Embed presentation
Download to read offline

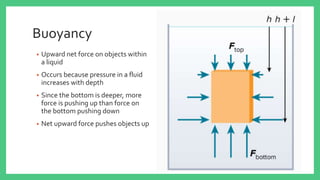
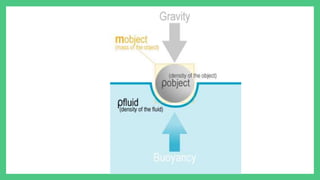

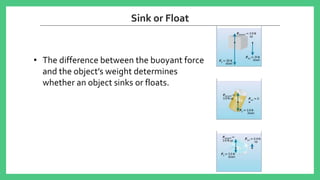
The document explains buoyancy as the upward force experienced by objects in a liquid due to pressure differences, which increases with depth. It details Archimedes' principle, stating that the buoyant force equals the weight of the fluid displaced by an object. The outcome of whether an object sinks or floats is determined by the relationship between the buoyant force and the object's weight.




