Presented at All Things Open 2025
Presented by Brett Smith - SAS Institute, Inc.
Title: Supply Chain Robots, Electric Sheep, and SLSA
Abstract: A talk about creating automation, shifting left, attack vectors, attestations, verification, zero-trust, and SLSA.
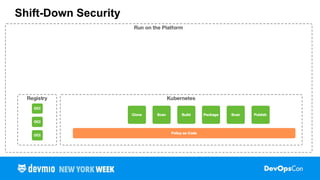
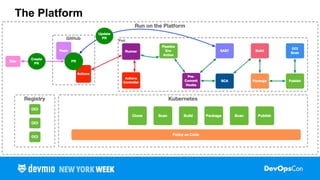
In the talk I cover creating automation, shifting left, attack vectors, attestations, verification, zero-trust, and how the SLSA spec helps implement solutions for each. The main take away is that security needs to be applied everywhere in the pipeline. The talk should lead to a greater discussion around the challenges of securing the supply chain, supporting EO 14028 and ISO27001, and improving the security posture of your pipelines.
Attendee Takeaways
Answers for the following questions:
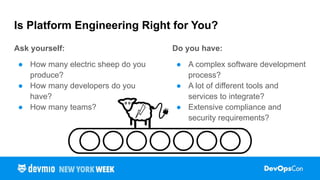
- Why do we need supply chain automation?
- What are common attack vectors in a supply chain?
- What techniques can we use to help secure the supply chain?
- What are the security benefits of supply chain automation and shift left?
- What specifications and tools can we use to help secure the supply chain?
Find more info about All Things Open:
On the web: https://www.allthingsopen.org/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/AllThingsOpen
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/all-things-open/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/allthingsopen/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/AllThingsOpen
Mastodon: https://mastodon.social/@allthingsopen
Threads: https://www.threads.net/@allthingsopen
Bluesky: https://bsky.app/profile/allthingsopen.bsky.social
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@allthingsopen
2025 conference: https://2025.allthingsopen.org/