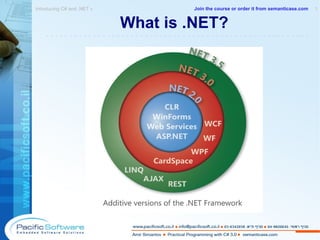
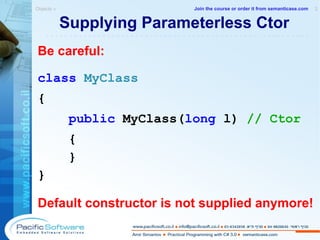
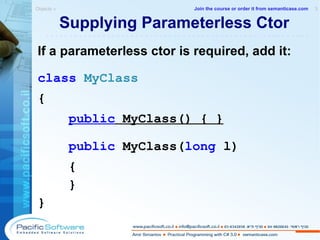
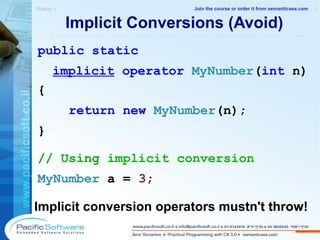
This document is a sample from an instructor-led course on practical programming with C# 3.0. It provides an overview of the course contents, including chapters on C#, .NET, objects, properties, indexers, operator overloading, and conversions. The document encourages following principles of encapsulation and avoiding unnecessary complexity through practices like operator overloading and implicit conversions.








































![Indexers Allows consumer to access an object as an array. var aquarium = new Aquarium (fishes); //Using an indexer which gets an int var firstFish = aquarium[ 0 ]; Indexers cannot be static in C#. Objects » 1 -------------------------------------------------------- Join the course or order it from semanticase.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampleamirsimantovcsharpcoursecs320080902pacificsoft-1232024042161398-3/85/C-3-0-Course-47-320.jpg)
![Indexers Here is the implementation of the indexer: public Fish this [ int index] { get { return fishes[index]; } } Kind of hybrid... Used like a property; Get parameters as a method. Objects » 2 -------------------------------------------------------- Join the course or order it from semanticase.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampleamirsimantovcsharpcoursecs320080902pacificsoft-1232024042161398-3/85/C-3-0-Course-48-320.jpg)
![Indexers //Using an indexer which gets a string var kingFishes = aquarium[ "King" ]; Is it clear what does the indexer return? What is the alternative to get the collection of king fishes? Do not use indexers if the meaning is not clear with the quickest glance! Objects » 3 -------------------------------------------------------- Join the course or order it from semanticase.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampleamirsimantovcsharpcoursecs320080902pacificsoft-1232024042161398-3/85/C-3-0-Course-49-320.jpg)







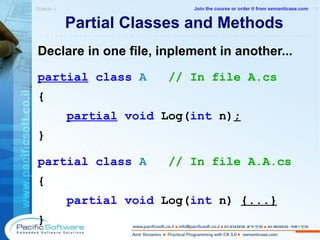

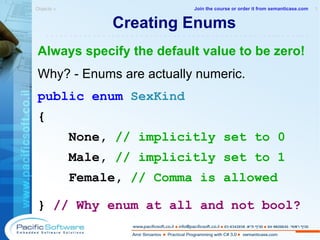
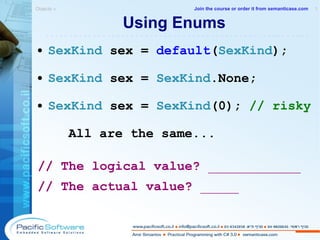

![Creating Bit Flag Enums [ Flags ] public enum FontStyle { Regular = 0x0, Body = 0x1, Italic = 0x2, Underline = 0x4, } Next values of the type will be: 0x8, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40... Bit flag enums without evaluation breaks bit logic. This ib because each enum value which is not explicitly evaluated takes the value of the preceding enum value plus 1. In bit flag enum type we want each enum value to be twice as much as the preceding one. Objects » 1 -------------------------------------------------------- Join the course or order it from semanticase.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampleamirsimantovcsharpcoursecs320080902pacificsoft-1232024042161398-3/85/C-3-0-Course-63-320.jpg)
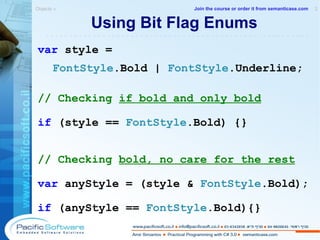

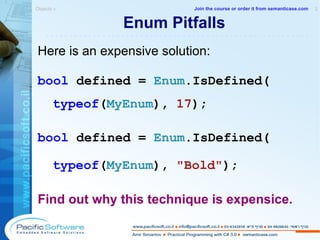



















![Keyboard Shortcuts Navigation Debugging F8 Move to next location F9 Add or remove a breakpoint F12 Move to definition F5 Start debugging SHIFT + F12 List all references SHIFT + F5 End debugging CTRL + ] Move to matching brace: { and } F11 Step into CTRL + I Move to what I type SHIFT + F11 Step out CTRL + SHIFT + 8 Move to where I was F10 Step over CTRL + F/H Show Find and Replace dialog CTRL + SHIFT + F/H Find or replace in many files CTRL + TAB Show files navigator ESC Return to code Visual Studio 2008 » 2 -------------------------------------------------------- Join the course or order it from semanticase.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sampleamirsimantovcsharpcoursecs320080902pacificsoft-1232024042161398-3/85/C-3-0-Course-87-320.jpg)








