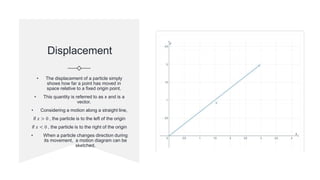
This document provides an overview of calculus-based kinematics. It defines the key terms of displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Displacement refers to how far an object has moved from a fixed point, velocity is the rate of change of displacement over time, and acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time. The document provides examples of using calculus derivatives and integrals to derive kinematic equations for problems involving displacement, velocity, and acceleration functions.