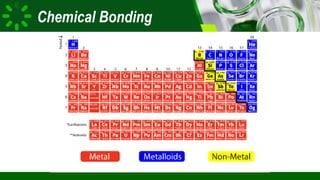
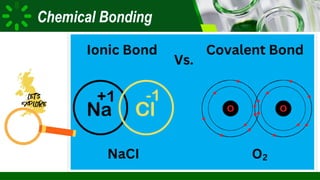
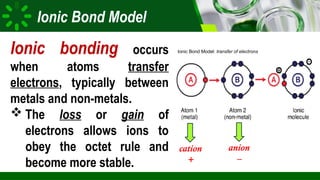
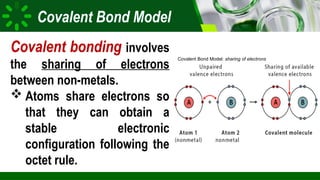
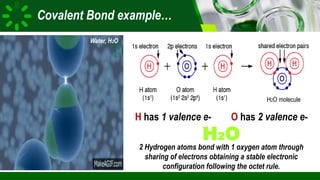
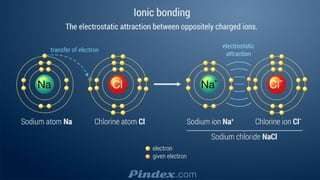
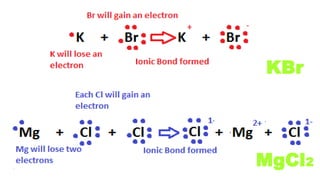
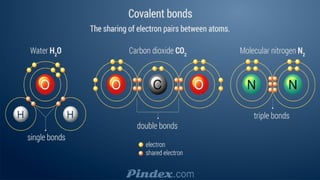
The document compares ionic and covalent bonding, explaining that ionic bonds form through electron transfer between metals and non-metals, while covalent bonds result from electron sharing between non-metals. It highlights the properties of both bond types, such as their melting points, electrical conductivity, and solubility in water. Examples provided include sodium fluoride for ionic bonds and water for covalent bonds.