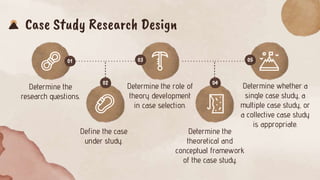
This document provides an overview of case study research. It defines case study research as a qualitative approach that examines a bounded system in depth. Case studies are appropriate when researchers want to answer descriptive or explanatory questions or study a process. The document outlines characteristics of case study research such as being particularistic, descriptive, and heuristic. It also discusses research design considerations for case studies including determining research questions, defining the case, and choosing between single, multiple or collective case studies. Finally, it reviews data collection methods and techniques for analyzing multiple case studies.