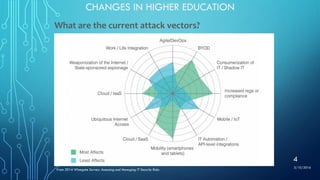
The document discusses centralized versus decentralized approaches to cybersecurity. Under a centralized model, there is single authority over policies and processes, while a decentralized model gives more autonomy to individual groups. The challenges of securing a decentralized higher education environment are also examined, where research environments have unique needs and varying levels of IT support across campus. Effective CISOs in this environment must find ways to address common threats with a unified approach, while also providing support to less resourced areas and ensuring security does not impede academic work. Partnerships are important to improve programs in a decentralized governance model.