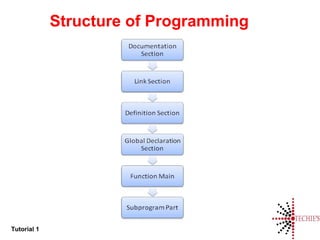
This document provides an introduction to C programming, including:
- A brief history of C's development in the 1970s and subsequent standardizations.
- The benefits of C like efficiency, portability, and structured programming.
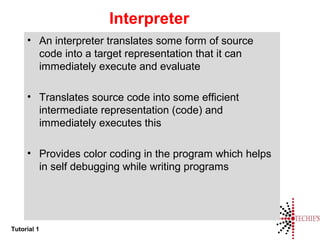
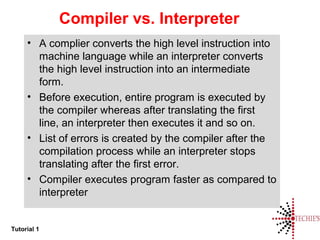
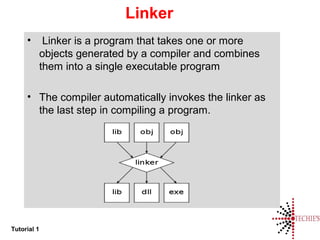
- Common terms for programmers like compiler, interpreter, assembler, linker, and loader.
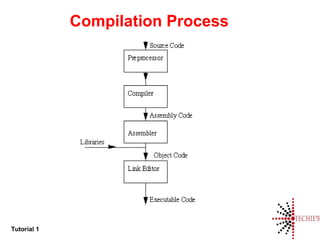
- An overview of the compilation process from source code to executable program.
- The session objectives are to cover the history of C, common benefits and terms, and the compilation process.