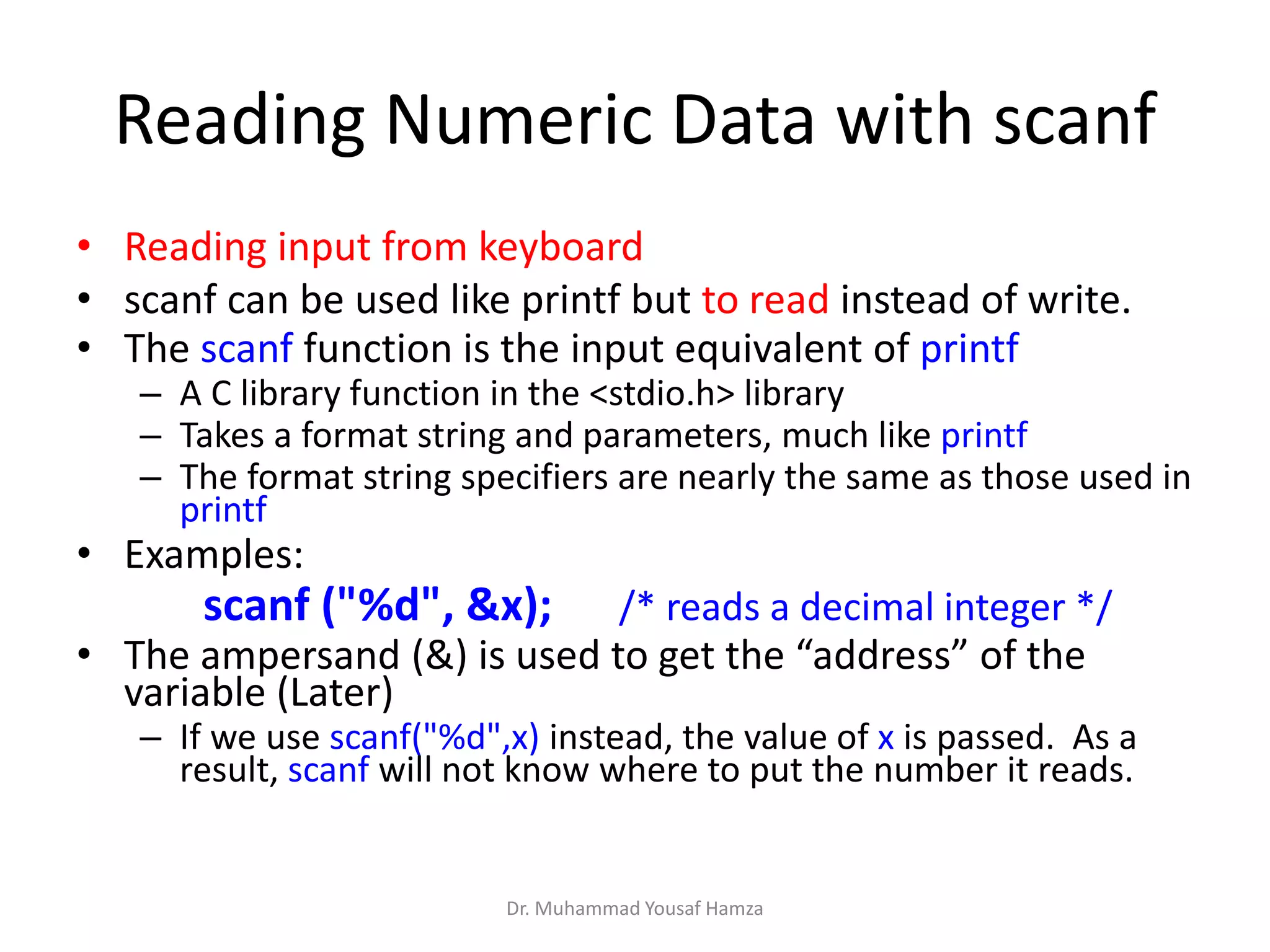
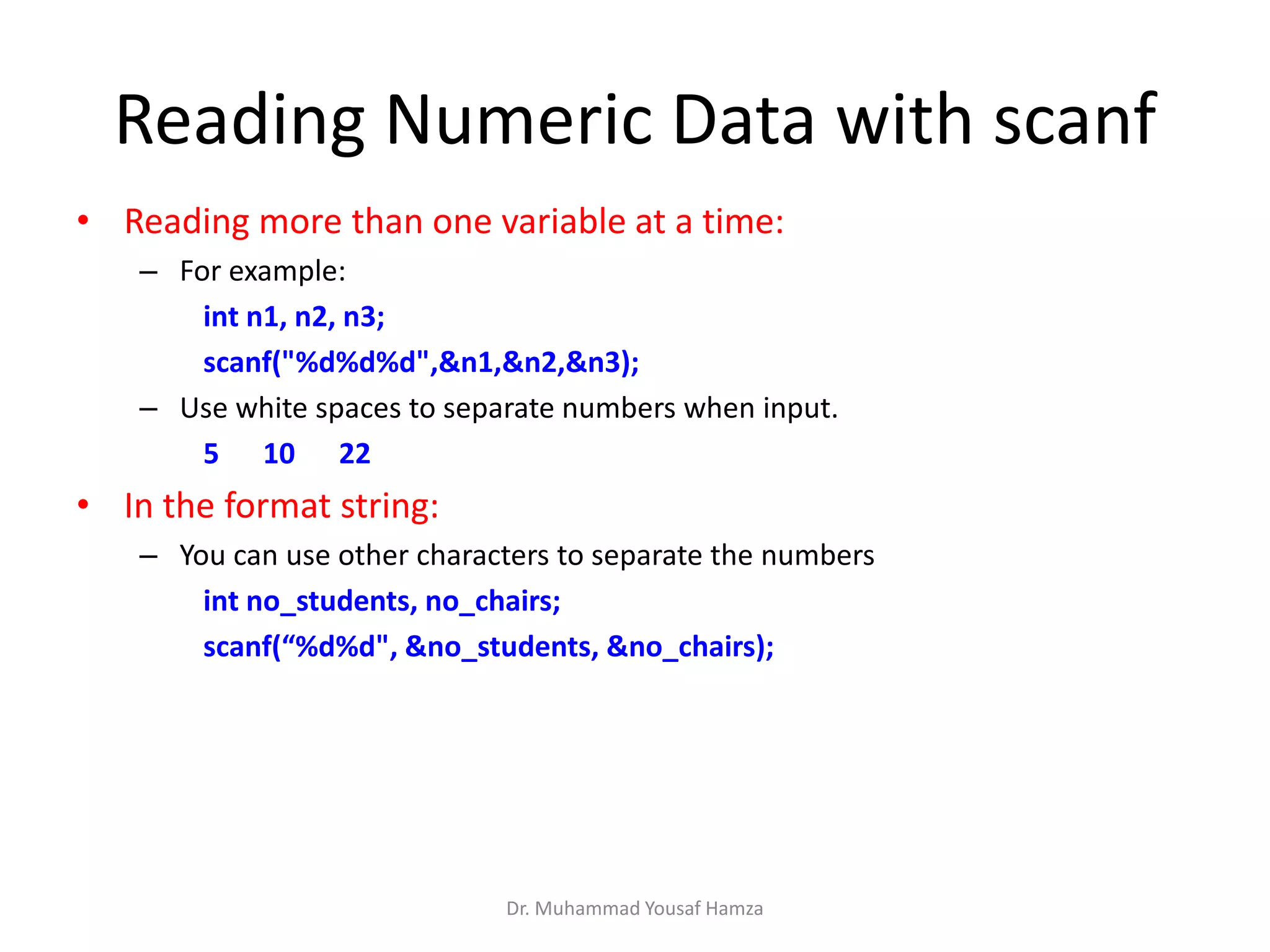
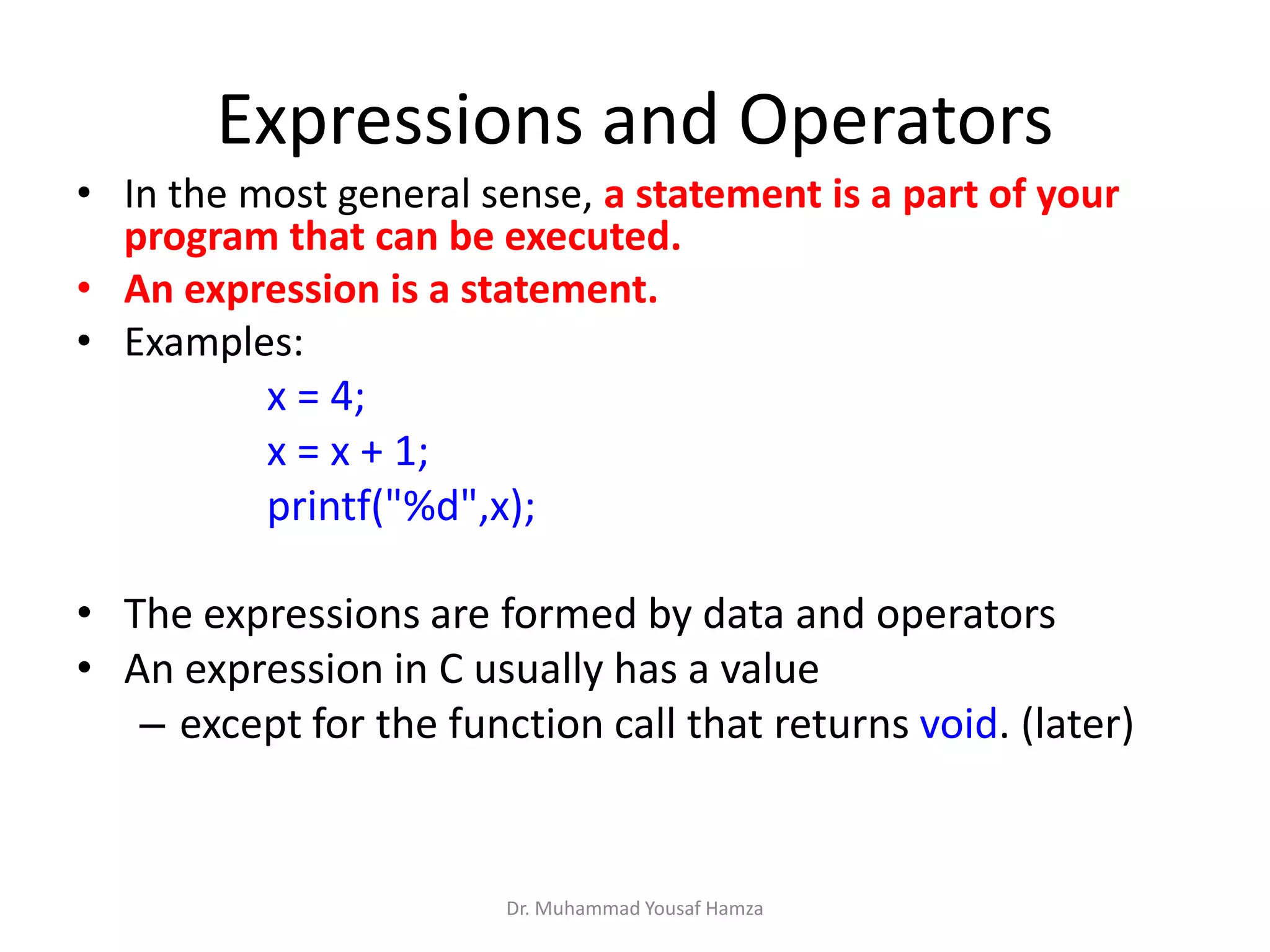
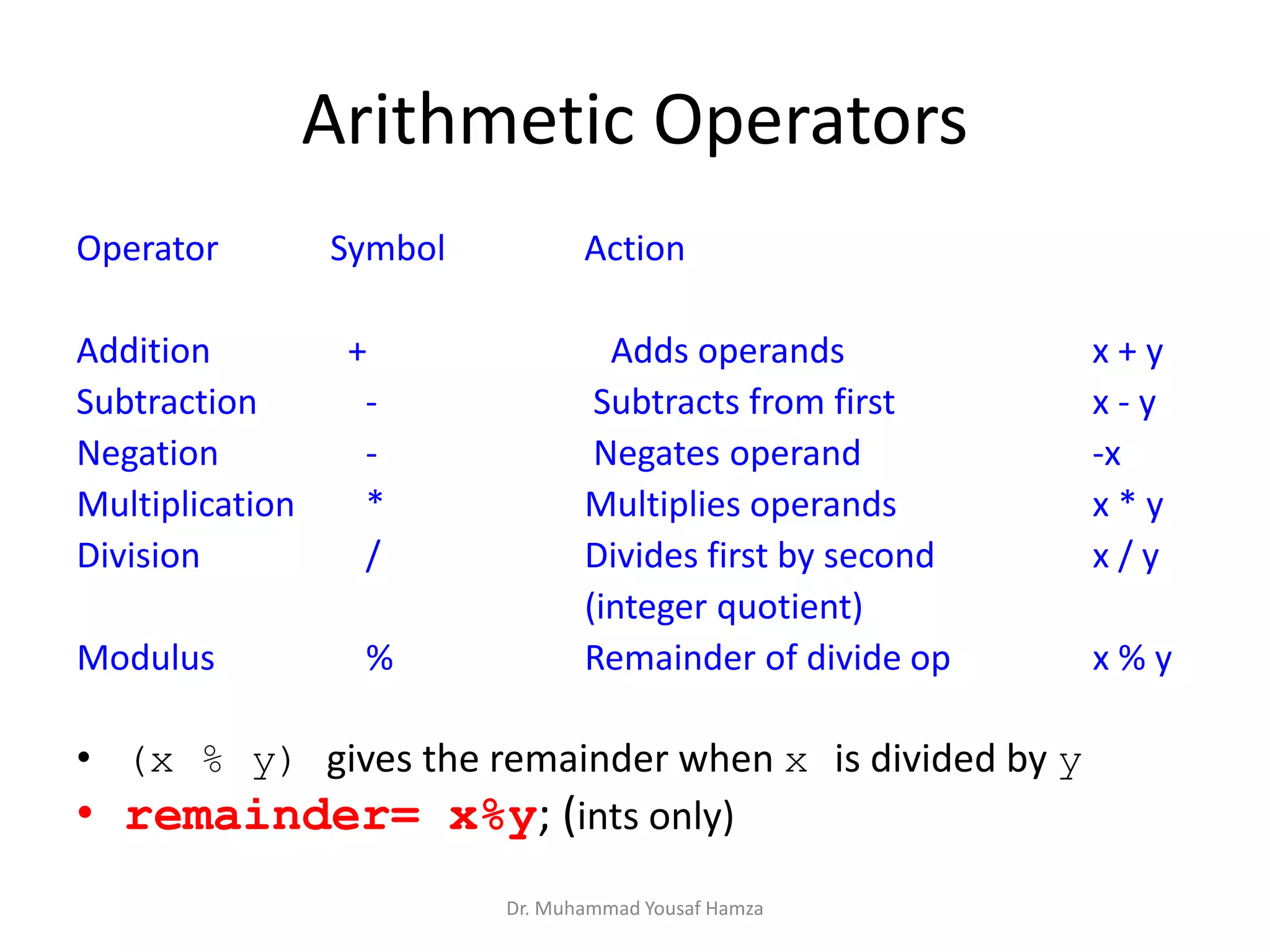
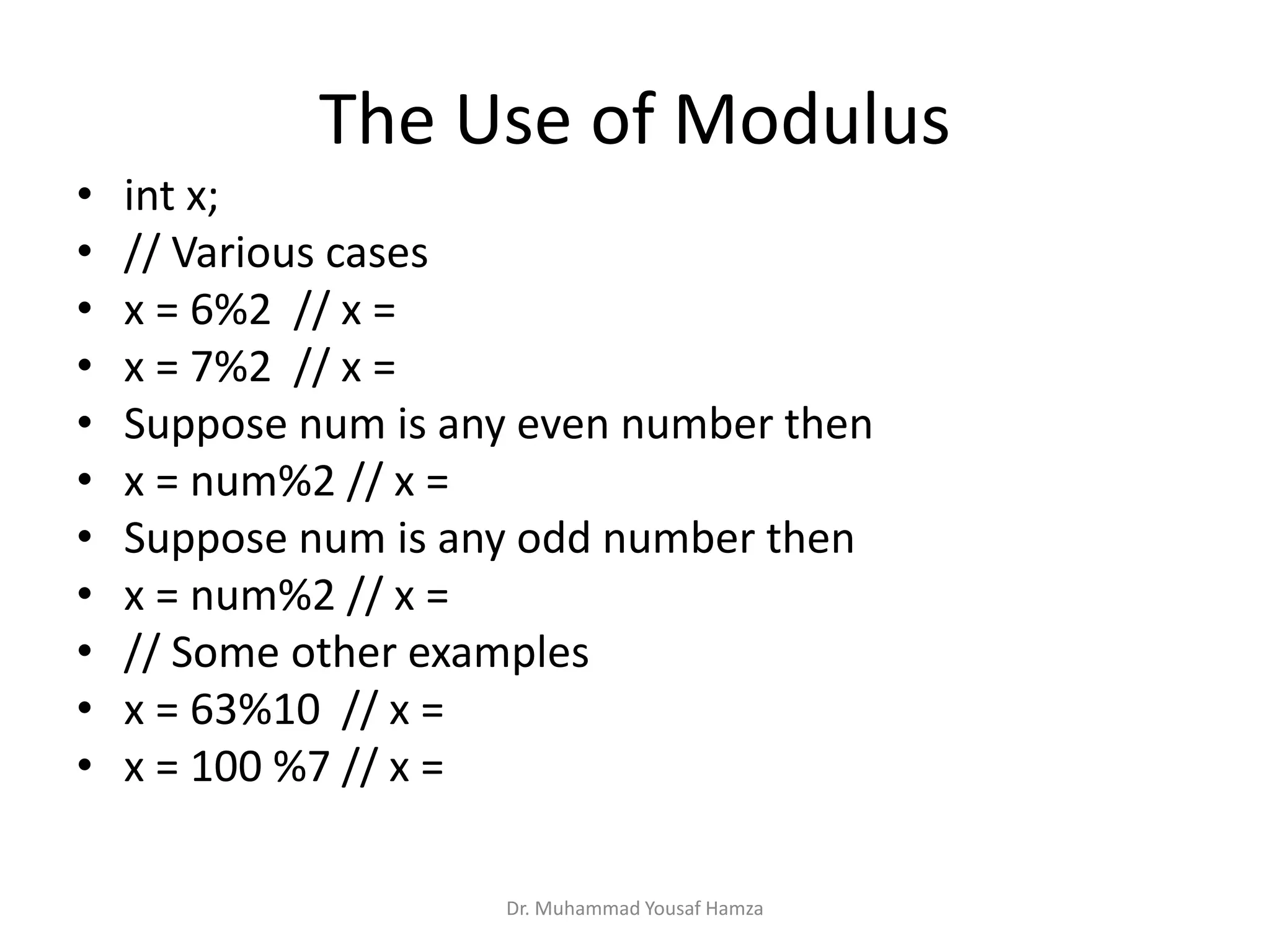
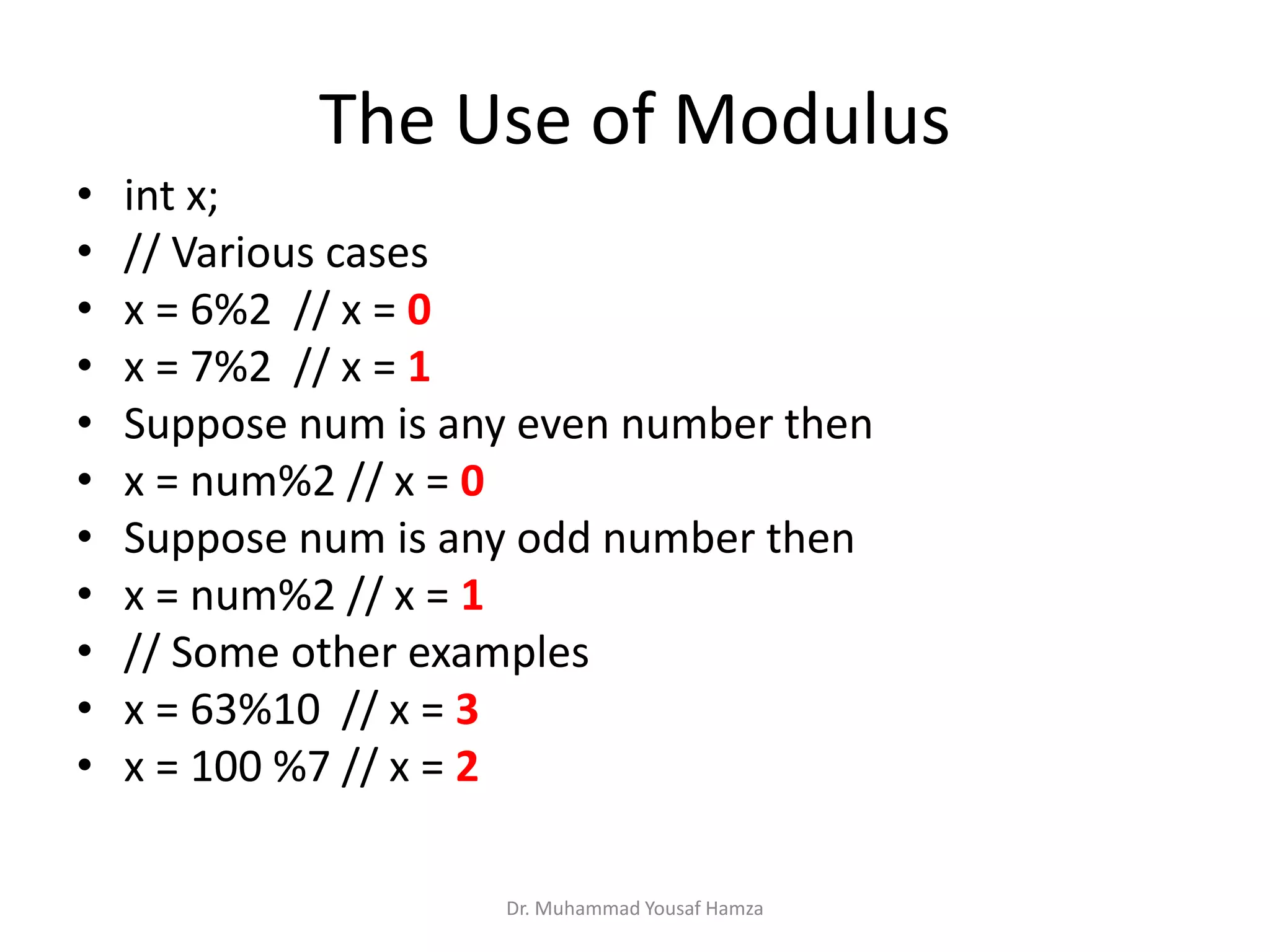
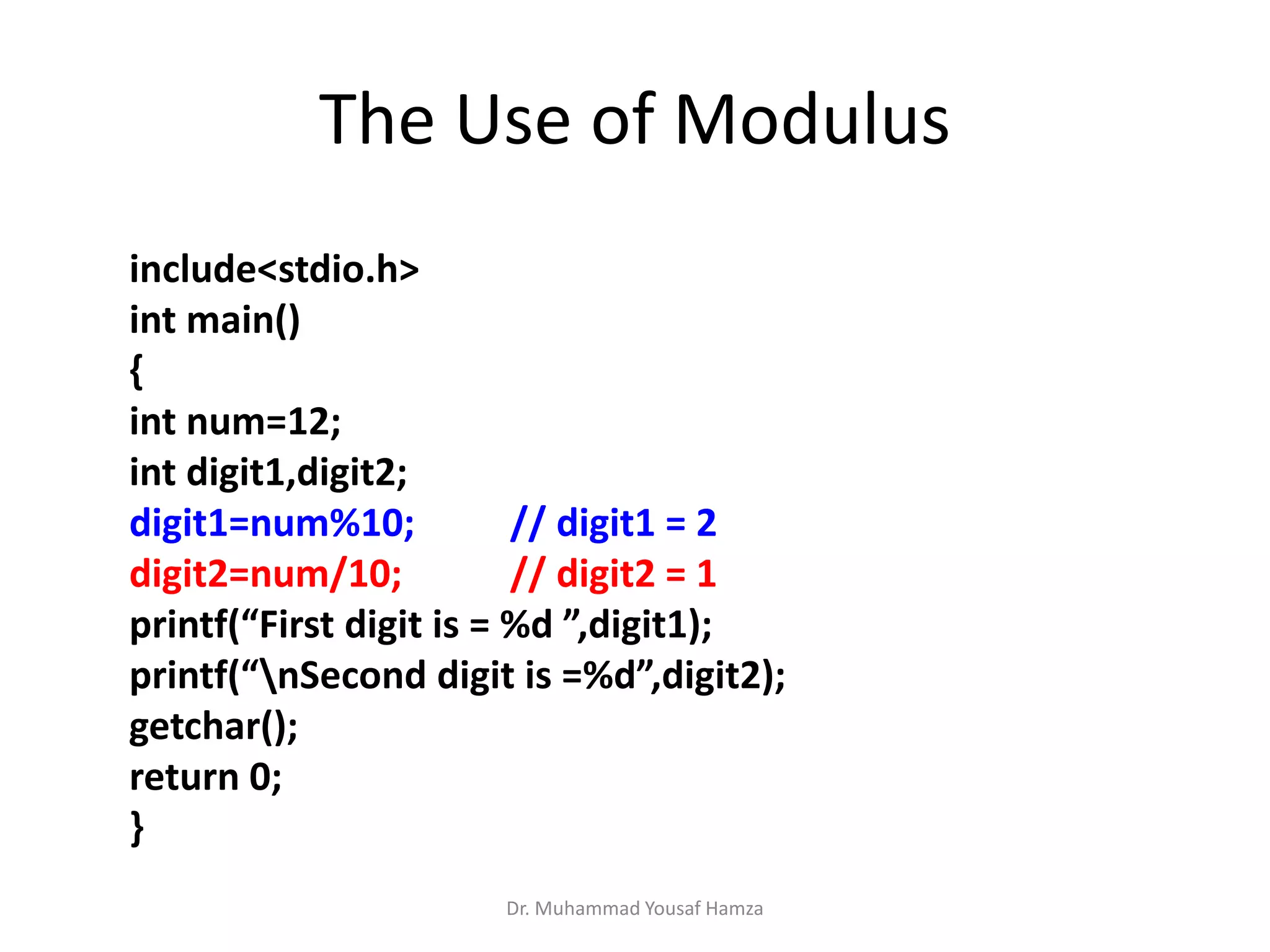
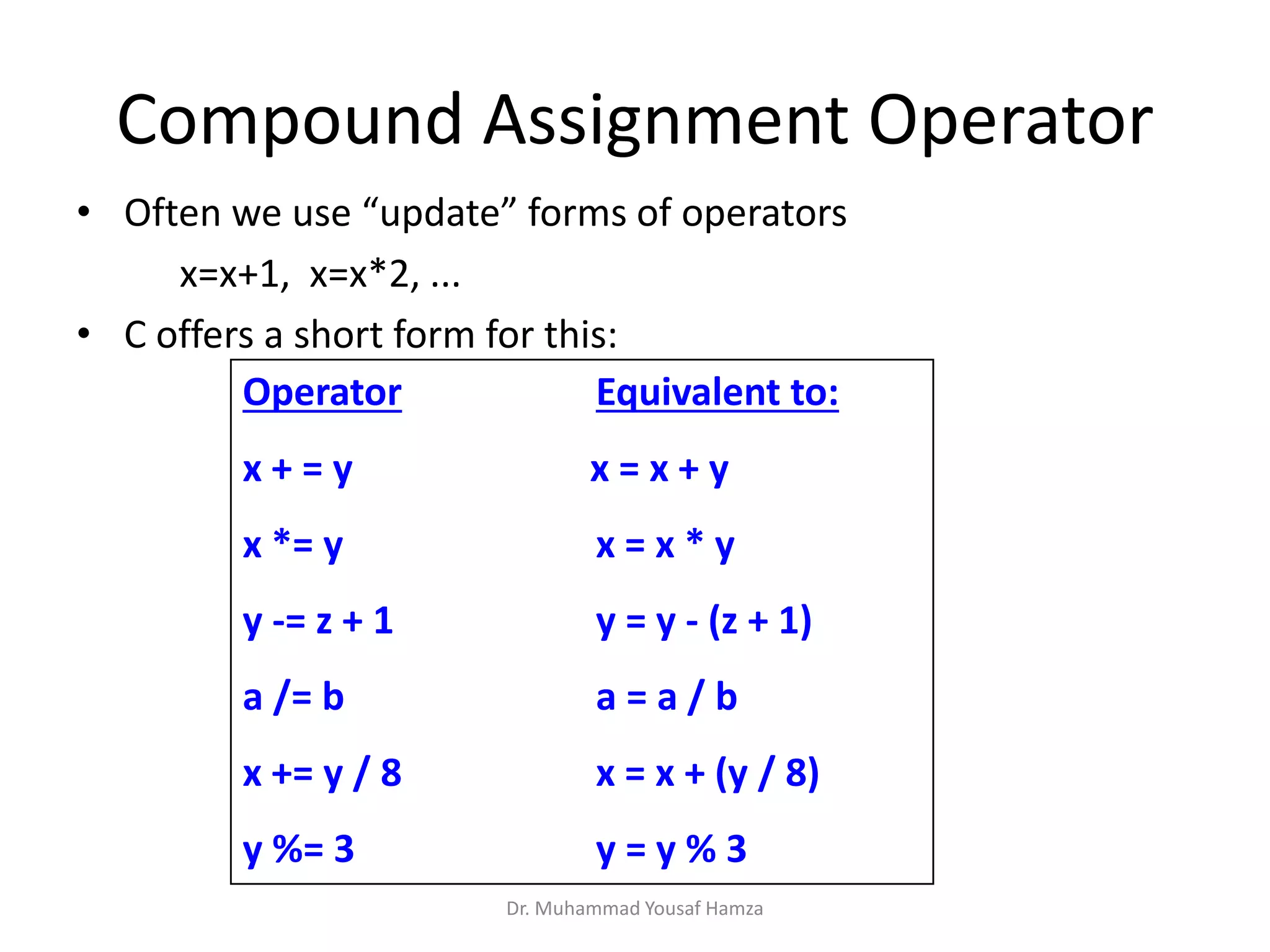
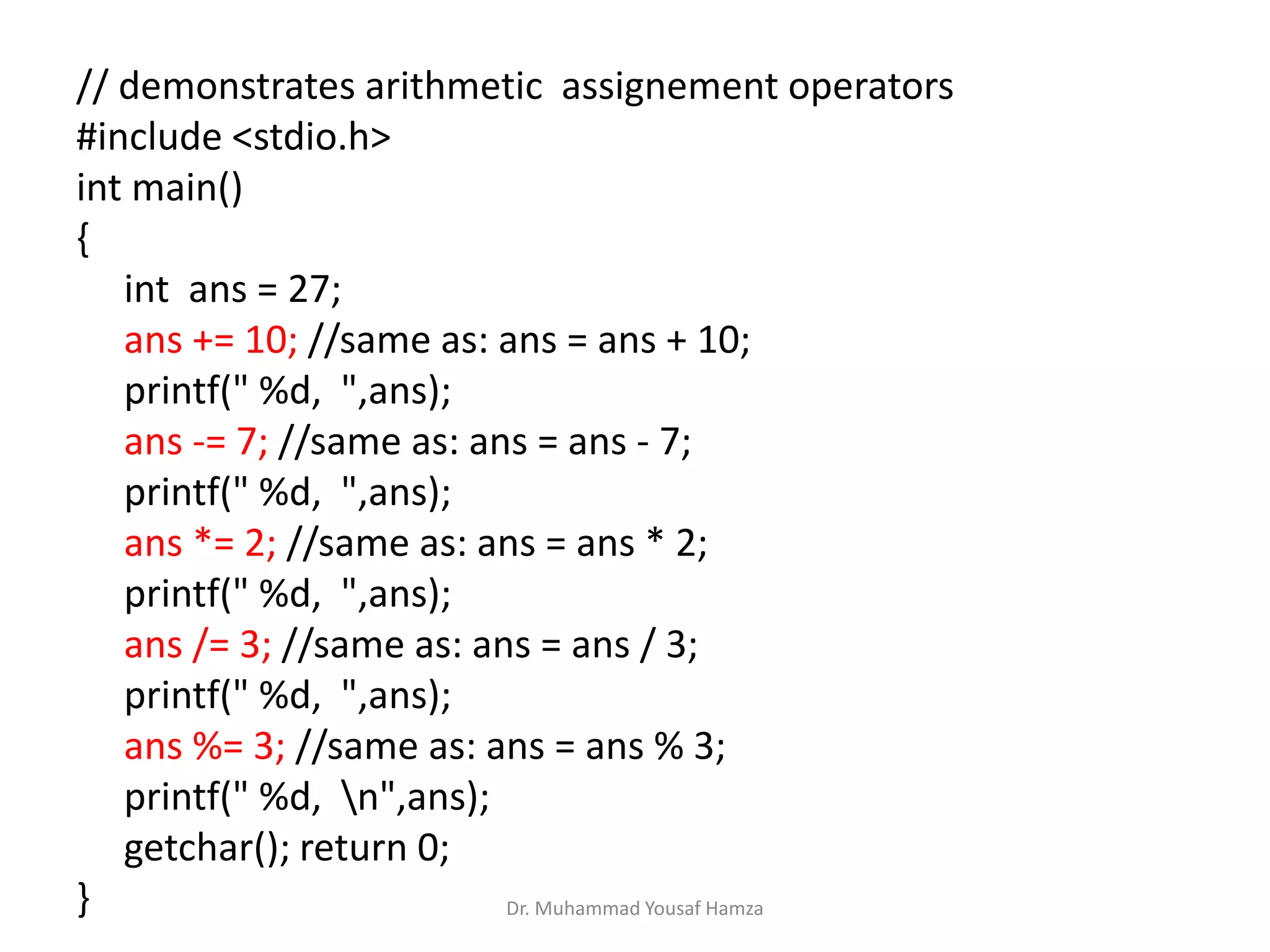
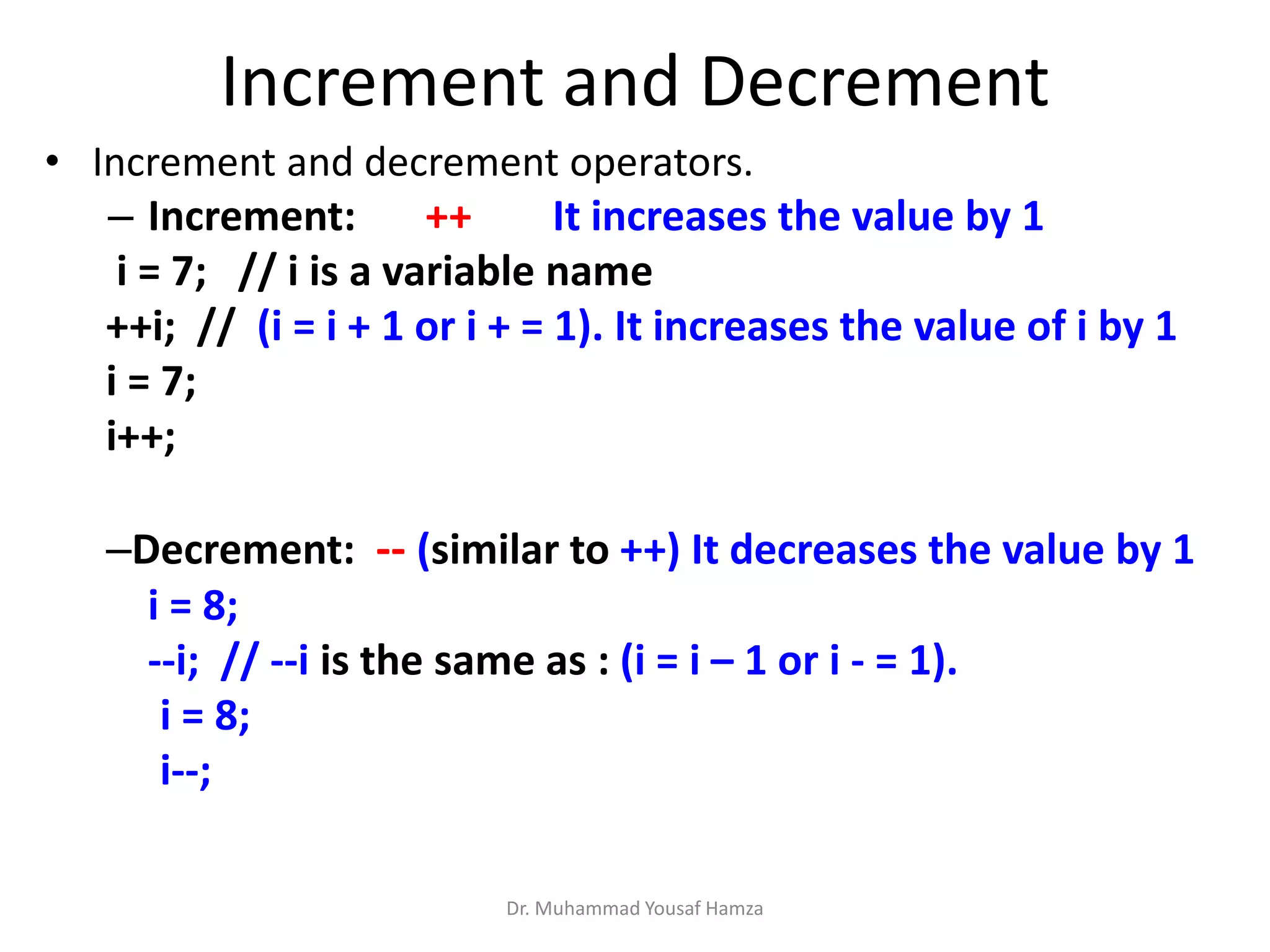
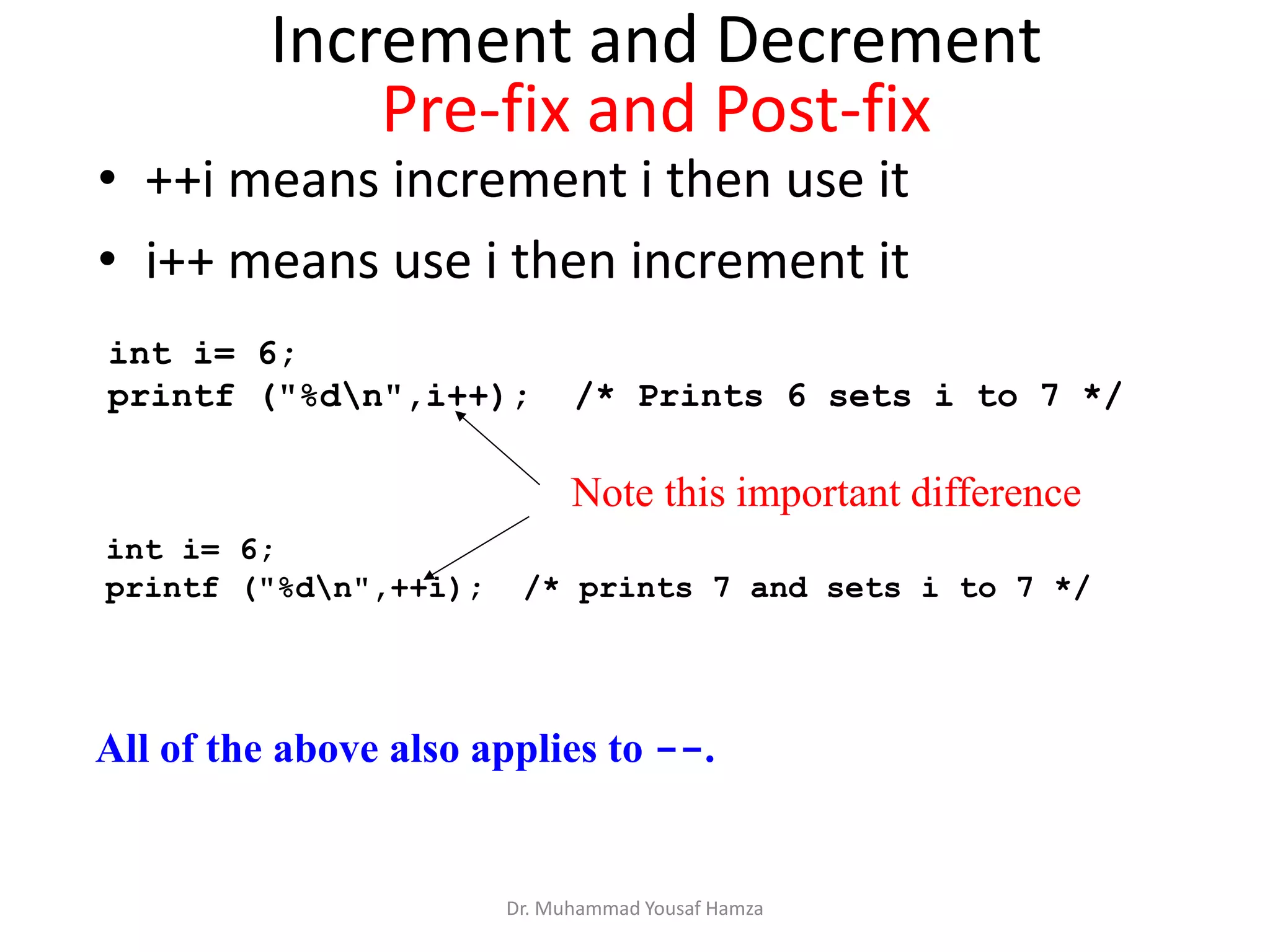
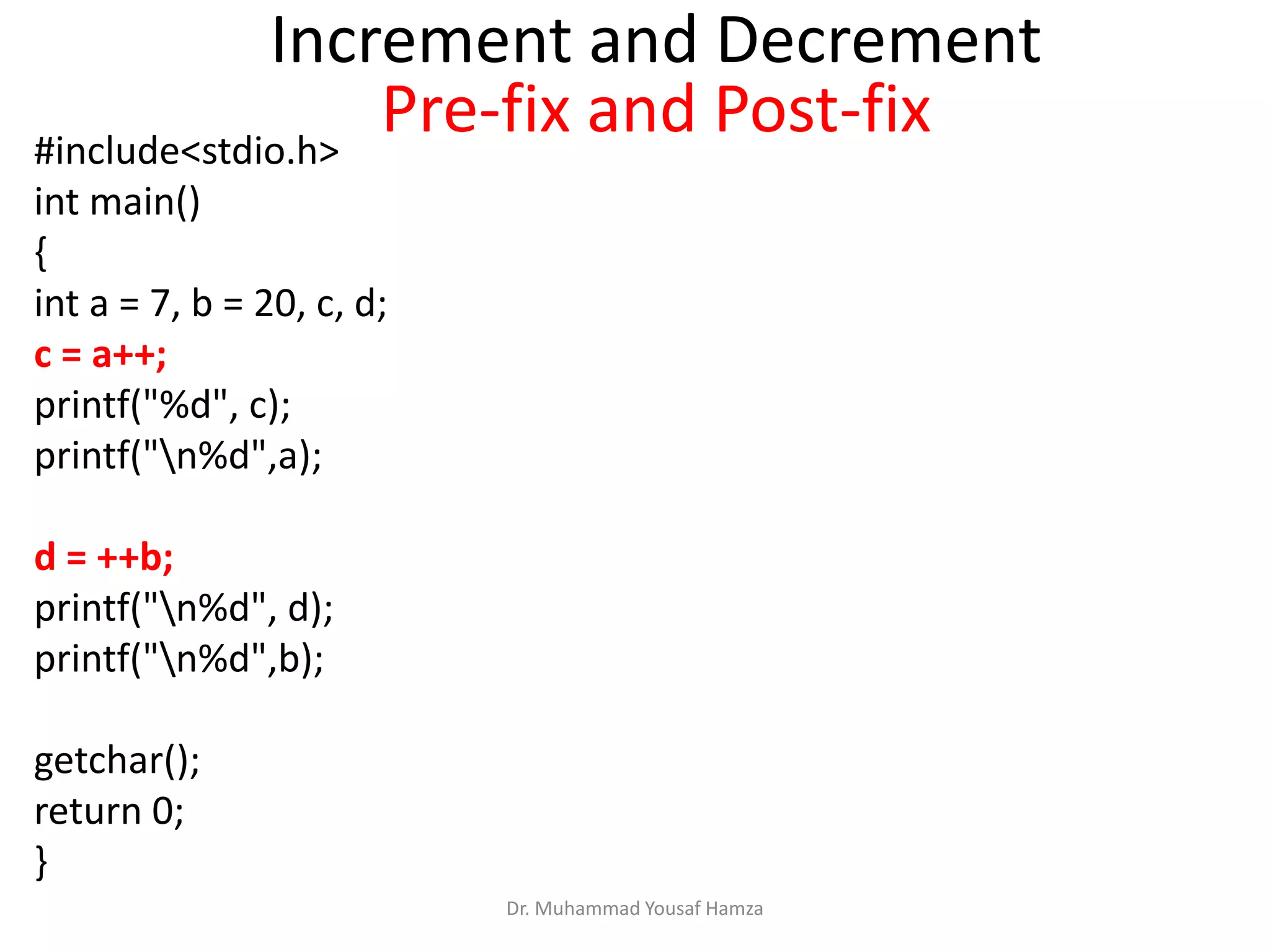
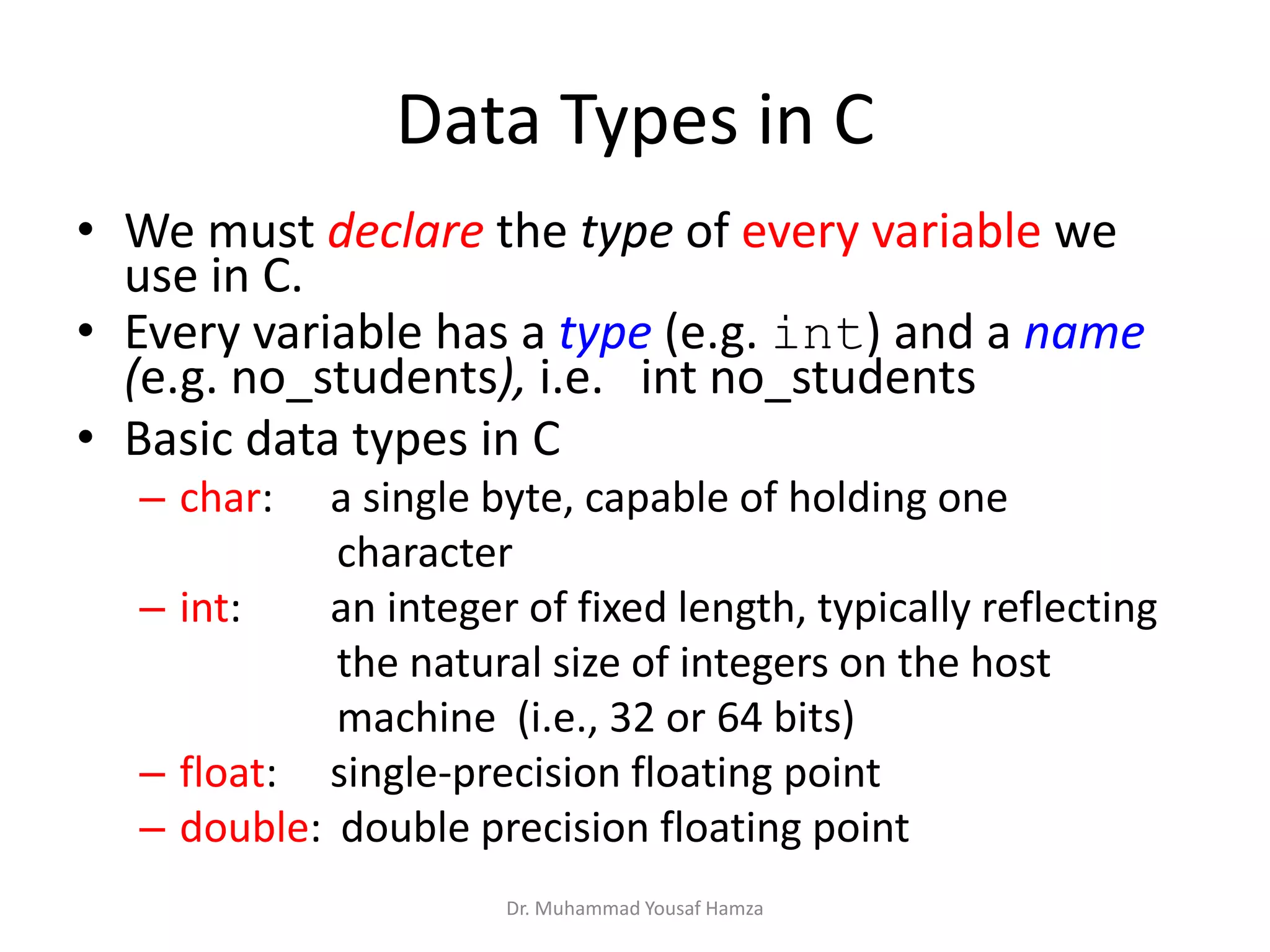
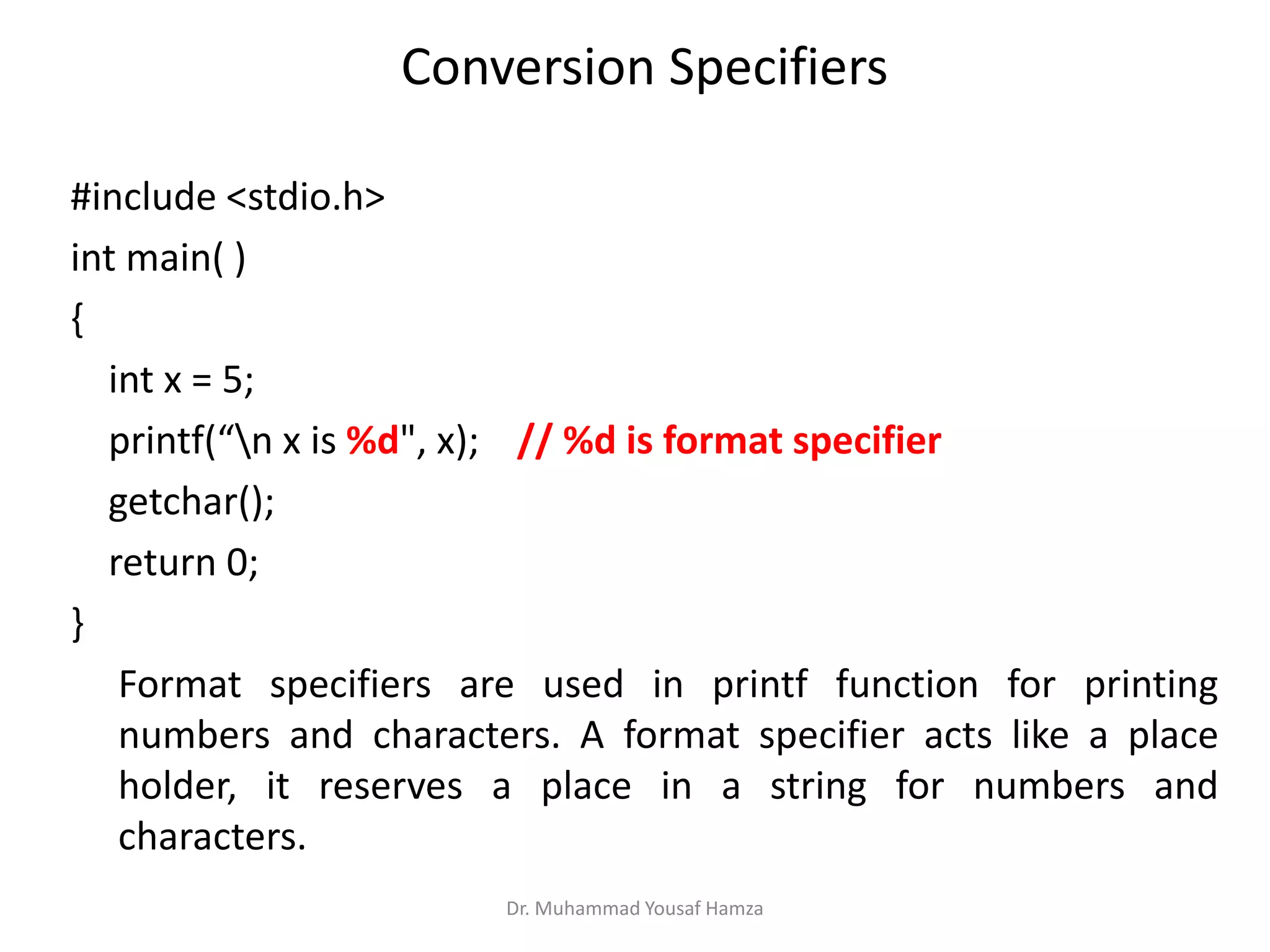
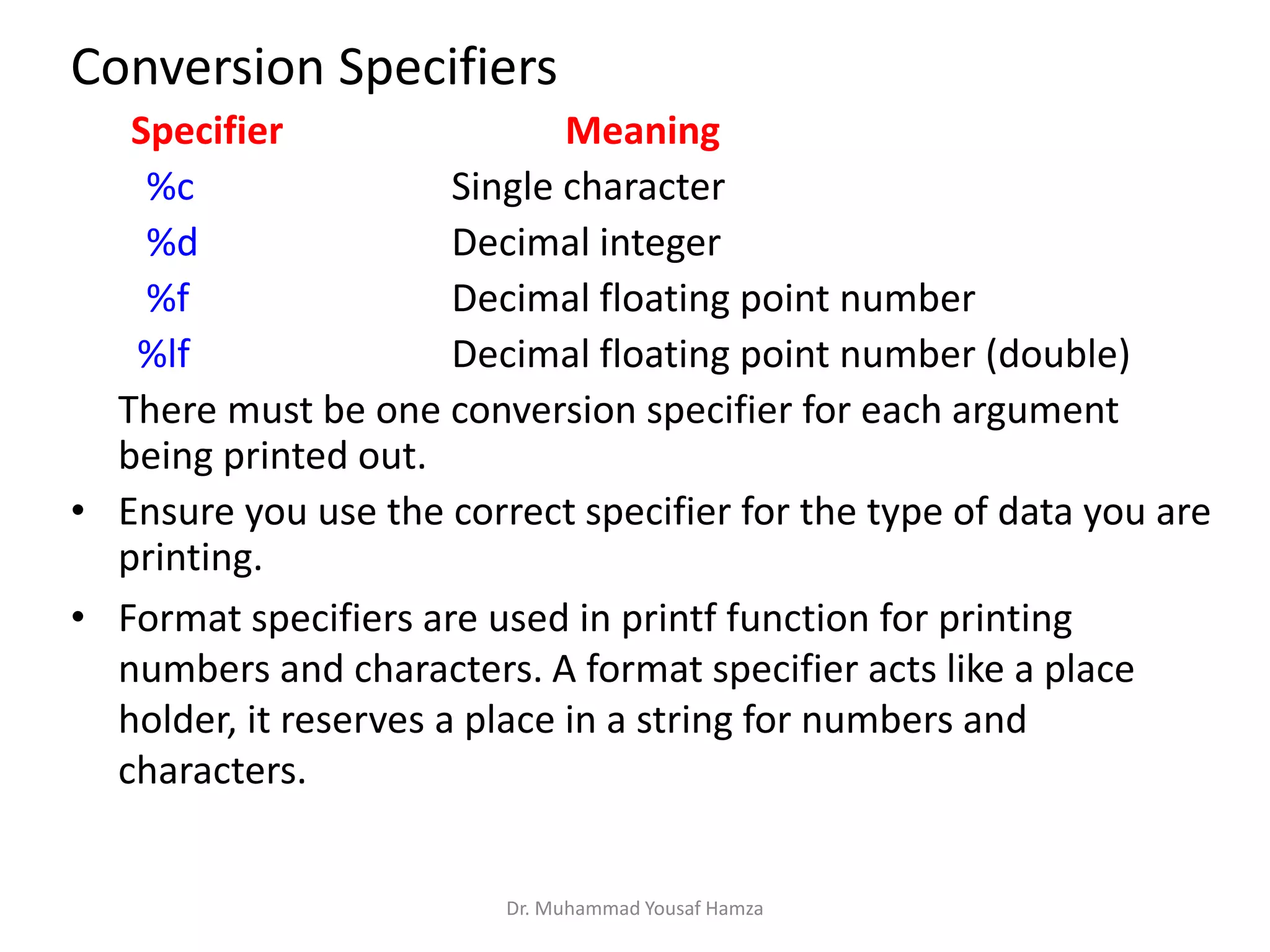
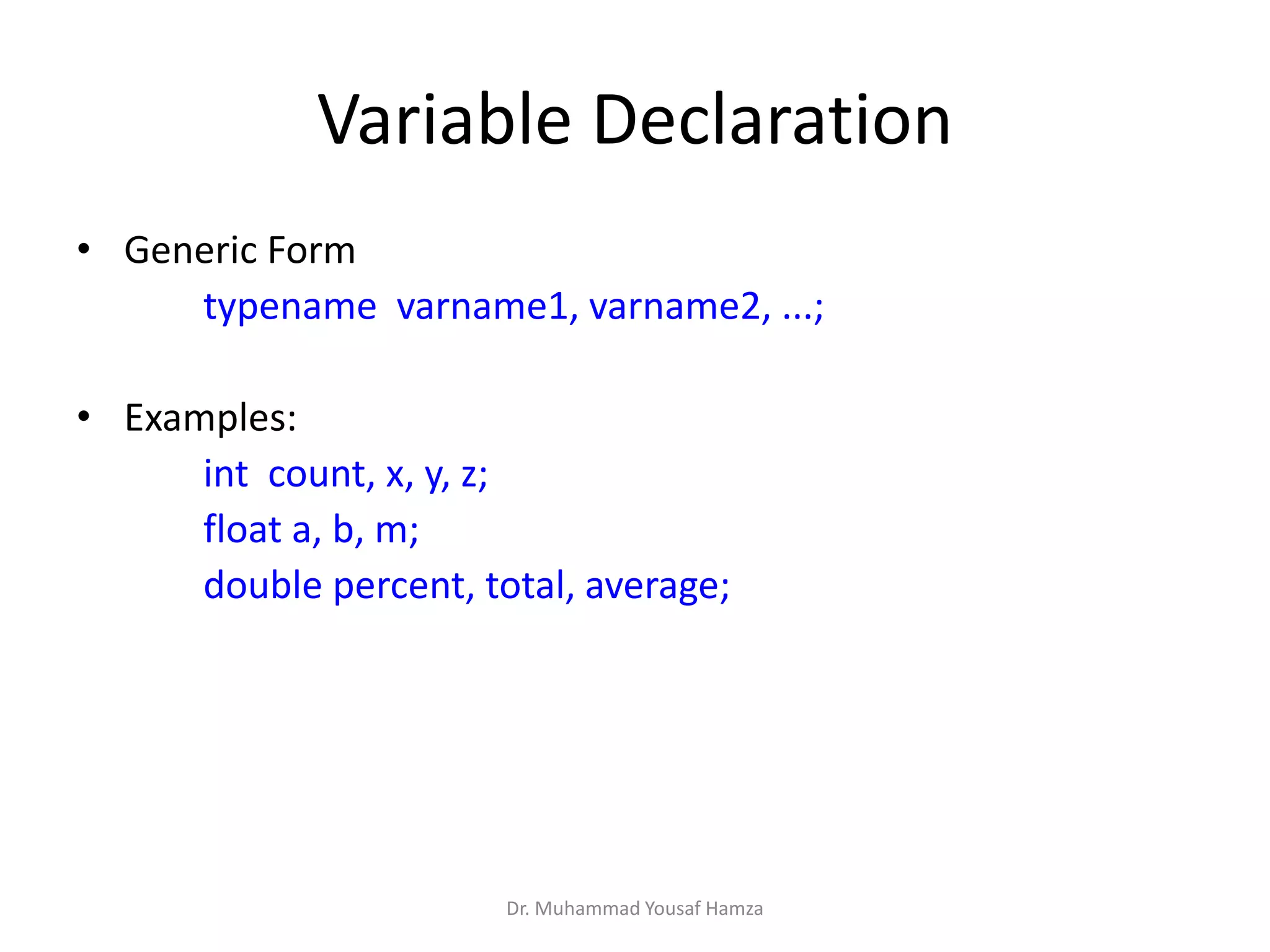
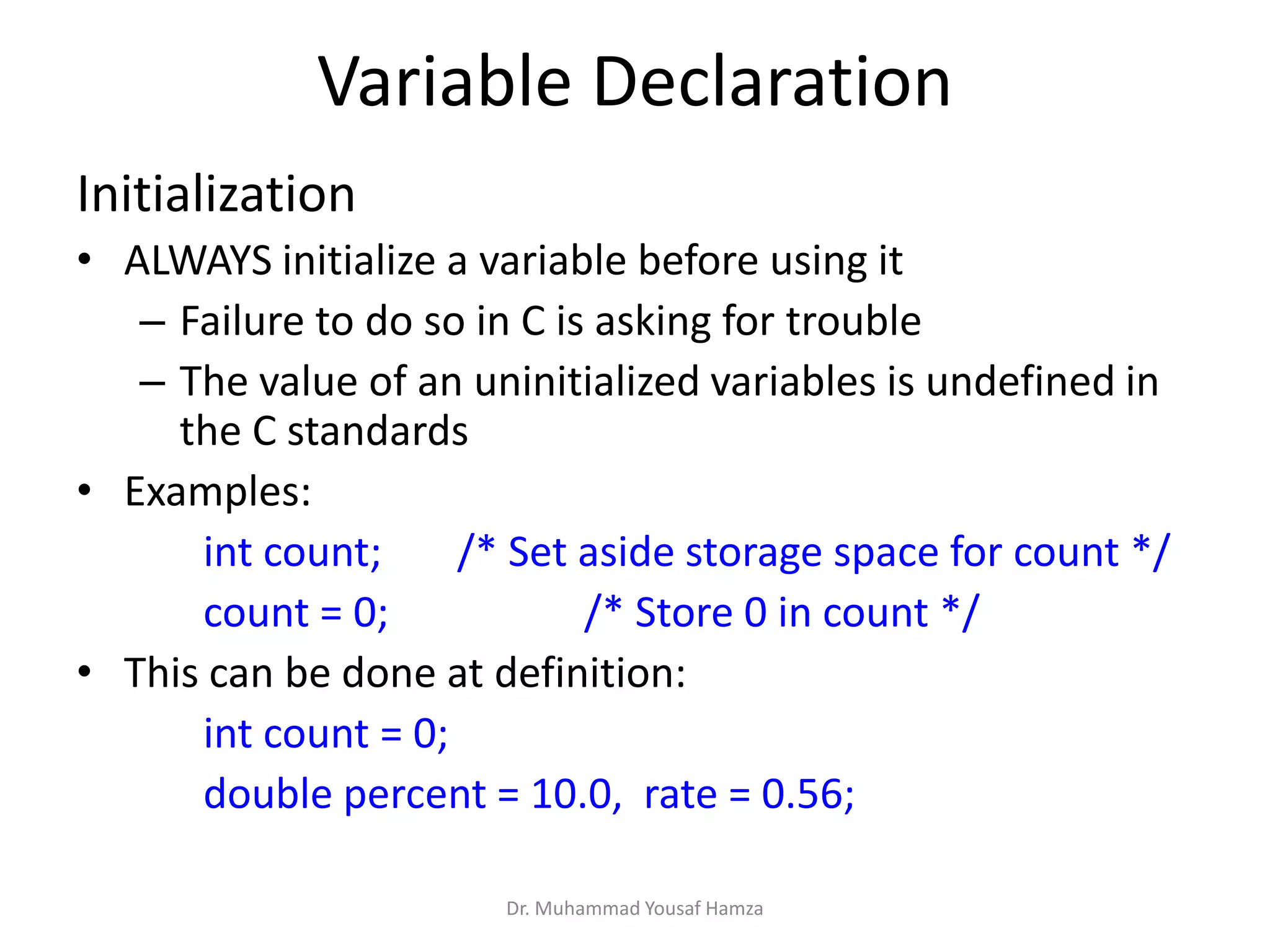
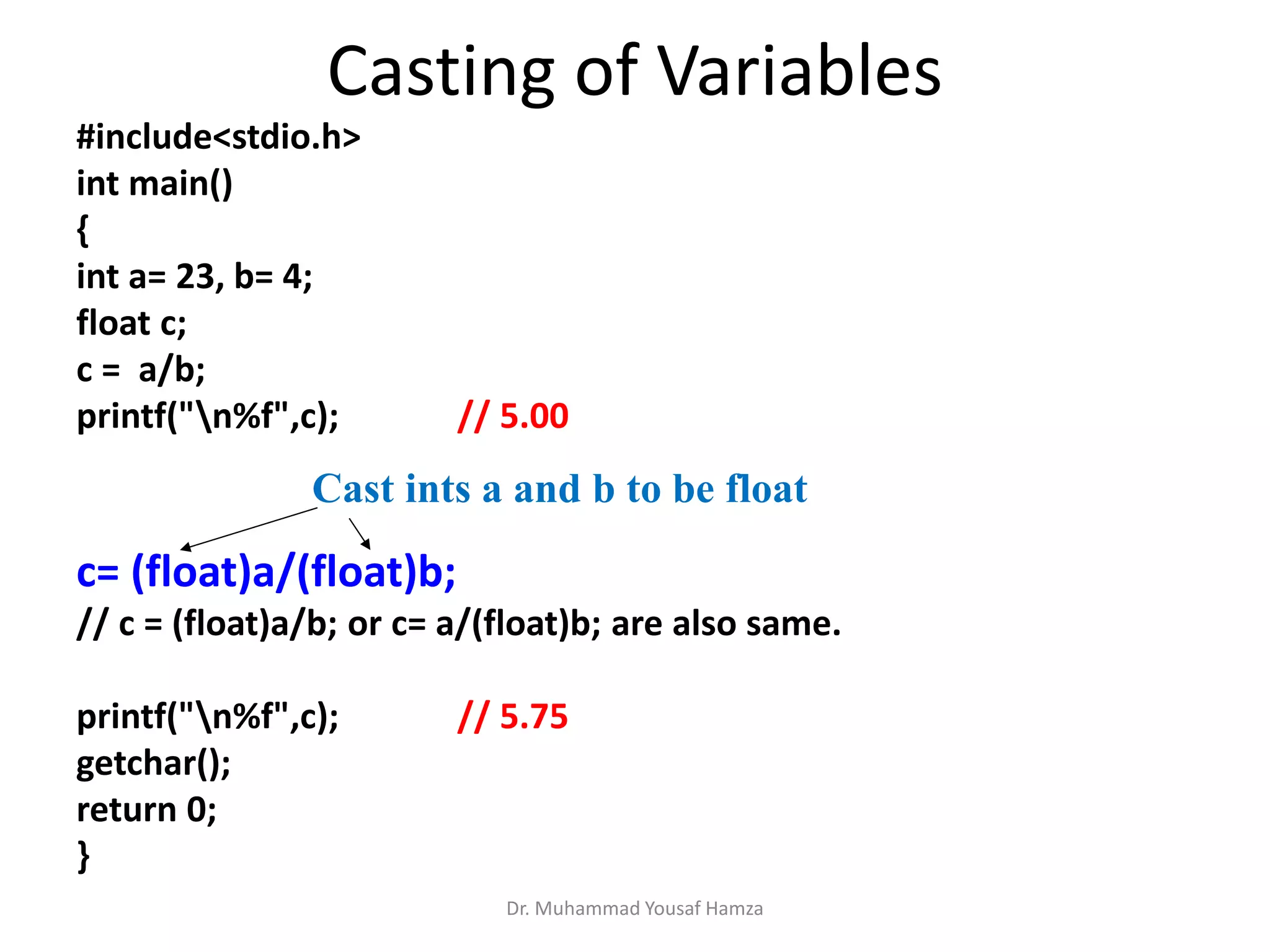
This document provides information about computing fundamentals and C programming concepts such as data types, variables, operators, and decision making structures. It includes code examples demonstrating the use of scanf to read input, basic arithmetic operators, if statements, and more. The document is authored by Dr. Muhammad Yousaf Hamza and covers fundamental C programming topics for beginners.