Embed presentation
Downloaded 53 times

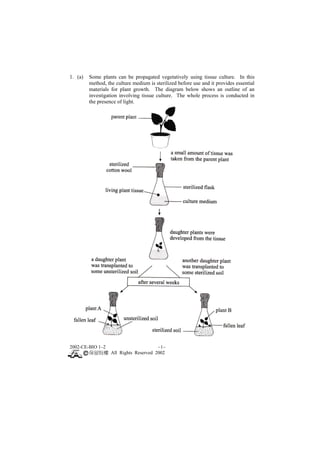




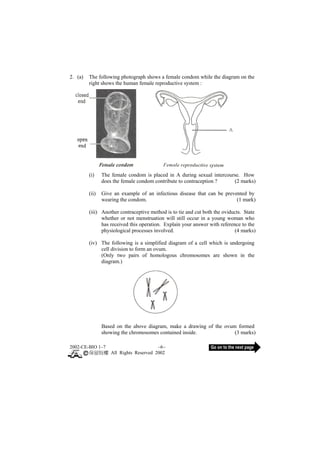








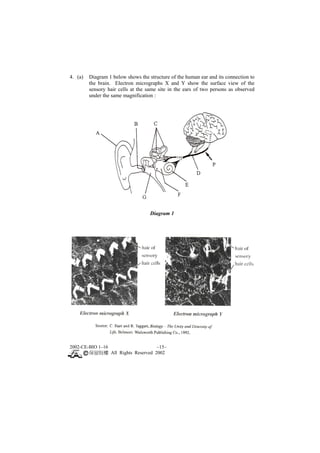



This document contains a biology exam paper from Hong Kong in 2002. It consists of 3 main questions, each with multiple parts: 1. The first question covers topics like plant tissue culture, human bone structure, and blood glucose levels. 2. The second question discusses female condoms, human reproduction, and leaf cell structures. 3. The third question analyzes data on food poisoning outbreaks in Hong Kong by cause and time period. It also discusses guidelines for safe school lunch packaging.


















