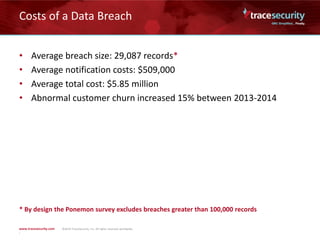
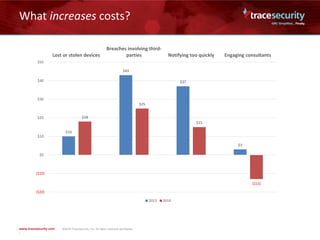
The document outlines the financial impact of data breaches, highlighting that the average cost of a cyber attack cleanup is $5.85 million, with a cost of $201 per record. It cites the Ponemon Institute's 2014 study, which shows breaches often involve cybercriminal acts, human error, or system glitches, and discusses factors that increase or decrease costs. Real-world examples illustrate the significant expenses associated with breaches, including notification and legal costs, and emphasize the need for a robust security posture and incident response plans.