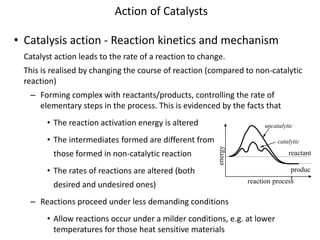
Catalysis involves a catalyst participating in a chemical reaction to alter the reaction rate without being consumed. A catalyst interacts with reactants and products, changing itself during the process. It then returns to its original form after the reaction. Catalysts increase reaction rates by lowering activation energy or changing reaction pathways and intermediates. They allow reactions to proceed under milder conditions like lower temperatures. Catalysts are classified by physical state, substance type, and mechanism of action. They have many industrial and environmental applications, including improving process efficiency in petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries and reducing pollution.