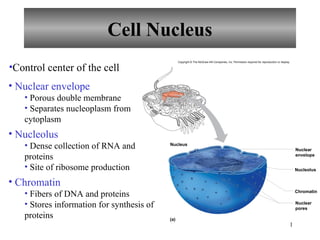
The document provides an overview of cell nucleus structure and function, including the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and chromatin. It also explains cellular transport processes, distinguishing between passive processes like diffusion and osmosis, and active processes such as active transport and endocytosis. Additionally, it mentions facilitated diffusion, which requires a carrier molecule for the transport of substances across membranes.