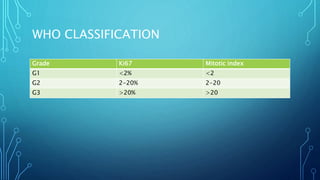
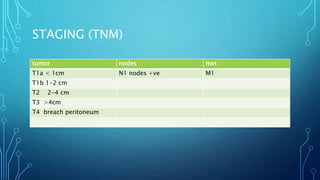
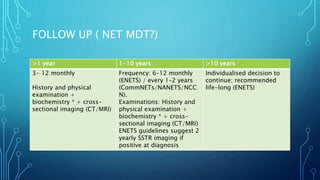
This document discusses carcinoid tumors, which are rare neuroendocrine tumors. It covers their incidence, locations of origin in the gastrointestinal tract, histological classifications based on differentiation and proliferation rates, WHO grading system, clinical features and symptoms, diagnosis methods, staging system, treatment approaches based on localization and metastasis, risks of carcinoid crisis during surgery, follow up protocols, and references consensus guidelines for further reading.