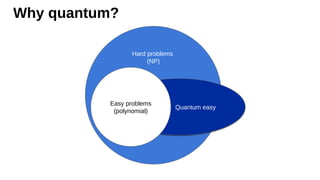
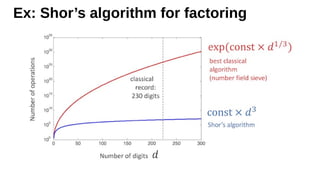
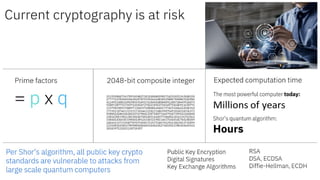
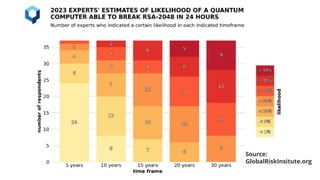
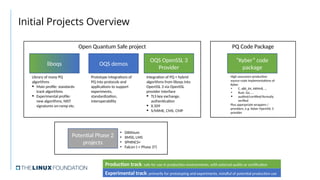
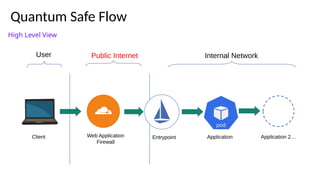
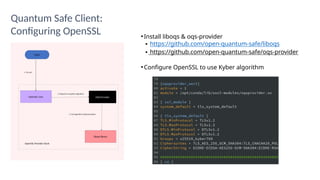
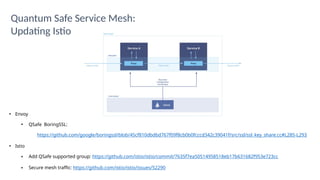
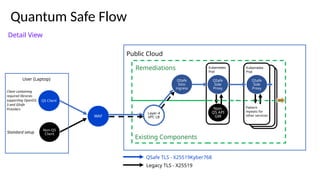
The document outlines strategies for building quantum-safe applications using open-source tools, emphasizing the importance of post-quantum cryptography and risk mitigation. It covers key aspects such as understanding risks, protecting applications, and integrating quantum-safe algorithms into existing systems. Additionally, resources for further learning and inventorying cryptographic assets are provided.