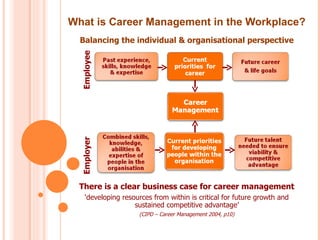
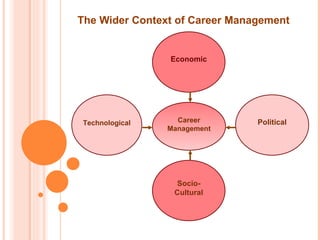
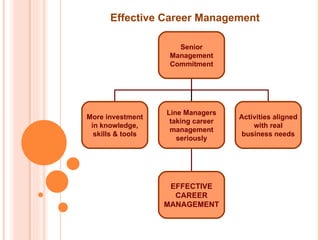
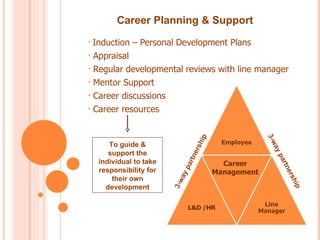
The document discusses the concept of career management, describing it as a lifelong process of planning, setting goals, and developing strategies in the workplace. It emphasizes the importance of balancing individual employee needs with organizational objectives, while outlining various techniques and practices for effective career management. Additionally, it highlights the difference between career management and talent management, suggesting a holistic approach to optimizing employee capabilities for organizational benefit.