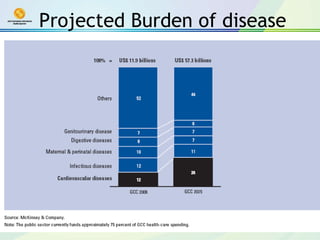
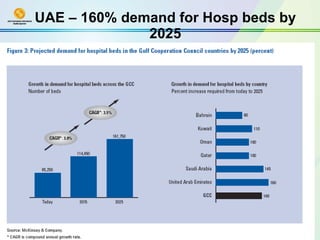
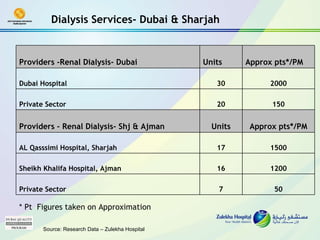
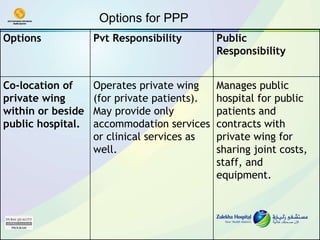
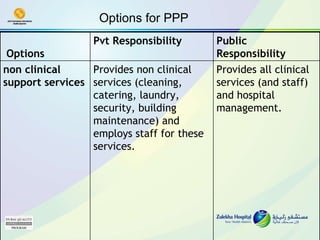
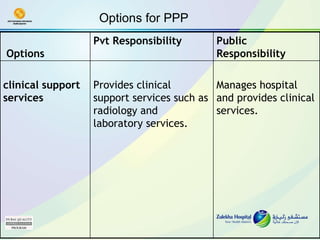
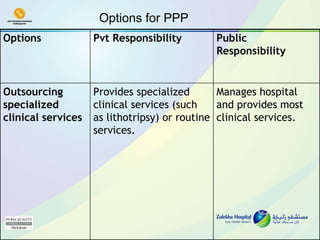
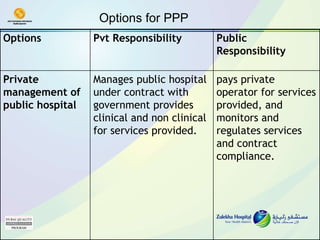
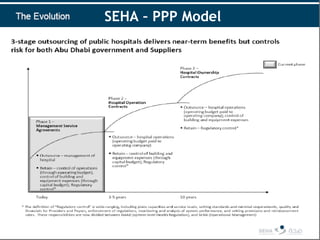
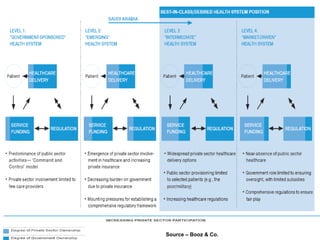
The document discusses public-private partnerships (PPPs) in healthcare in the UAE. It outlines several issues facing public hospitals globally and in the UAE, including rising costs and demand outpacing budgets. It then presents various models for PPPs, such as private management of public hospitals or provision of specialized clinical services. Case studies from Saudi Arabia and India show successes with the PPP approach in controlling costs and improving services while maintaining regulatory oversight.







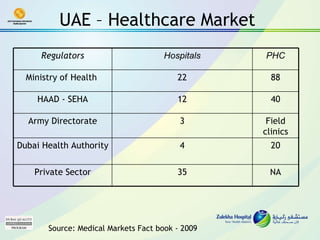
![Population -5.6million [2009 census]; · The number of beds per 1,000 people in UAE is 2, still below the international average of 3 · Private healthcare providers in UAE receives 70% of their income from insured patients. Rapid shift in Health insurance due to Legislation Source: WHO - Business Monitor International](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdocumentsandsettingsgraimydocumentsmymusicppp-hospbuild-100607075922-phpapp02/85/Public-Private-Partnering-Taking-UAE-Healthcare-ahead-9-320.jpg)