The document summarizes key information about cells, including:
1. It describes the cell theory which states that all organisms are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
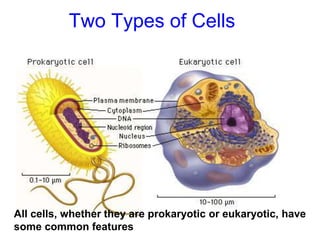
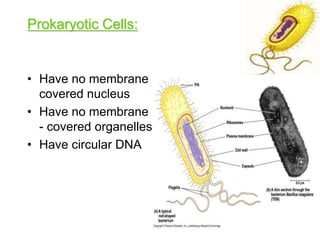
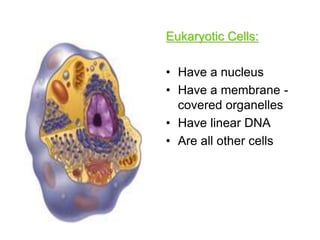
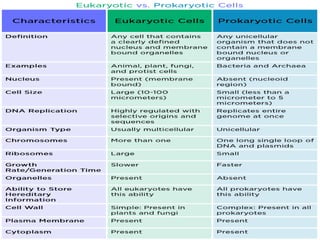
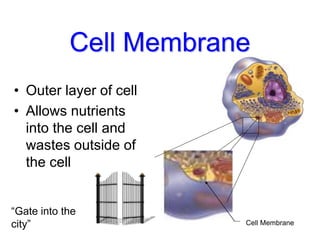
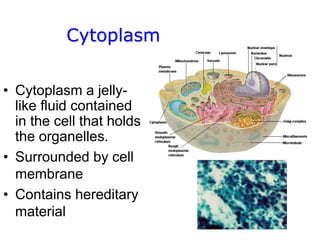
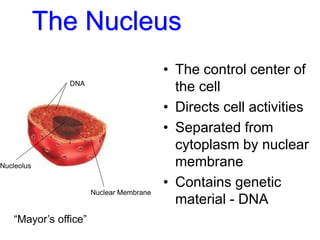
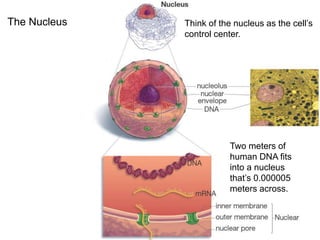
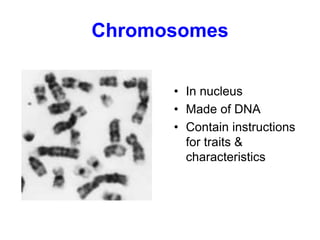
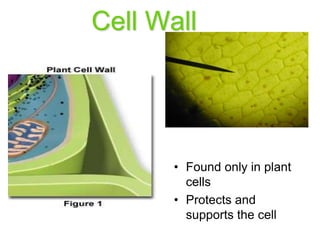
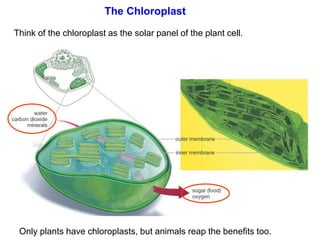
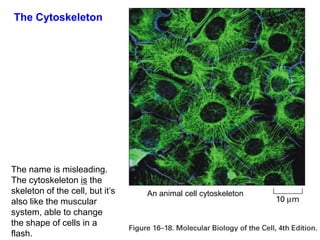
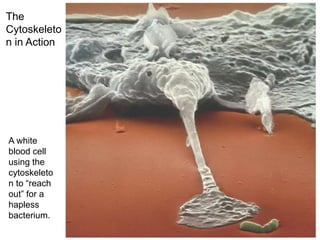
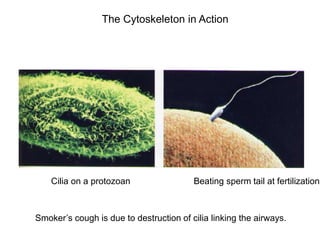
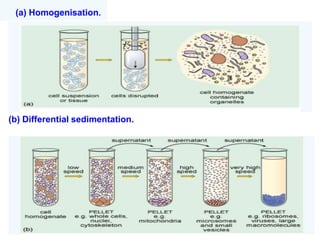
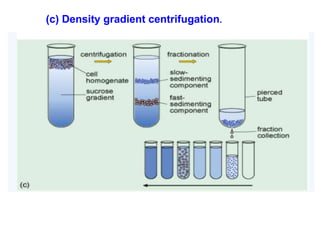
2. It defines the cell as the smallest unit capable of performing life functions and describes common structures of plant and animal cells like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
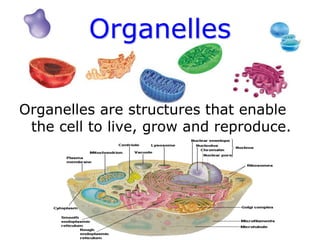
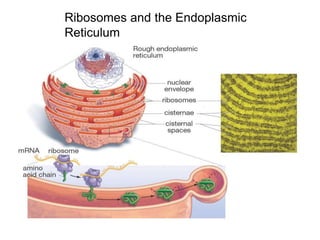
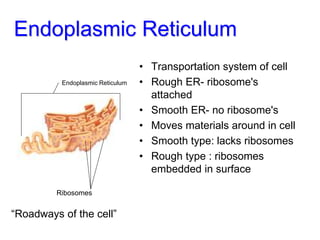
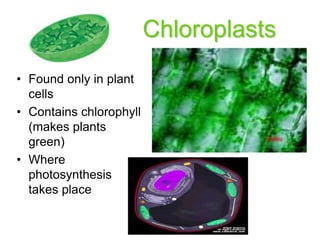
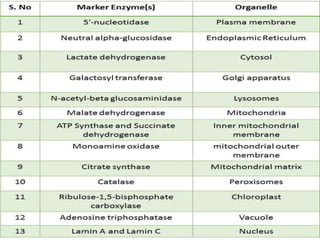
3. It explains the functions of various organelles like the mitochondria which produces energy, ribosomes which produce proteins, and chloroplasts which perform photosynthesis in plant cells.