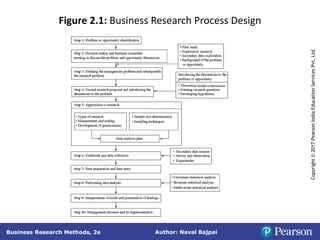
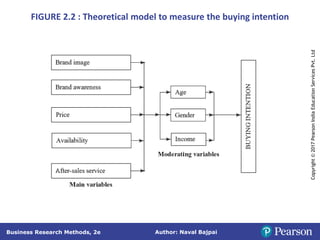
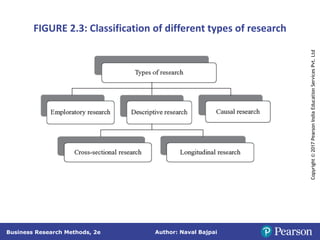
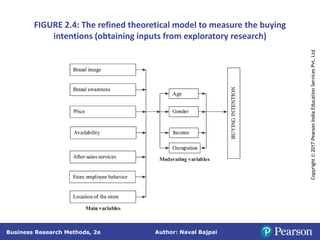
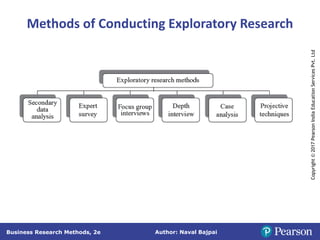
This document outlines the steps in conducting business research. It discusses exploratory, descriptive, and causal research. Exploratory research explores problems through secondary data analysis, expert surveys, focus groups, depth interviews, case studies, and projective techniques to understand issues, identify variables, and develop hypotheses. Descriptive research involves collecting data to describe characteristics and causal research determines relationships between variables through experiments and quasi-experiments. The research process involves identifying a problem, defining it as a research question, developing a proposal, determining methods, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting findings.