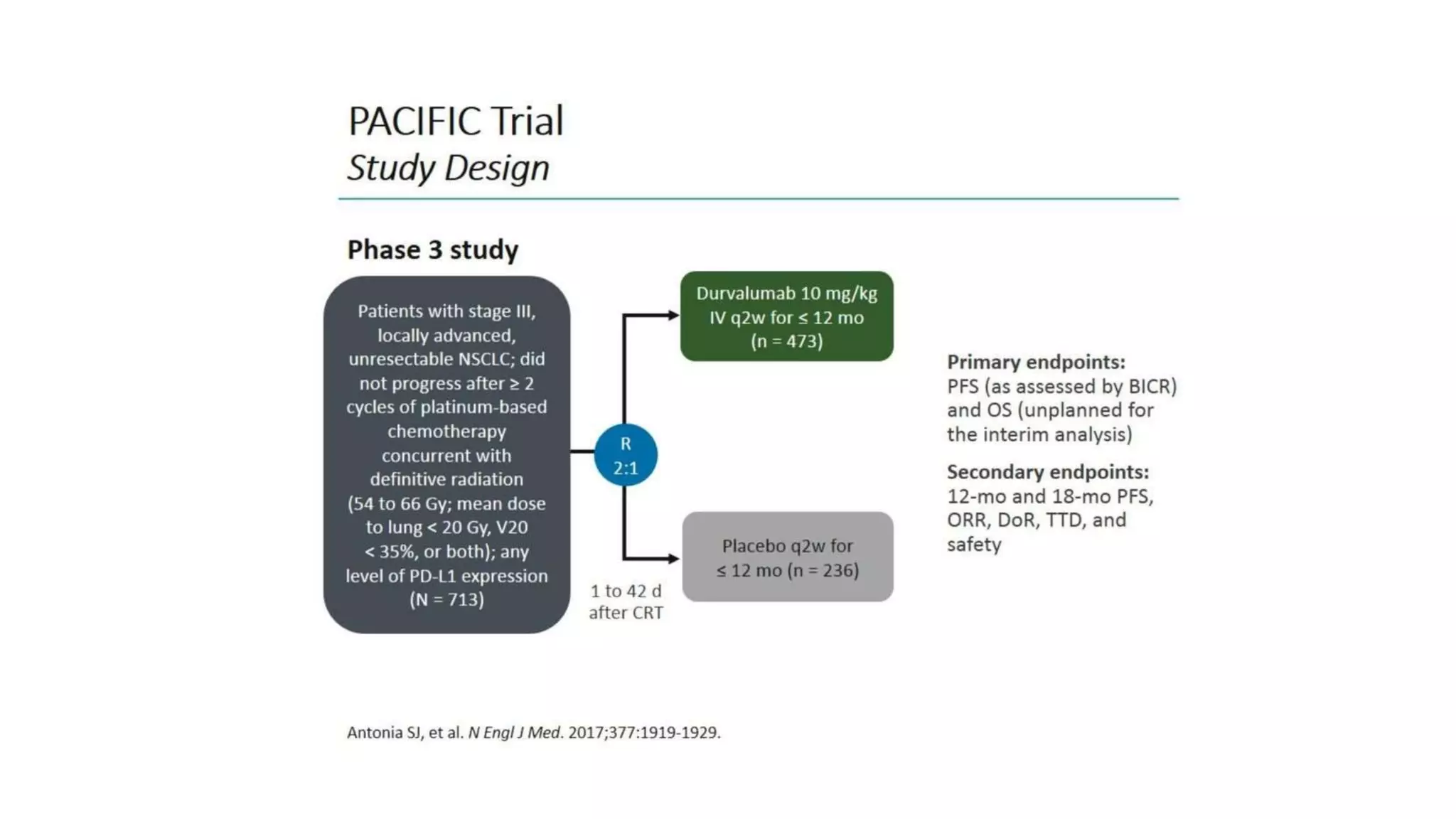
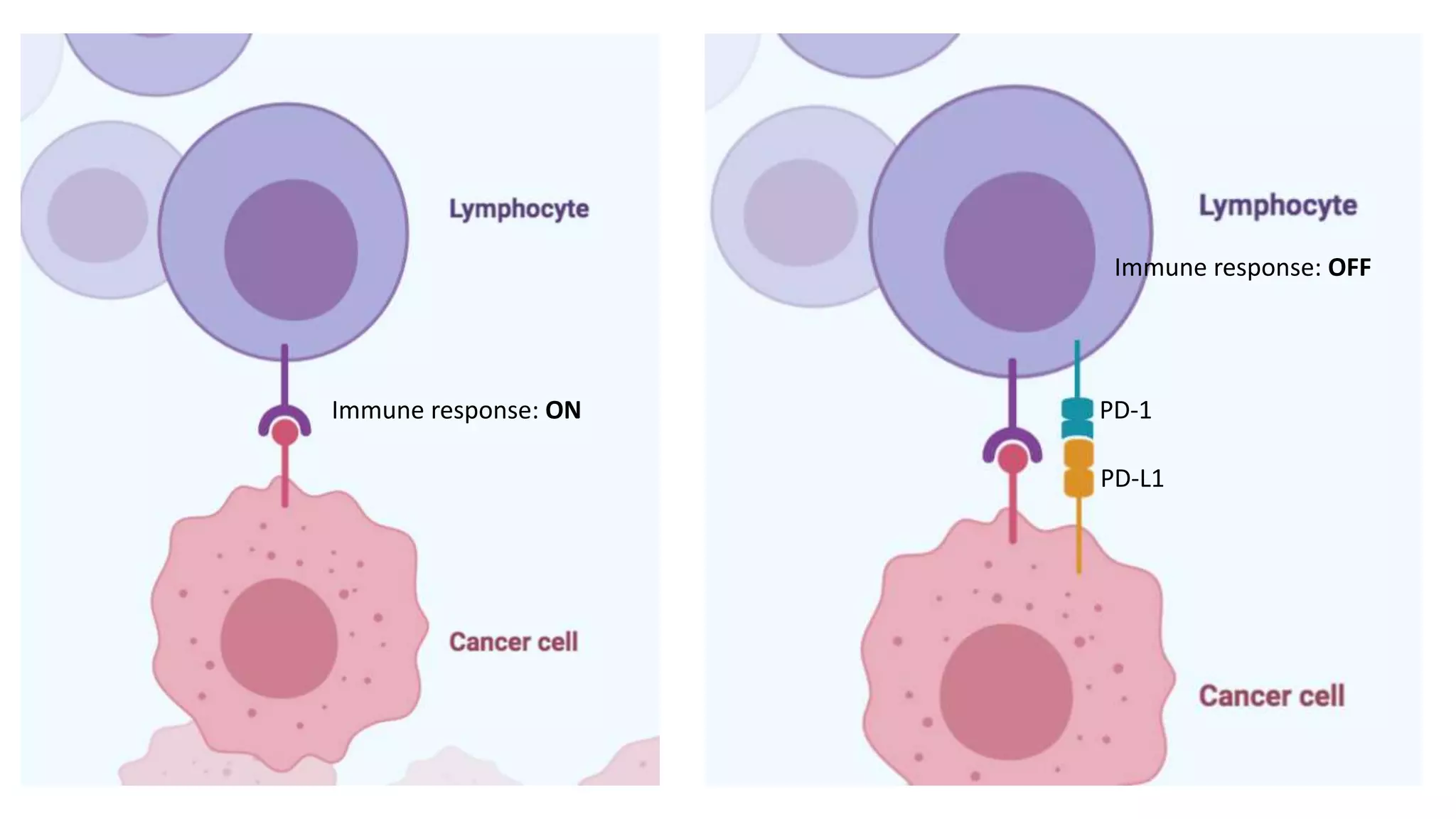
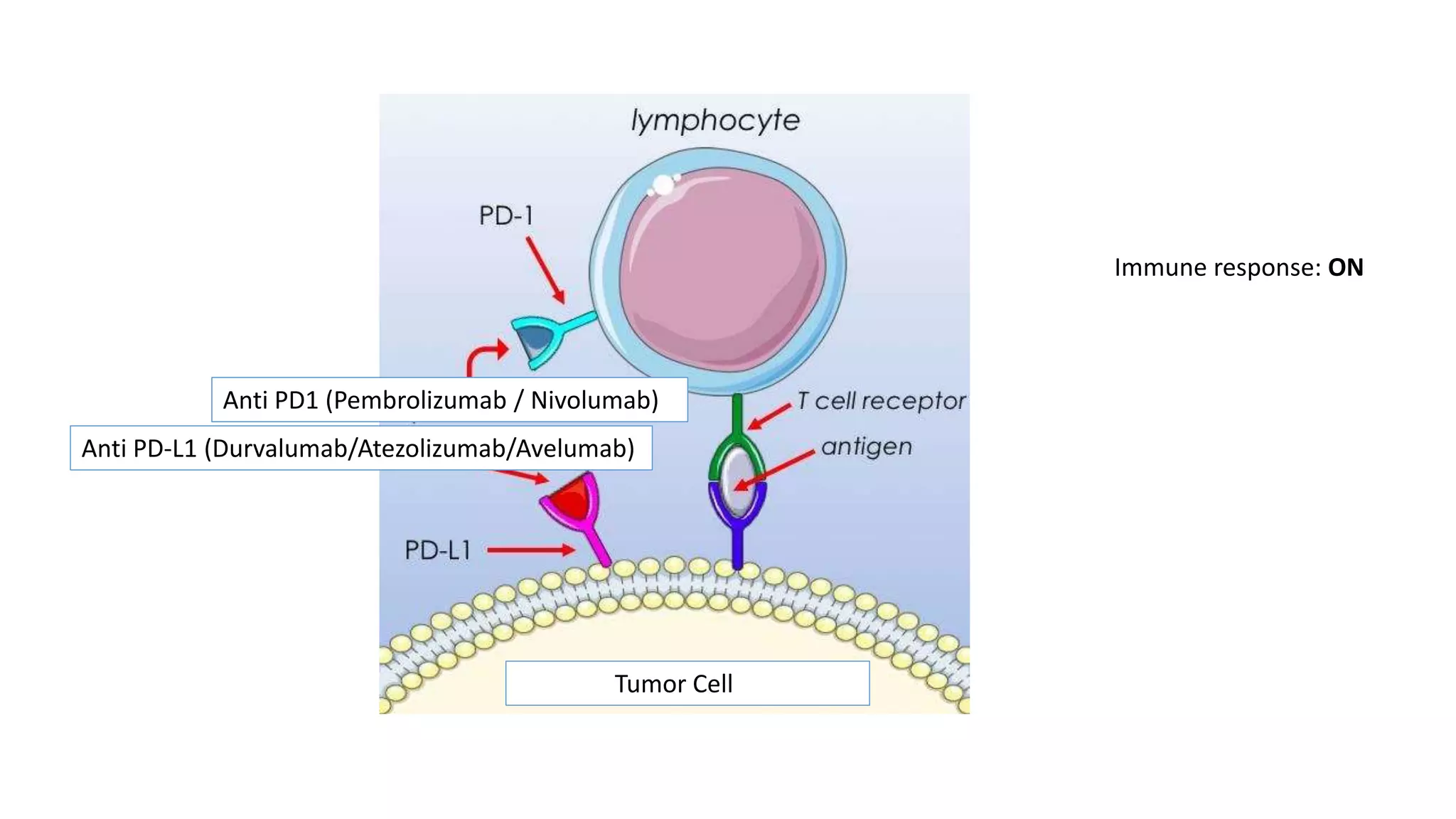
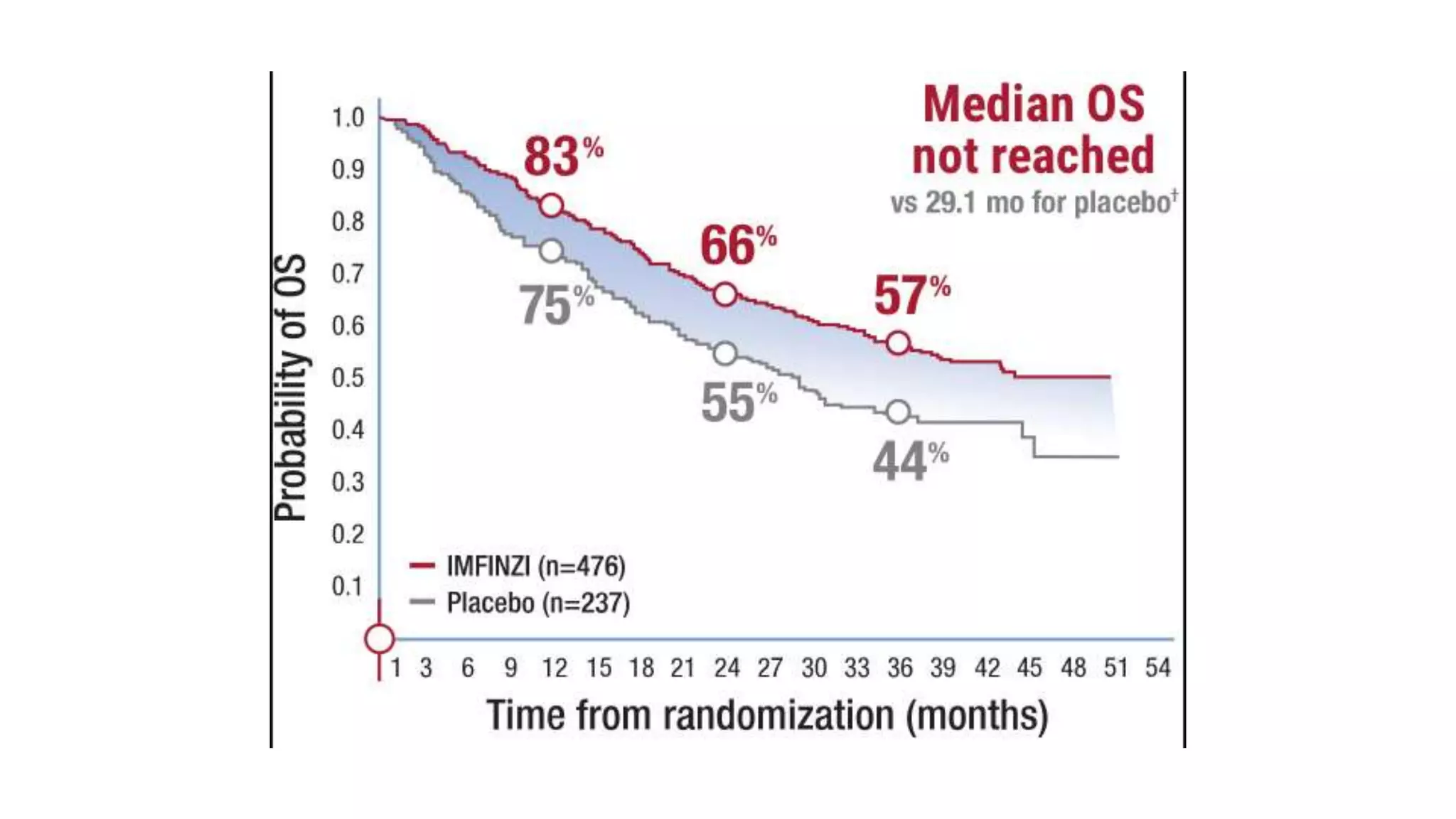
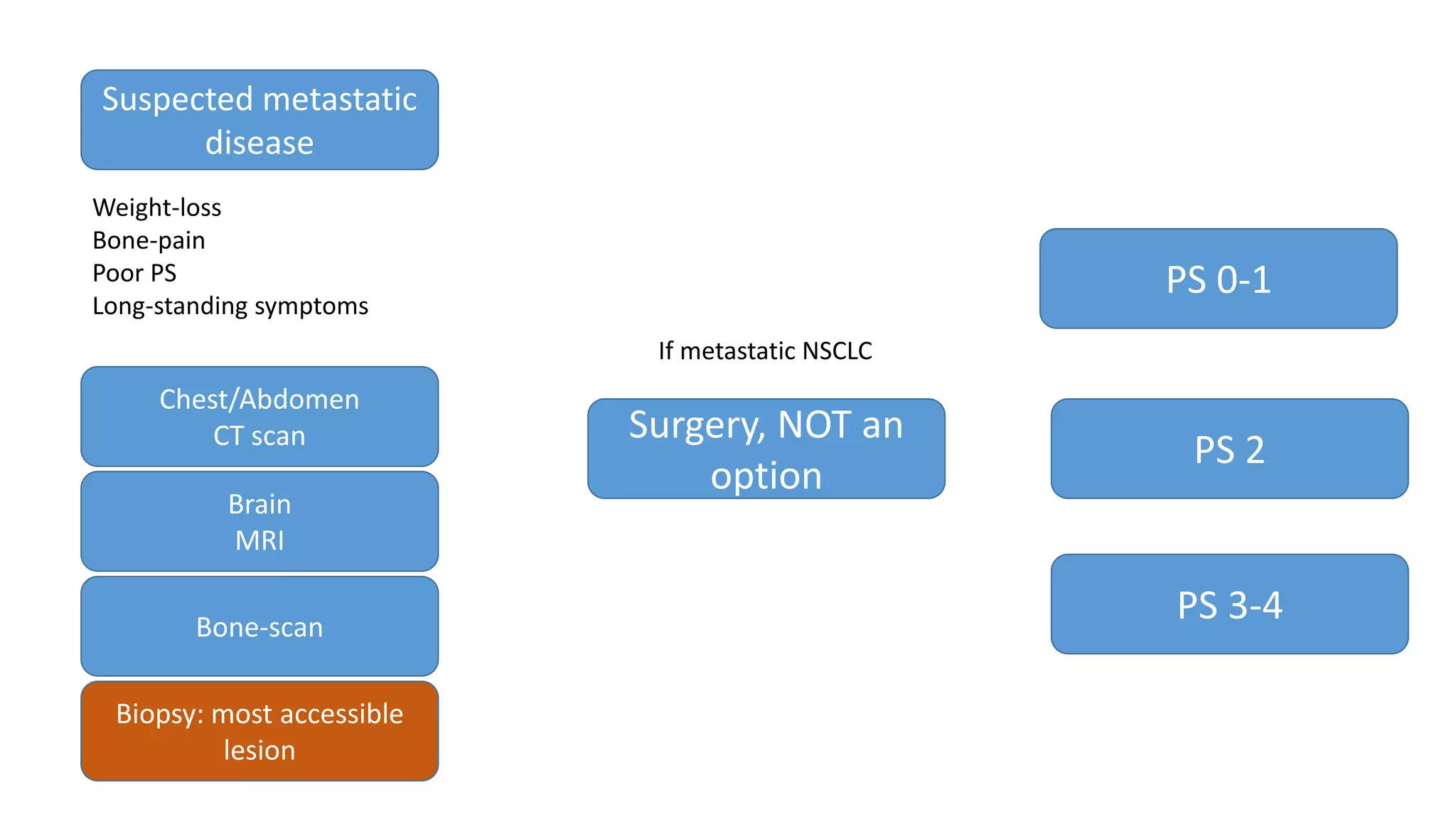
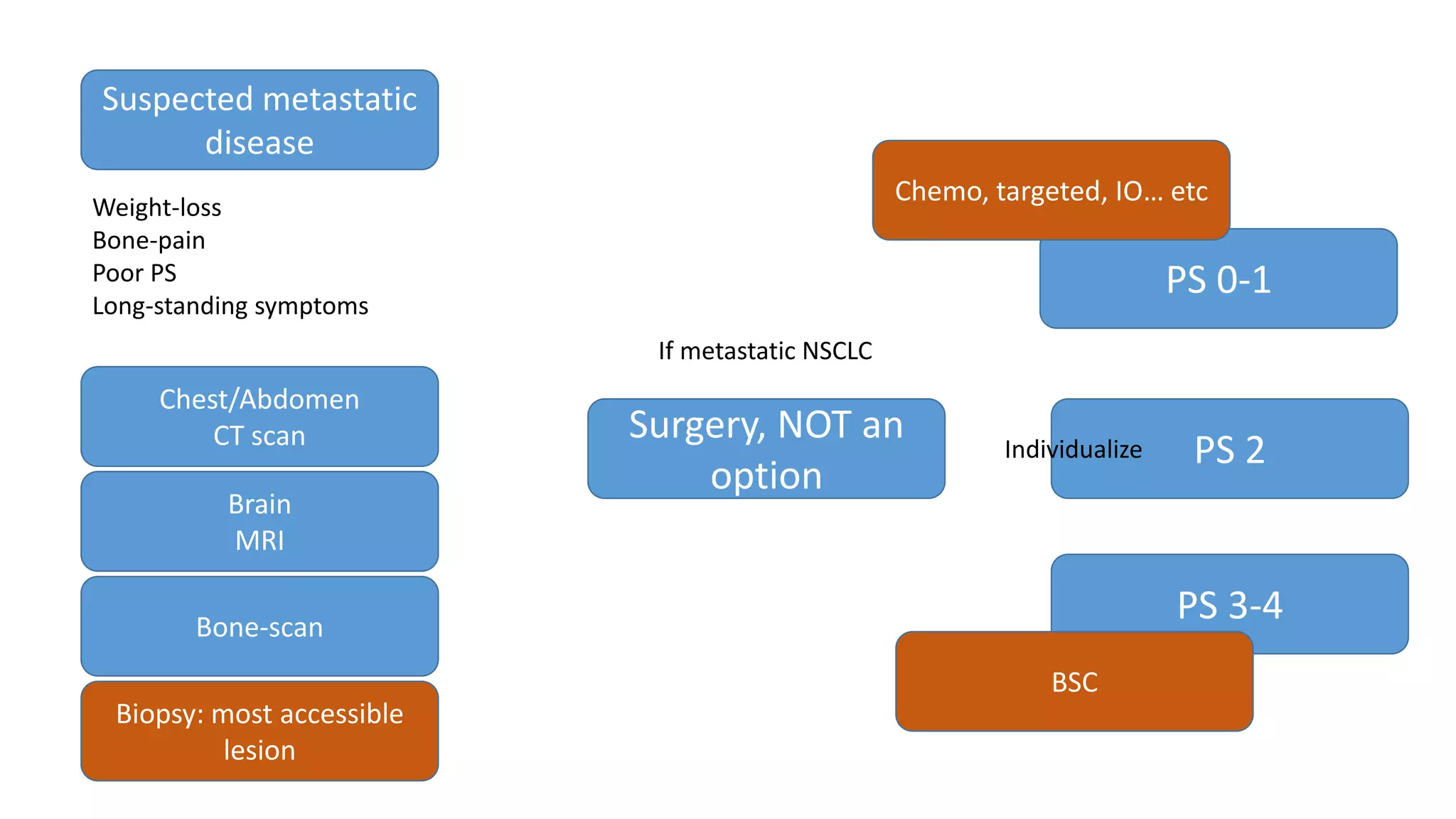
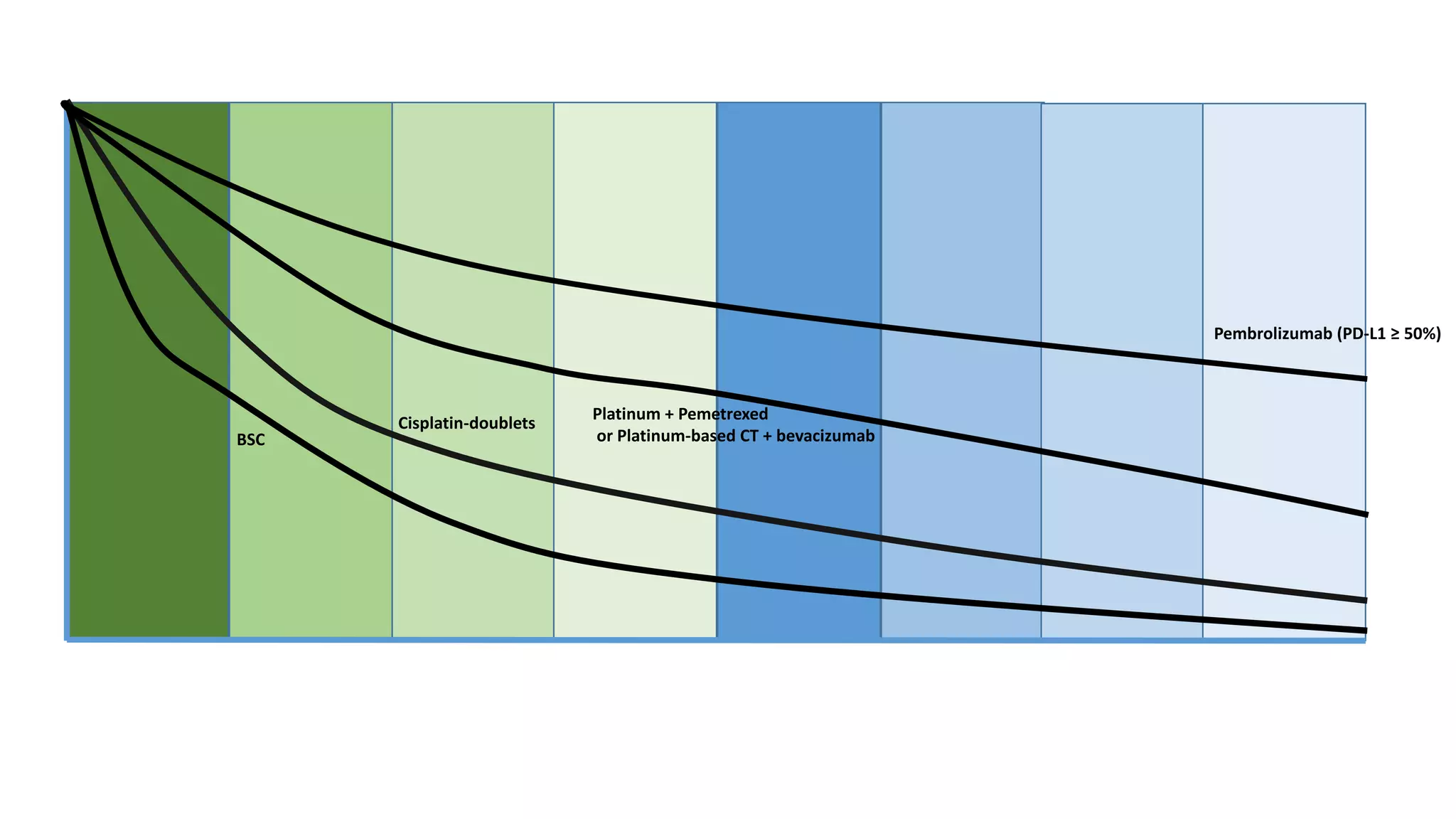
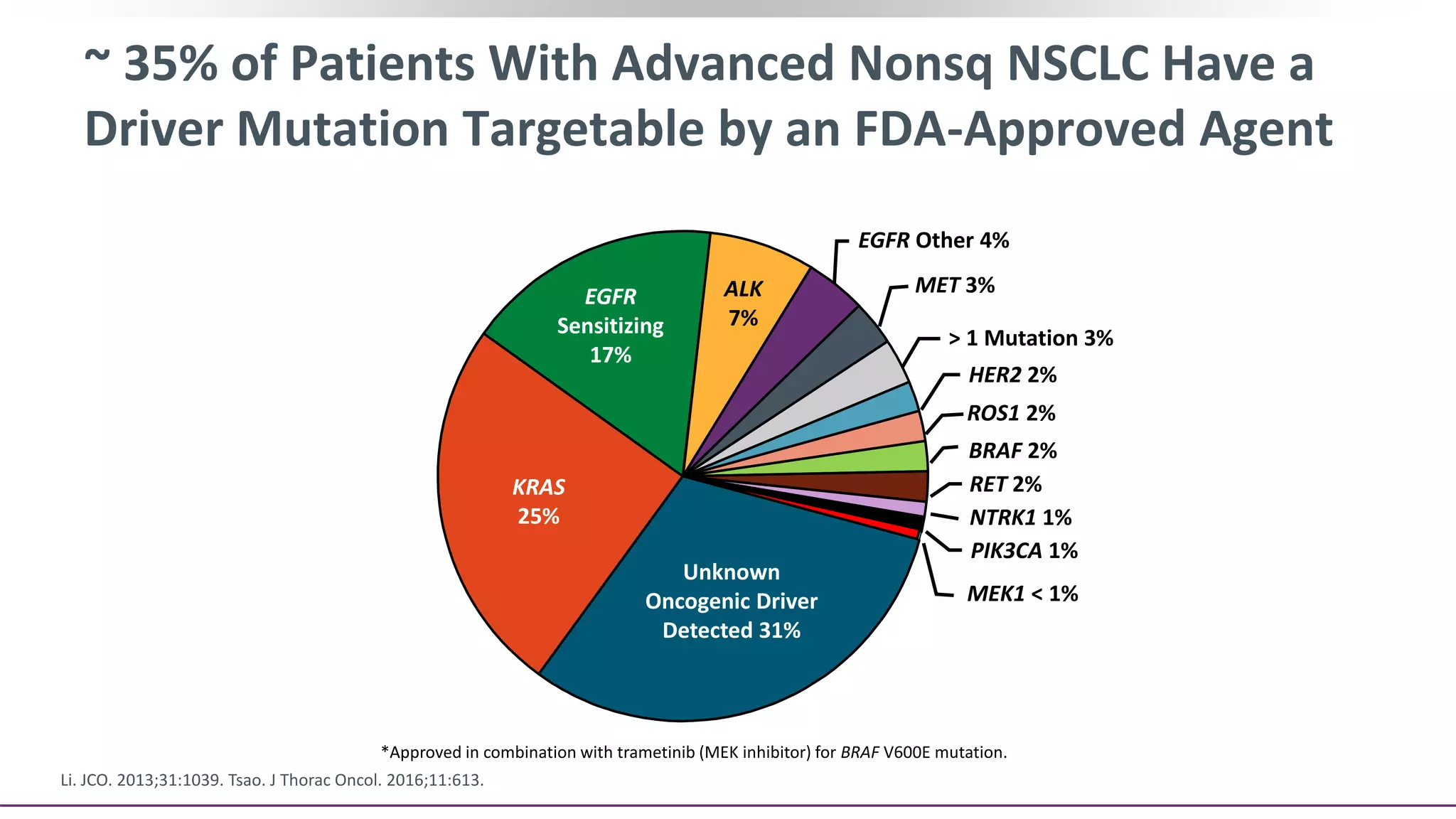
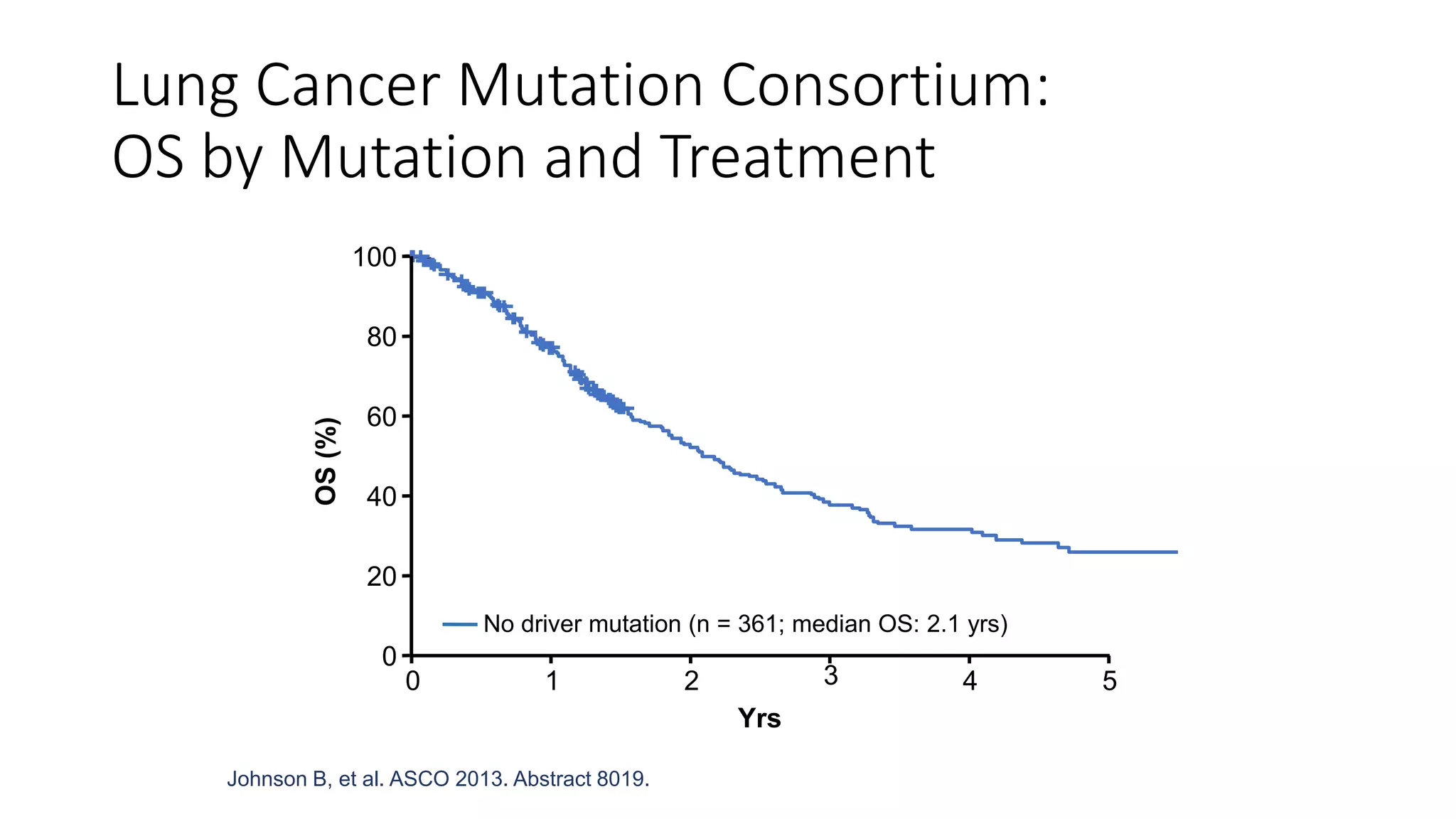
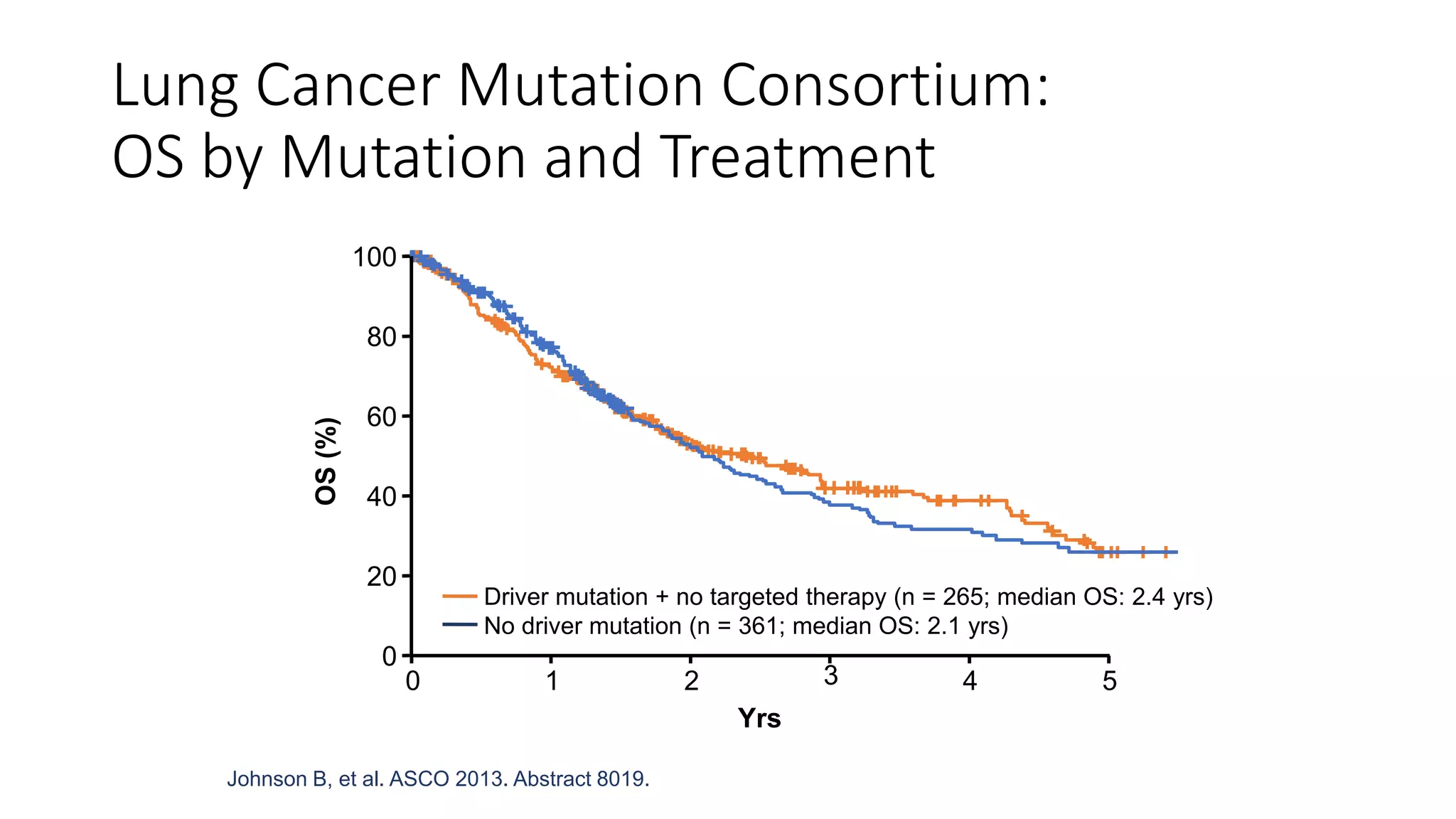
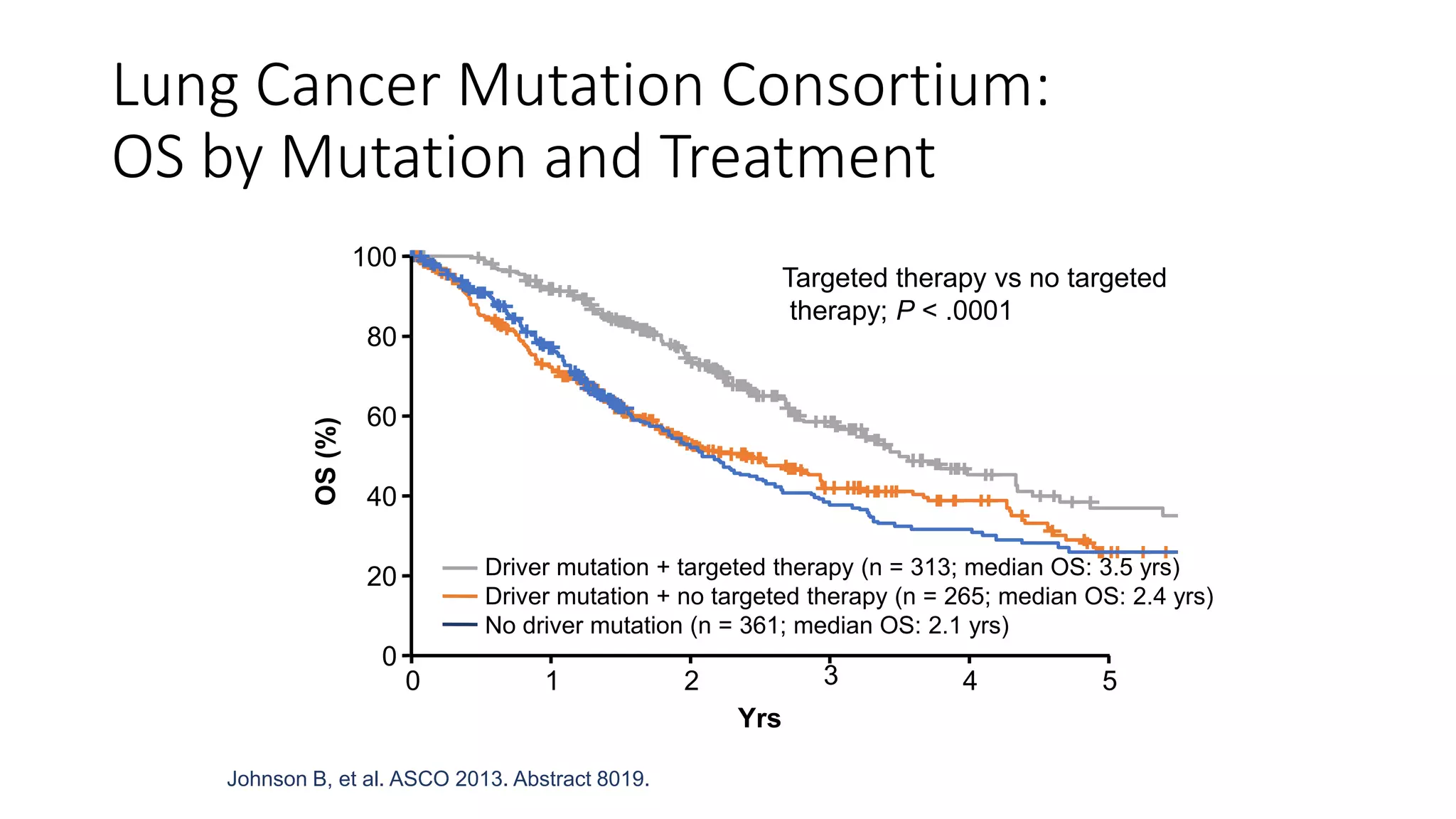
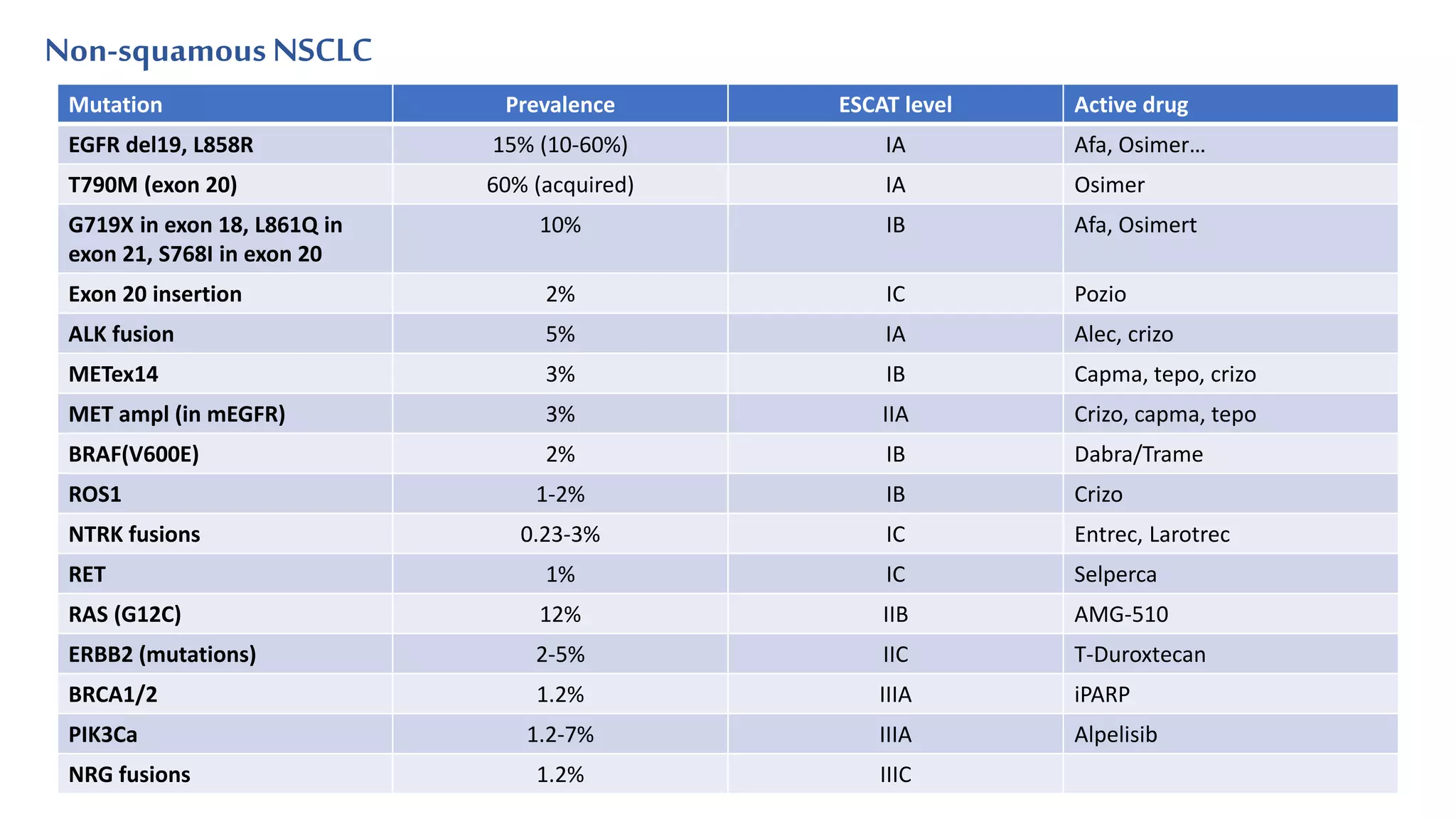
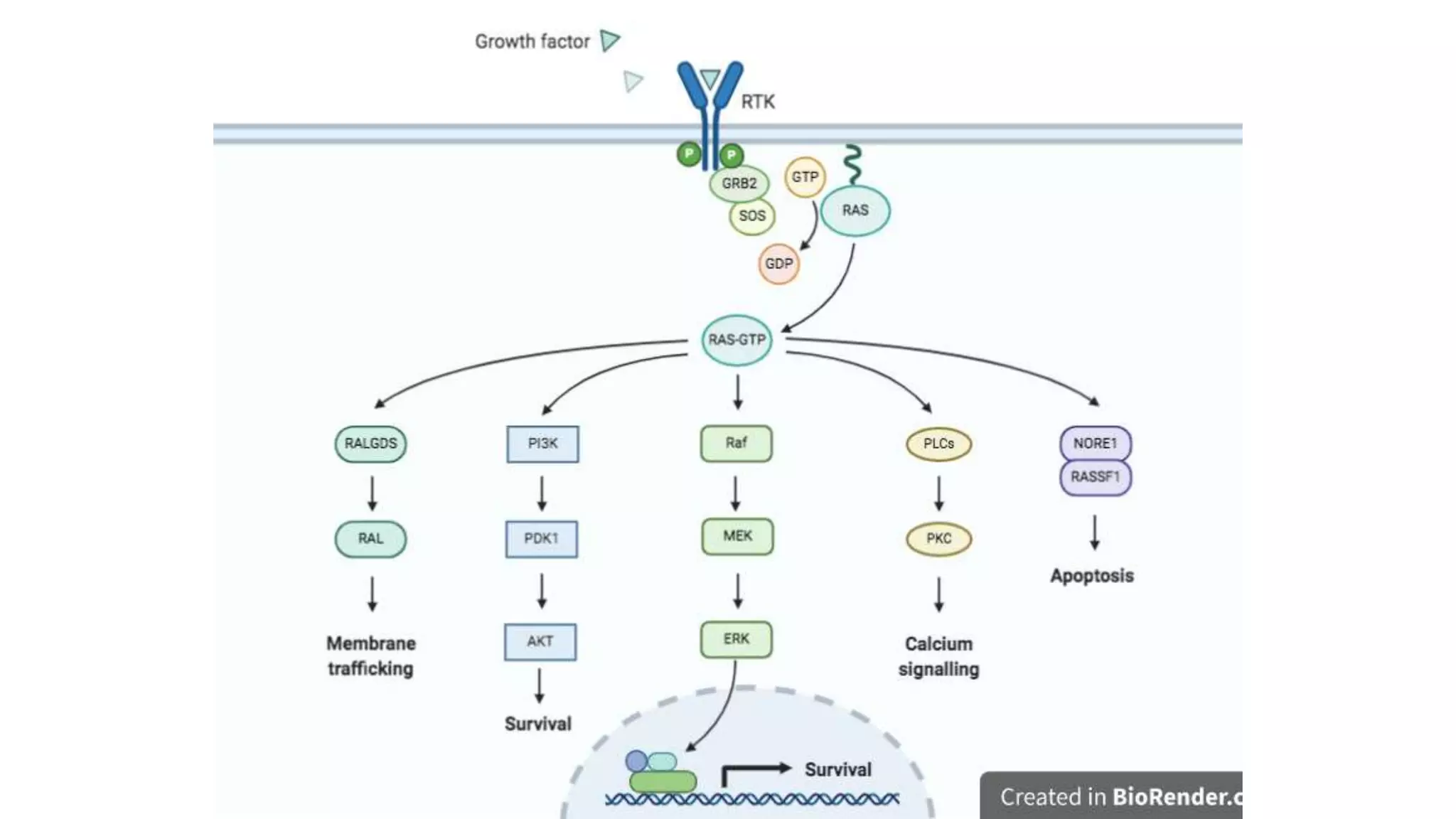
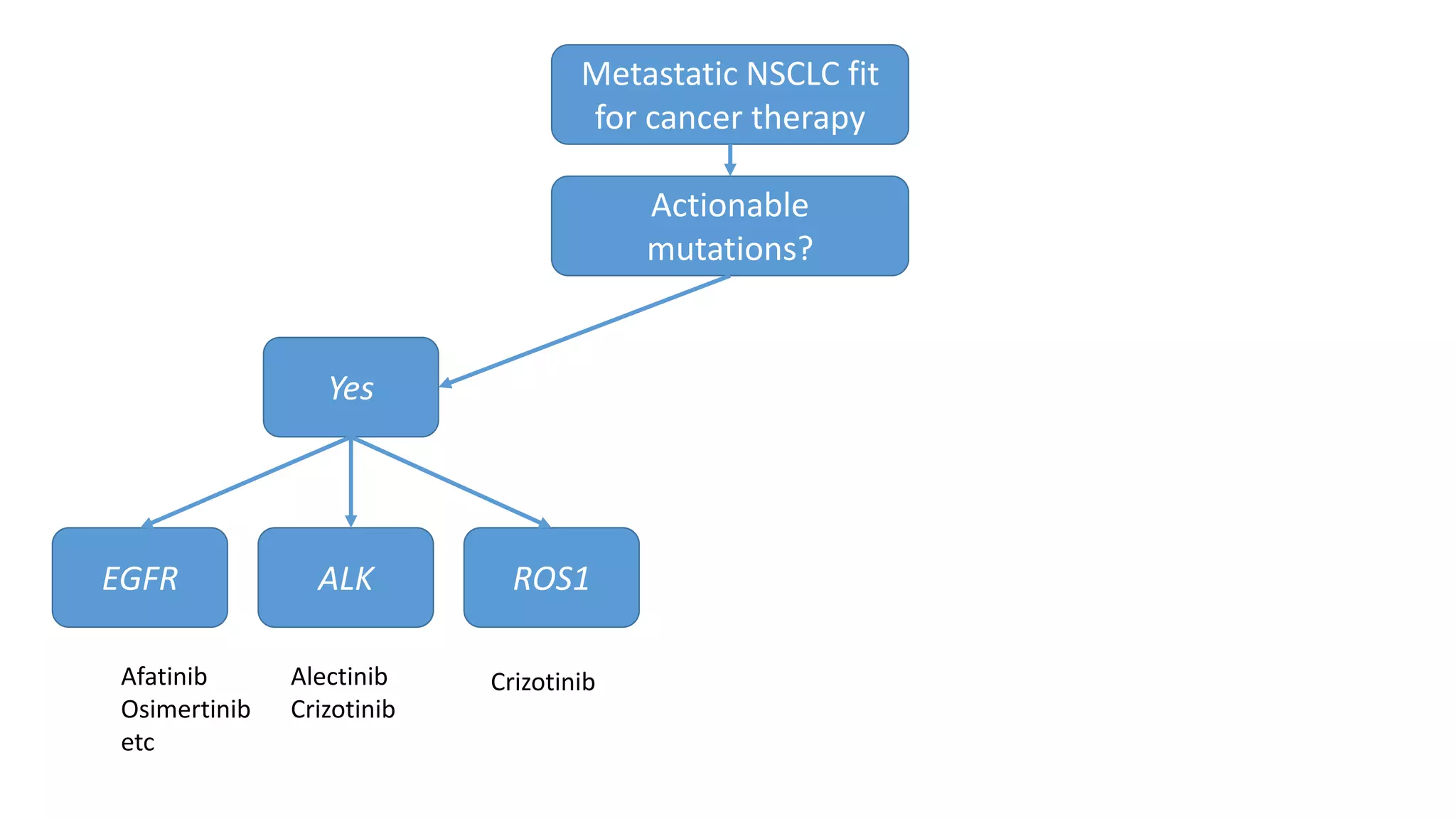
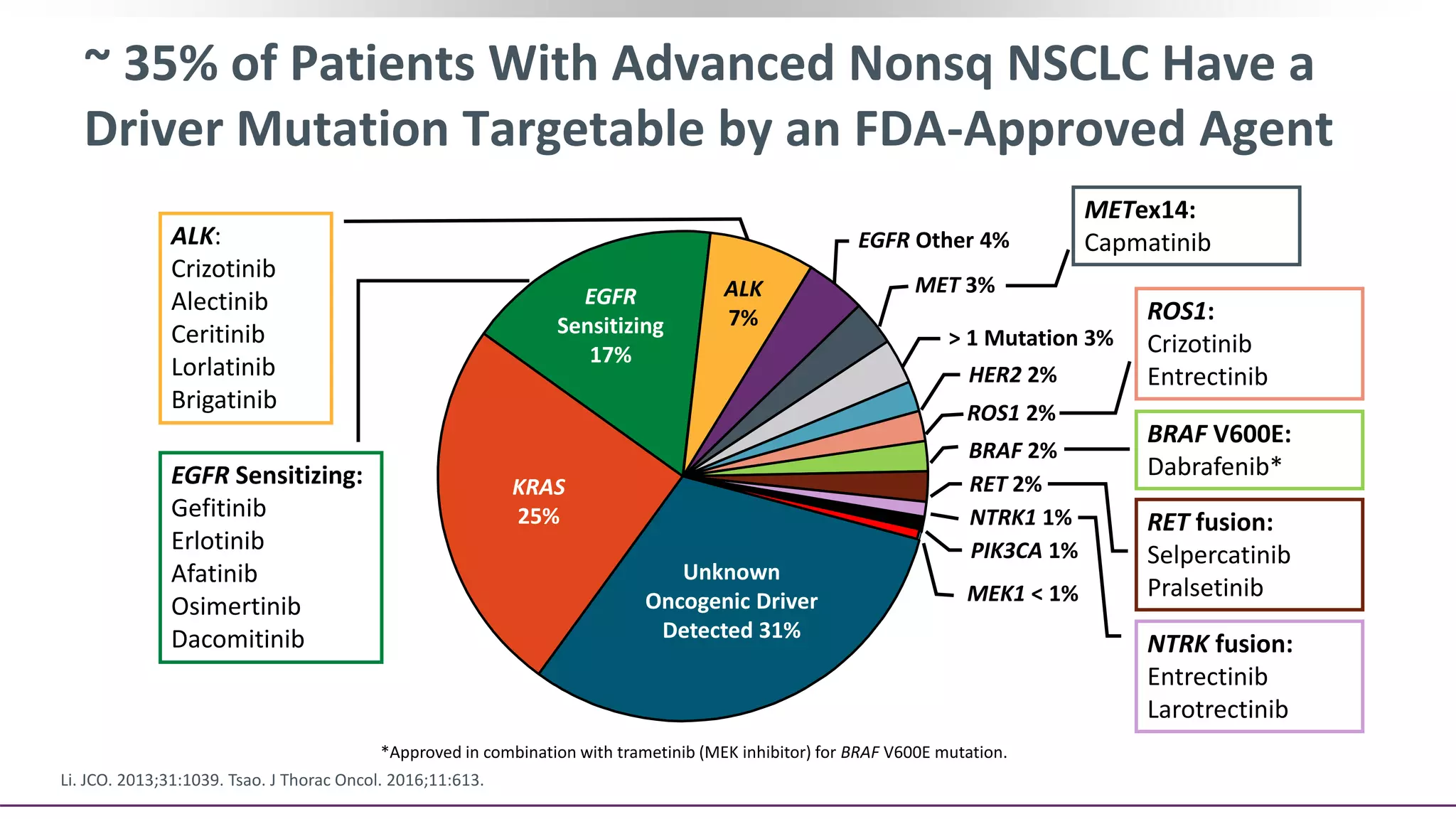
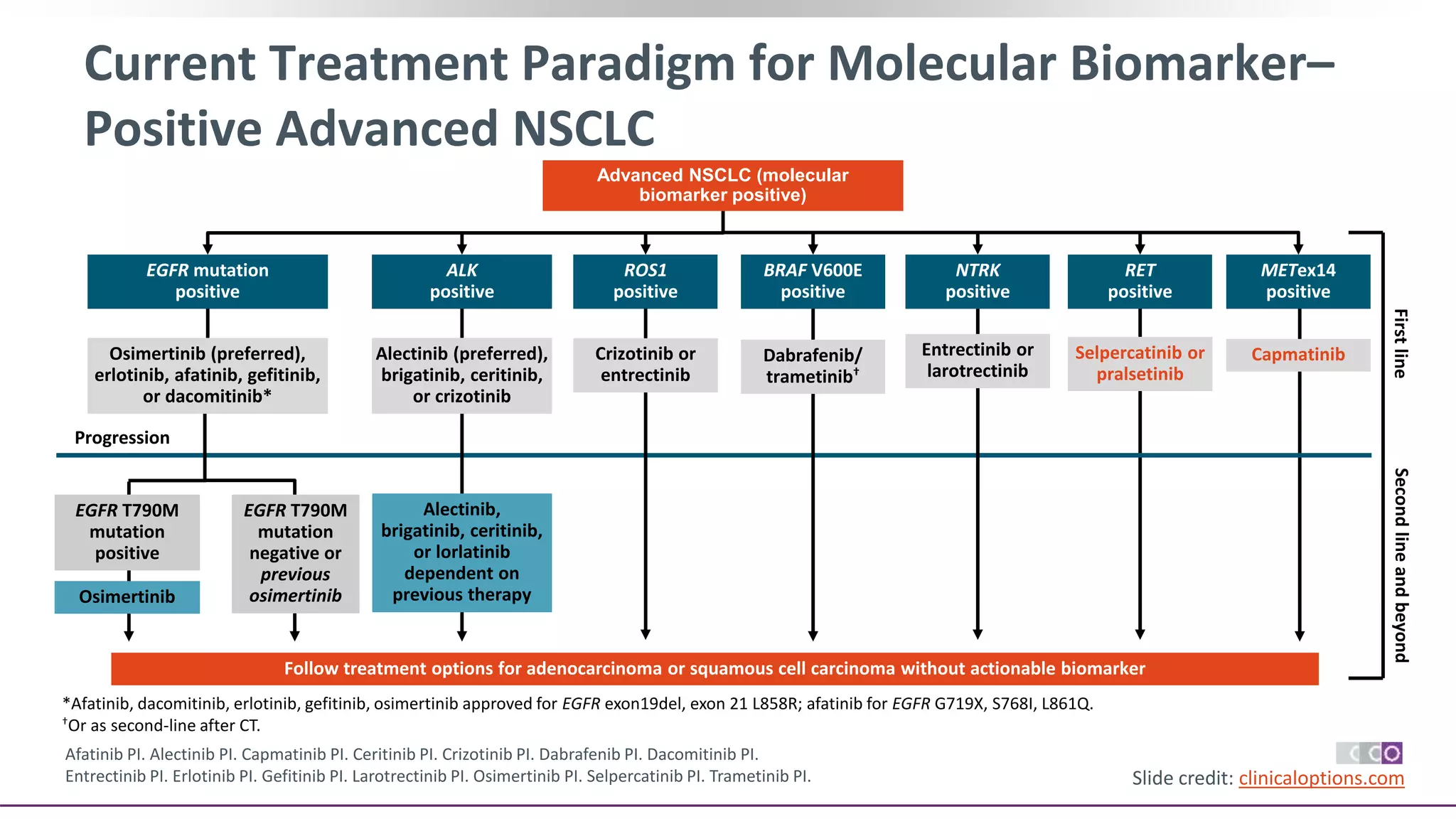
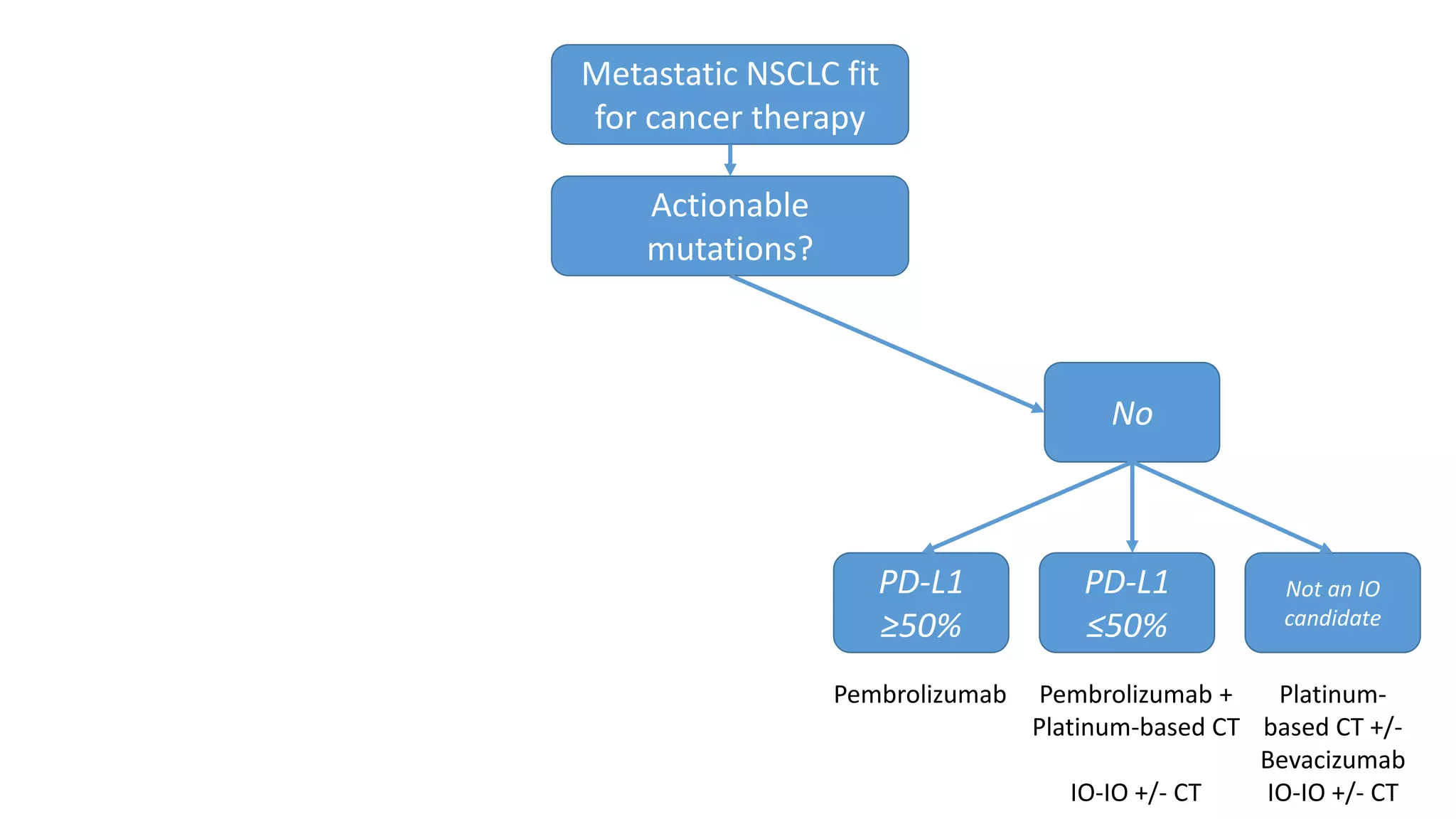
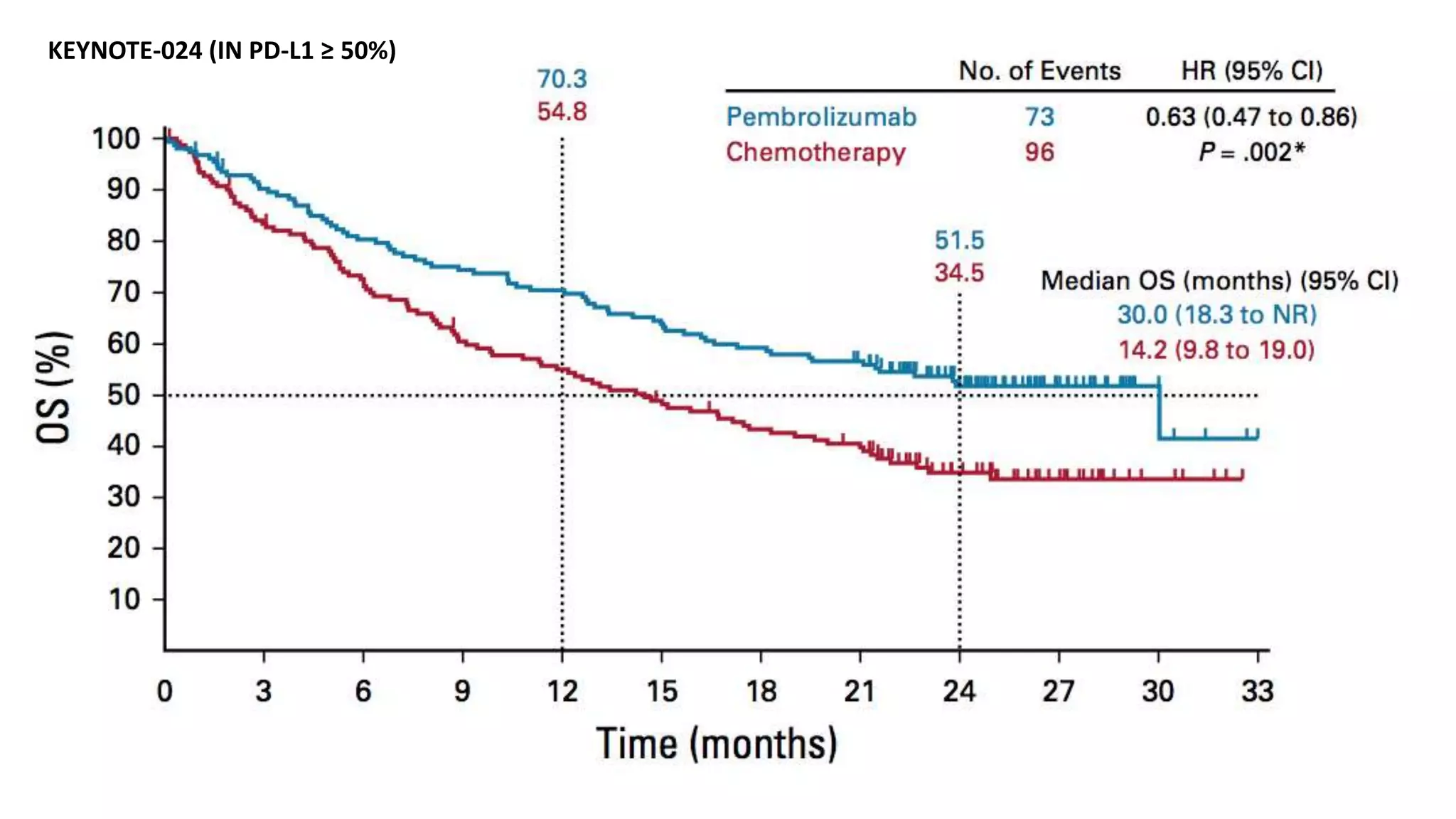
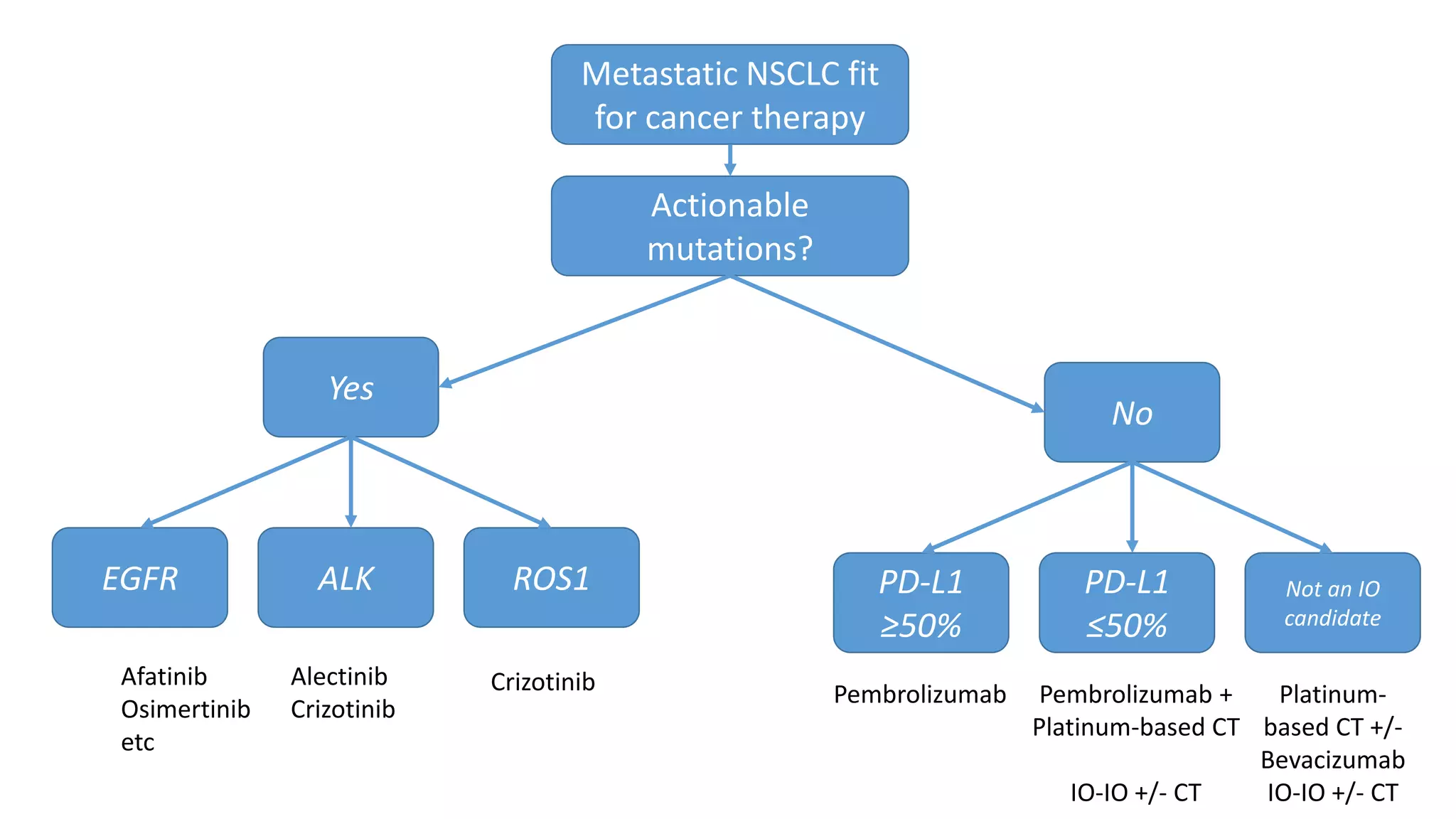
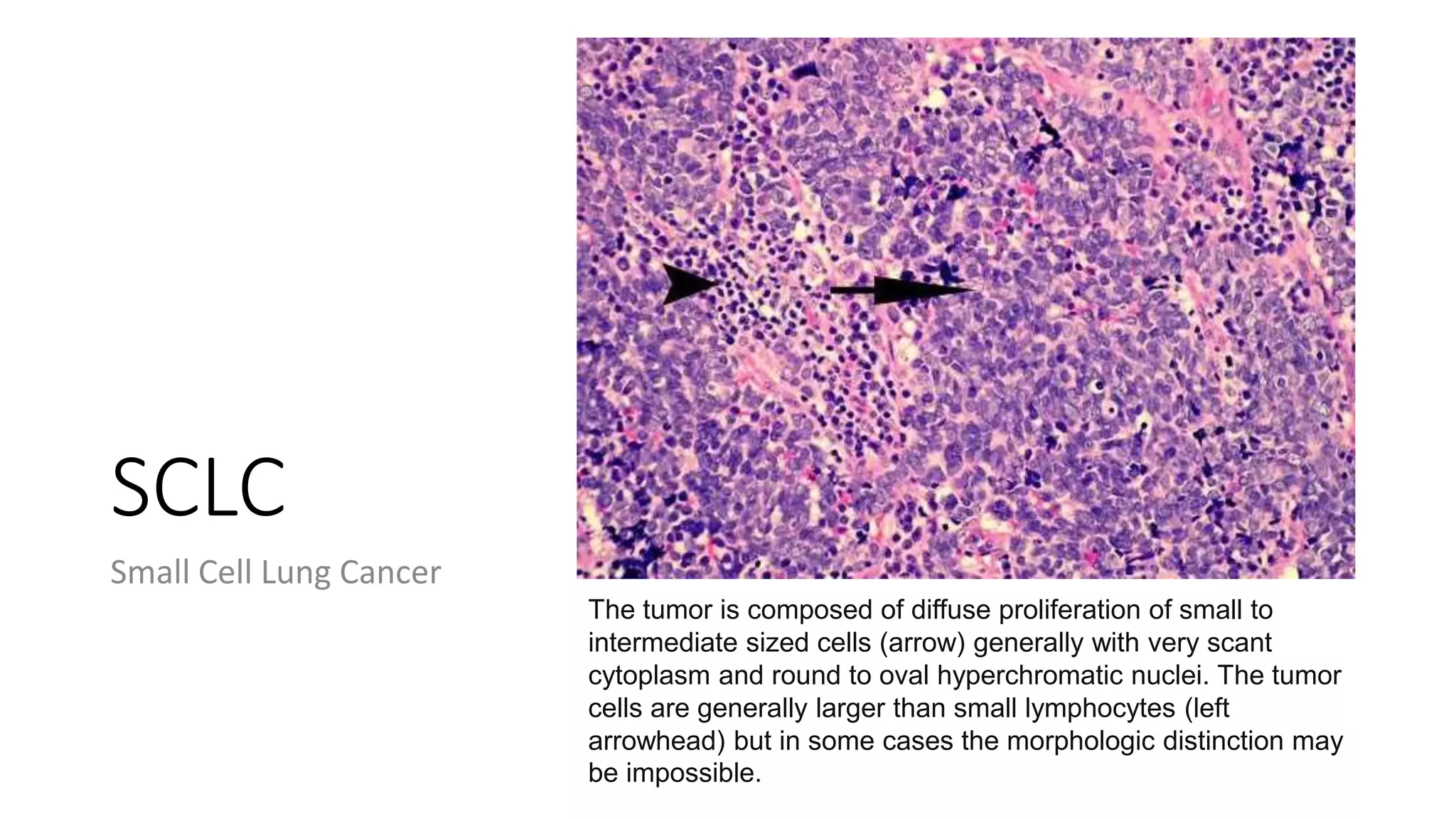
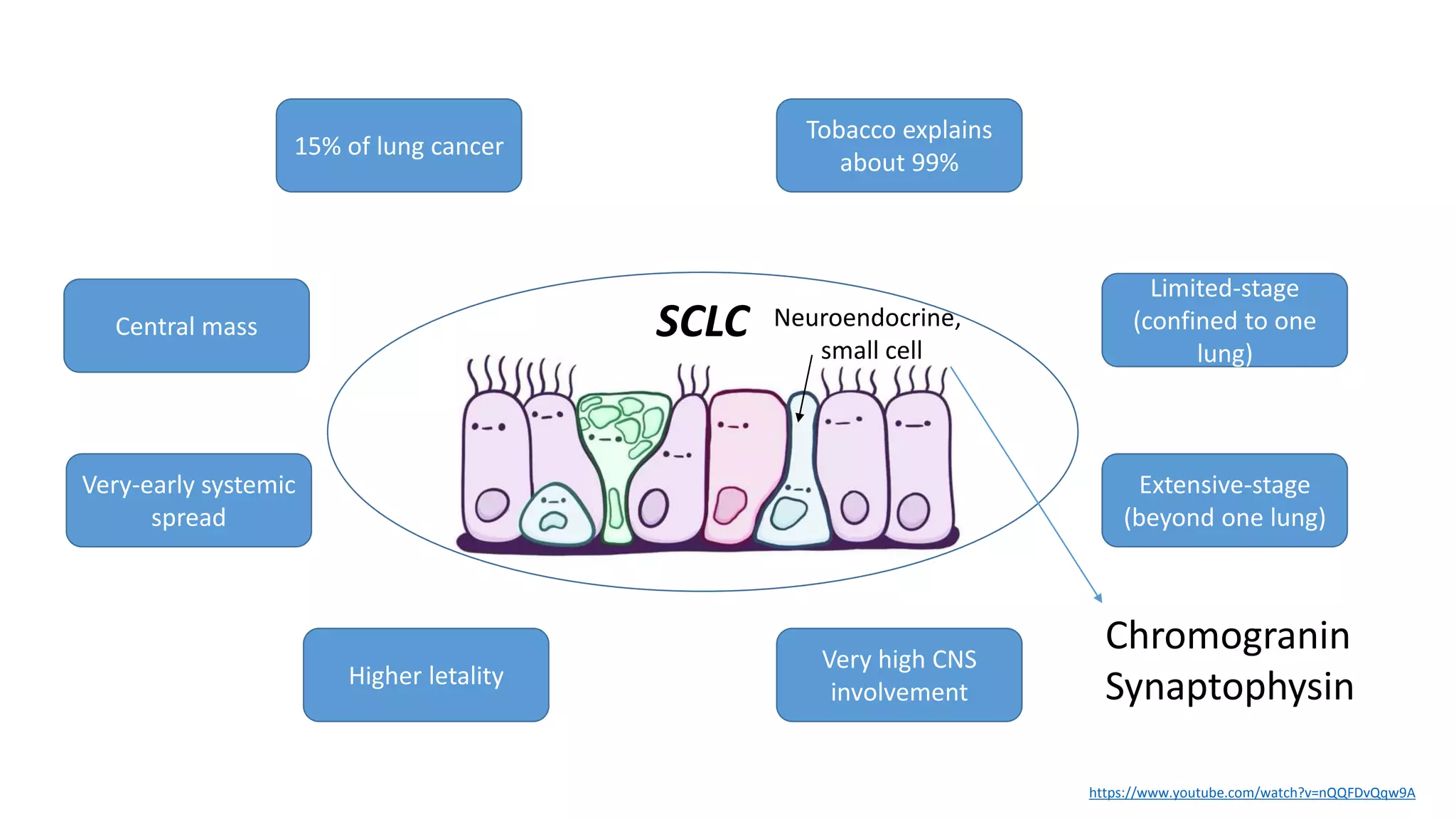
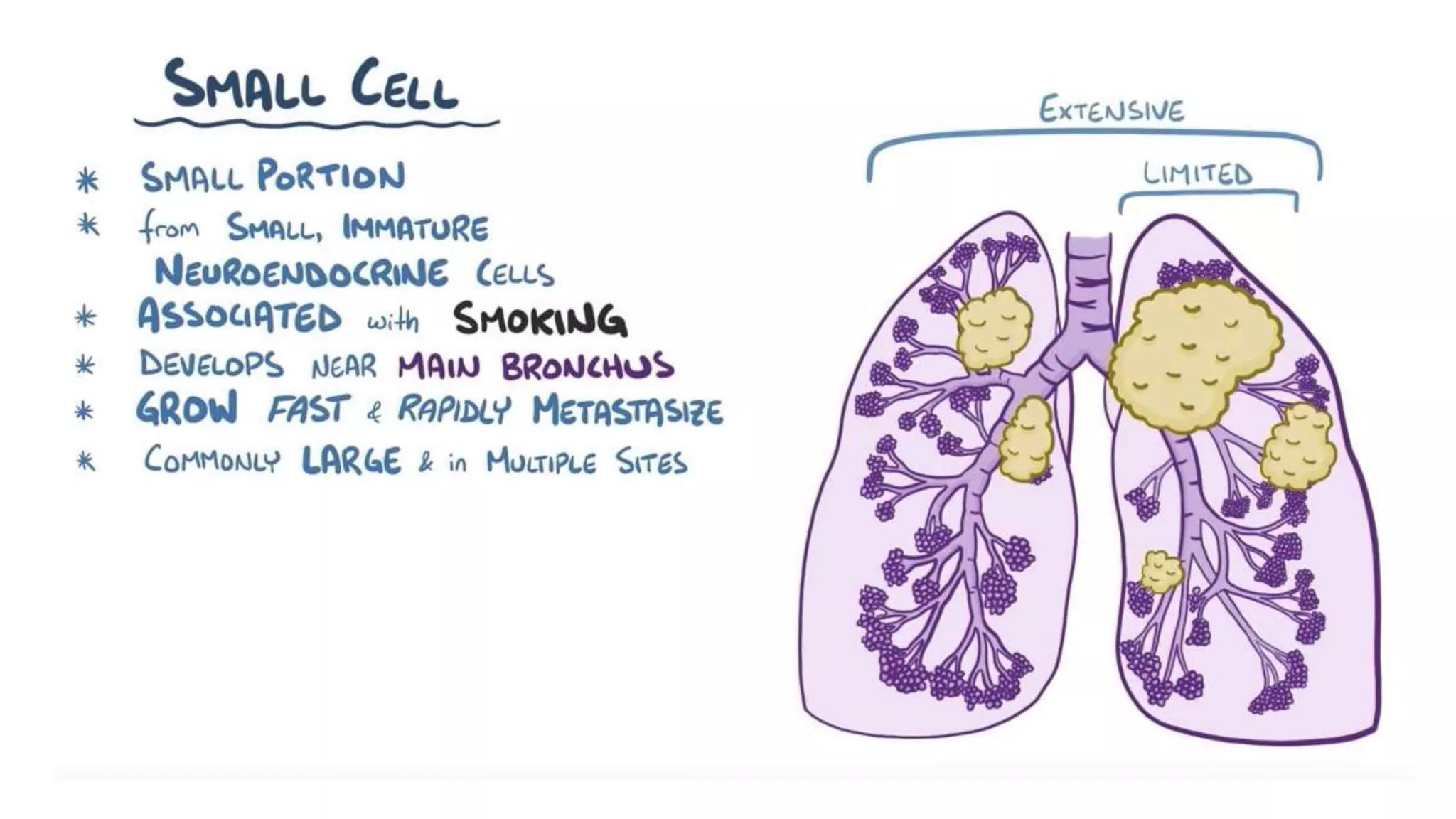
The document discusses lung cancer treatment and biomarkers. It begins by covering small sample handling and immunohistochemistry markers like p63 and TTF1 that can help classify lung cancer subtypes. It then discusses genomic testing for drivers like EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and BRAF and associated targeted therapies. The TNM staging system and its impact on treatment options like surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy are reviewed. About 35% of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients have a targetable driver mutation that can be treated with approved targeted therapies to achieve longer survival compared to conventional chemotherapy.