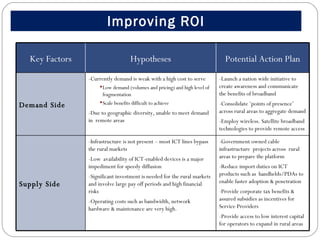
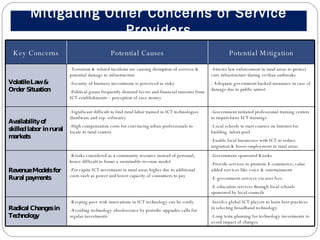
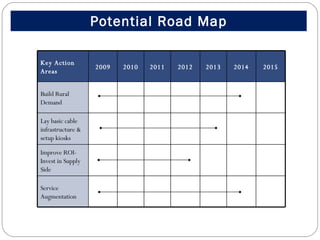
The document outlines a strategic proposal to bridge the digital divide in a densely populated nation with less than 10.5% broadband penetration, particularly in rural areas. It identifies key challenges such as low demand, inadequate infrastructure, and high costs, and suggests a comprehensive action plan focusing on building awareness, improving technology access, and incentivizing service providers. The roadmap includes establishing basic infrastructure, enhancing skills through training programs, and creating sustainable revenue models to promote rural ICT adoption.